





Autoimmune hemolitic anemia
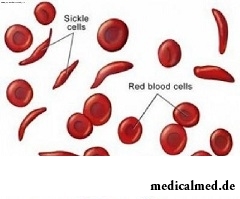 Hemolitic anemias represent set of both inborn, and acquired diseases which are characterized by destruction of erythrocytes in cells or in vessels. Autoimmune hemolitic anemias (in abbreviated form AHA) – the most often found kind of hemolitic anemias.
Hemolitic anemias represent set of both inborn, and acquired diseases which are characterized by destruction of erythrocytes in cells or in vessels. Autoimmune hemolitic anemias (in abbreviated form AHA) – the most often found kind of hemolitic anemias.
Autoimmune hemolitic anemia: etiology, pathogeny, classification and clinical picture
Hemolitic anemia can develop owing to the conflict of a blood group or a Rhesus factor between mother and a fruit or owing to transfusion of donor blood. Them call isoimmune.
Carry cases when own immune system develops antibodies to own erythrocytes to the second group. They are called autoimmune hemolitic anemias. When performing diagnostic blood test at patients about AHA IgG immunoglobulins (IgM and IgA is rare) show an aberration.
In most cases autoimmune hemolitic anemias meet in the form of various specific and nonspecific symptoms against the background of other diseases of blood; can proceed both in an acute form, and in the form of chronic process.
In acute cases the disease begins with weakness, an asthma and heartbeat, temperature increases, vomiting and jaundice, pains in heart and in a waist are noted.
Chronic autoimmune hemolitic anemia often proceeds almost asymptomatically with periodic aggravations. Against the background of remission note increase in a liver and spleen at a palpation, quite often jaundice.
In the developed blood test at patients AHA note, in particular, the normal or raised hemoglobin, increase in SOE, normal level of thrombocytes. In an acute form and at aggravations of a chronic current the quantity of leukocytes whereas their level is in a remission stage normal increases.
The diagnosis "autoimmune hemolitic anemia" most often is more precisely differentiated by specialists after conducting specific diagnostic testings.
Kinds of treatment of autoimmune hemolitic anemias
Tactics of treatment of autoimmune hemolitic anemia at the acute course of a disease or an aggravation of chronic process without fail includes hormonal therapy. The average daily dose of Prednisolonum of 60-80 mg is divided into three receptions in the ratio 3:2:1. In case of inefficiency of treatment it can be increased to 150 mg and above, and in process of improvement of a condition of the patient – gradually decreases (by 2,5-5 mg a day with the purpose to avoid a recurrence) at first to a half of an initial dosage and further up to full drug withdrawal.
At chronic disease, treatment of autoimmune hemolitic anemia demands purpose of Prednisolonum, but in a daily dose of 20-25 mg. Administration of drug is carried out under laboratory control, and in process of normalization of indicators of blood its dose smoothly decreases to supporting - 5-10 mg a day.
Sometimes and justified in therapy also purpose of drugs from group of immunodepressants AHA is reasonable, and at heavy hemolitic crises infusional therapy is shown: individually picked up packed red cells, Haemodesum, etc. for intoxication. Sometimes pour a blood plasma, the washed or frozen erythrocytes, resort to a hemodialysis method (an artificial kidney) and a prazmofereza (removal of a liquid part of blood – plasma – together with antibodies).
A number of patients AHA differs in the increased resistance to effect of hormonal drugs. Disease is characterized at them by a frequent recurrence and practically does not give in to medicamentous correction. AHA at this category of patients apply radical treatment to treatment – a splenectomy (removal of a spleen) which considerably improves quality of life.
Despite the highest level of development of modern medicine treatment of hemolitic anemias is very difficult, and the diagnosis quite often adverse.
According to researches, the women drinking several glasses of beer or wine in a week have the increased risk to develop breast cancer.

Dogrose – one of the most widespread adornment and medicinal plants growing practically in all territory ours...
Section: Articles about health
For the last decades the diabetes mellitus of the second type became really world problem. The number of cases annually increases, and average age of patients for whom the illness is diagnosed, steadily decreases. Specialists consider that one of osno...
Section: Articles about health
Vitamin complexes belong to the most popular drugs, probably, in our country there is no person who was not hearing about advantage of vitamins and never their accepting. The more vitamins, the better, we consider and as it appeared, cruelly we are mistaken. Whether vitamins, whether so harmlessly general hobby for polyvitaminic complexes and whether it is possible to do without them are so useful? Let's try to understand....
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. In opinion д...
Section: Articles about health
Small appetite at the child – the complaint which pediatricians should hear practically from each mother. Most often it is carried to the category of children's whims, however the refusal of food in certain cases can be to alarming symptoms therefore it cannot be ignored....
Section: Articles about health
For the help to doctors in the choice of optimal solutions for treatment of various diseases the Cochrane scientific organization (Cochrane) conducts joint researches with representatives of scientific community around the world. The analysis of a series of the conducted researches of the drug Oscillococcinum® relating to group of cold remedies became one of the last methanolyses....
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair with the help about...
Section: Articles about health
Life of the modern child is extremely active and difficult. Information strain which is experienced by the school student and did not dream pupils of last times. Careful parents, wishing well to the children, will organize a set of additional classes in circles, sports...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads, to slopes of ravines, on heathlands. Also several cultural versions different from wild plants are removed by larger and juicy root crops....
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In некото...
Section: Articles about health
Impossibility to conceive the child – a trouble of many Russian families. During quite long time was considered that main "culprits" of troubles such are women. Modern physicians claim that the situation is different: about a half of failures at...
Section: Articles about health
They say that to ensure health and longevity of people it is obliged. Really, at competent approach to these questions, minimization of an adverse effect of many factors does not represent a special problem. Practically everyone has an opportunity to play sports, to pick up an optimum operating mode and rest, to adjust healthy food, to refuse addictions. It is more difficult to exclude hit in an organism of harmful substances through a respiratory organs: not all are able to afford to live in the area with хо...
Section: Articles about health
Among a set of the perfumery and cosmetic goods which are released today the special group is made by the means containing anti-bacterial...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too h...
Section: Articles about health
The naturopathy sometimes moves as the new direction of medicine, something like fashionable hobby, and there is nothing farther from the truth. This most ancient direction, the word "naturopathy" is translated as "treatment by the nature", and, no doubt, treatment by natural gifts was the first and only, available to the person in ancient times. Despite modern achievements of medicine, the naturopathy remains urgent and today, anyway the person - a part of the nature, and природн...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects on...
Section: Articles about health
It seems, quite recently you brought the baby from maternity hospital, but time flew by, and here it is already going to join the first in life children's collective. How to prepare the child for visit of a garden? What needs to teach him to facilitate process адап...
Section: Articles about health
There is an opinion that at low temperatures safety of products is ensured longer and better thanks to what the refrigerator is considered the most suitable place for storage of food. In most cases it is fair, however there is a number of products for which low temperatures – the main reason of their premature damage. Storage in the refrigerator leads to their bystry rotting, emergence of a mold, is followed by loss of vitamins and tastes. What products it is better to remove...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person...
Section: Articles about health
Long time antibiotics were considered as a panacea from all diseases and were appointed even at insignificant symptoms of an infection. Even now not everyone knows in what force of antibiotics how and when they should be accepted. Let's discredit 7 popular myths about such drugs...
Section: Articles about health
The medicine promptly develops, and the fact that else quite recently it seemed by miracle can now. We are not surprised any more to the fact that people with artificial joints and extremities can play sports, organ transplantation became a routine, and the latest cancer medicine allowed to achieve reduction of mortality in tens of times. Miracles of plastic surgery thanks to which people in 60 years are in the flower of beauty and freshness, too not a sensation any more....
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, reason душевног...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot replace completely modern synthetic drugs, but their use becomes frequent serious help in simplification a leak...
Section: Articles about health
Each person supports all life a SARS about 200 times. The peak of incidence falls on cold season, but it is possible to get sick with a temperature and a pharyngalgia, and sometimes and very possibly, even during a heat. The reasons for development of catarrhal diseases there is a set: from the weakened immunity till an excess portion of ice cream....
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs п...
Section: Articles about health
Scientists have no unambiguous opinion on a proximate cause of emergence of a carcinoma cutaneum today. Only the factors promoting development of this illness are precisely established. Treat them: long impact on skin of ultraviolet rays, radioactive...
Section: Articles about health
The Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) are plants or animals (as a rule, agricultural) to whose genotype purposeful changes were made. Opposition of supporters and opponents of inclusion of such organisms in foodstuff always was very acute. Not only scientists and dietitians, but also a large number of the people who are not specialists in this question are involved in active disputes today....
Section: Articles about health
