





Periodontitis
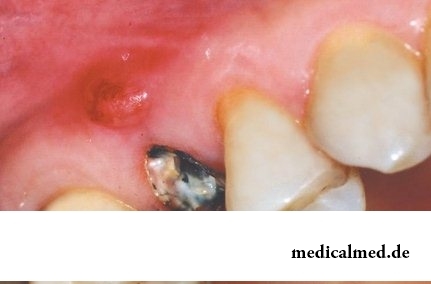
The periodontium is a complex of fabrics which are between a fang and an alveolus (a tooth hole). One of widespread complications of caries (35-50% of total number) is periodontitis.
Periodontitis – an acute and chronic inflammation of a periodontium at which there is a disturbance of integrity of the sheaves holding tooth in an alveolus, a resorption of a bone tissue up to developing of cysts. The resorption of a bone of an alveolus results in pathological mobility of tooth.
Classification of periodontitis
The classification of periodontitis given below accepted in Russia has small discrepancies with its classification abroad. The Russian stomatologists allocate:
- Acute periodontitis which is in turn subdivided on serous and purulent.
- Chronic periodontitis – fibrous, granulating and granulematozny
- The aggravated chronic periodontitis.
Reasons (etiology) of periodontitis
Treats the most important etiological factors of periodontitis: oral cavity microflora, occlusion (smack), abnormal provisions of teeth, tooth deposits. Important value has the general condition of digestive tract, a disease of nervous and endocrine systems, disbolism in an organism, a vitamin imbalance.
Periodontitis at children, as a rule, arises for the infectious and traumatic reason.
Characteristic symptoms of periodontitis
The arising periodontitis which symptoms are characteristic and are easily diagnosed, it is necessary to try to prevent right at the beginning. The timely address to the doctor is for this purpose strongly recommended. Especially this recommendation concerns parents who have small children – systematic control of dental health of the child depends on you.
The first signs of developing of periodontitis is unpleasant feelings of the "aching" gums at meal with different temperature conditions, gingiva bleeding when toothbrushing and an unpleasant smell from a mouth.
Acute periodontitis is, as a rule, characterized by emergence at the initial stage of sudden severe pains without external irritant in sick tooth. The feeling of the "grown" tooth, pain can cease at impact on the inflamed site cold. At the subsequent stage of development of an inflammation pain gains the pulsing character, emergence of a face edema is possible. At this stage the hyperadenosis and temperature increase at the patient to 38C is characteristic. If not to address the stomatologist, then in 1,5-2 weeks acute periodontitis passes into chronic.
Chronic periodontitis is followed by noticeable increase in mobility of teeth, their situation changes, interdental cracks are formed. Bleeding of gums can arise even without mechanical impact on them. Systematic release of pus, abscesses and an acute pain is observed.
Chronic periodontitis is characteristic the frequency – the exacerbation of periodontitis is replaced by a process zatikhaniye, and the patient during these periods can calm down, once again, postponing visit of the doctor. During the periods when there is an exacerbation of periodontitis, the gingiva reddens and swells up, the dentagra is constant and amplifies from a touch to tooth. Fervescence is observed.
The exacerbation of periodontitis demands surgical methods for the purpose of removal of purulent contents. It interferes with a necrosis of fabrics, distribution of an inflammation, liquidates or weakens pain. After removal of pus the doctor begins treatment of periodontitis.
Ways of diagnosis of periodontitis
Diagnosis of periodontitis is carried out by traditional clinical methods which allow to reveal the center of a disease and extent of development of inflammatory process. Diagnosing periodontitis for children, the doctor meets difficulties of collecting the anamnesis at the first stage – poll as the child perceives pain emotionally and can not always accurately report the feelings.
Clinical diagnosis of periodontitis includes:
- patient's poll;
- survey of an oral cavity;
- sounding of an entrance to a pulp cavity;
- carrying out temperature tests;
- the palpation – is especially effective at children owing to features of a structure of children's jaws;
- definition of mobility of tooth in way of progress and cave-in;
- more exact establishment of the diagnosis are used: X-ray inspection, radioviziografiya, electric pulp test and transillumination.
Treatment of periodontitis
Having diagnosed periodontitis, treatment the doctor appoints, as a rule, complex and step-by-step. Treatment of acute periodontitis, as a rule, demands immediate intervention and includes:
- elimination of the center of an inflammation (pus conclusion);
- complex physiotherapeutic to a protsed
- subsequent sealing.
At inefficiency of treatment there is an odontectomy.
If the patient already had a transition from acute to chronic periodontitis, treatment is carried out depending on complexity and development of a disease. And from at what stage of a disease of the patient falls into the professional's hands, efficiency of all subsequent procedures depends.
Periodontitis at children is accompanied by some features of use of above-mentioned methods of treatment. Conservative therapy not in all cases allows to achieve elimination of the center of an infection. For treatment of periodontitis at the child, the doctor has to carry out careful and full diagnosis to be sure that inflammatory process did not extend to a rudiment of a second tooth
When lovers kiss, each of them loses 6,4 calories a minute, but at the same time they exchange nearly 300 species of various bacteria.
History of use of an anesthesia during operations contains more than 160 years. Annually in the world hundreds of thousands surgical вм are carried out...
Section: Articles about health
Household skills which to us so diligently imparted in the childhood it appears, not always bring only benefit. According to results of the last researches, some habits which for a long time were considered useful and even necessary can become...
Section: Articles about health
Any person who faced a disease knows that treatment costs expensive. It belongs also to consultations of qualified specialists, and to the diagnostic procedures which are not included in the list of obligatory medical services. The question of cost of medicines is not so unambiguous: almost each drug is produced several producers at once, and the price of medicine can differ many times. In such situation there is a sense to understand in what differ from each other original environments...
Section: Articles about health
Tick-borne encephalitis – one of the most dangerous viral diseases which causative agents transfer and is given to people by ixodic mites. Эт...
Section: Articles about health
Visit of doctors – business not the most pleasant, and many people do not hurry to undergo necessary planned inspections. Such behavior is extremely thoughtless and improvident. Our health is necessary not only to us: wellbeing of darlings, children, grandsons and престар...
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. Trainings will help it to become strong and hardy, will improve coordination of movements, and also will exert positive impact on mentality: it will become more collected and purposeful....
Section: Articles about health
It is pleasant to state a possibility of improvement of quality of life of people with problems of functioning of secretory system. By efforts that...
Section: Articles about health
For the person who daily since morning gathers for work it is very important to wake up vigorous and ready by day of work. Actually, each of us experiences difficulties with this, at first sight, simple business from time to time. On a condition of an organism after ночн...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing an optimum set of nutrients, and which is best adapted in order that the baby normally developed and it was protected from harmful factors of external environment, unusual for it. Unfortunately, breastfeeding process not always does without complications. Sometimes, that the kid begins to bite a breast, giving to mother an essential inconvenience. Some women...
Section: Articles about health
The chia plant, or the Spanish sage, is from South America. The indigenous people of the continent since ancient times used in food it семена:...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically cystitis 25-30% of women up to 40 years have. With age this indicator raises, besides many do not get to statistics because do not see a doctor. The most sad that after the regular visits to doctors, long reception of antibiotics...
Section: Articles about health
Today about 30 diseases, sexually transmitted are known. Wide circulation of these illnesses is extremely promoted by the dual attitude towards them: on the one hand, most of people know about "shameful" diseases very little and do not aim at receiving detailed and reliable information, considering that such problems personally will never concern them. With another – there are delusions about STD which instill unreasonable confidence that troubles such...
Section: Articles about health
The medicine promptly develops, and the fact that else quite recently it seemed by miracle can now. We are not surprised any more to the fact that sport...
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, not too modest, and excessively curvy shapes become the reason of sincere discomfort sometimes. Except psychological problems, a big bust sometimes with...
Section: Articles about health
Osteoporosis this general disease which main sign is decrease in density of a bone tissue. On distribution width it takes the fourth place among noninfectious diseases. The illness develops at mature age more often: in our country about a third of women and a quarter of men suffers from it 50 years are more senior....
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters in any...
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be studied already up and down, and each person, at least once by it had (and the number of such people in our country aims at 100%), a dolzha...
Section: Articles about health
Smoking not only exerts a negative impact on the state of health of the consumer of tobacco products, but is an air polluter the substances potentially dangerous to people around. In recent years significantly the number of the people aiming to get rid of an addiction increased. Business this difficult: having left off smoking, the person immediately begins to suffer from abstinence. Besides, many yesterday's smokers feel at first great disappointment as улучш...
Section: Articles about health
Climax - process of fading of reproductive function of an organism in process of its aging. At women the main sign of its approach showing...
Section: Articles about health
For the help to doctors in the choice of optimal solutions for treatment of various diseases the Cochrane scientific organization (Cochrane) conducts joint researches with representatives of scientific community around the world. The analysis of a series became carried out by one of the last methanolyses...
Section: Articles about health
For most of the working people the problem of having a snack is particularly acute enough. Sooner or later there is a question: what can be eaten quickly between a breakfast and a lunch or a lunch and leaving from service so that to receive necessary power feed, but not to overload an organism with harmful components or excess calories? We bring to your attention the list of products which quite conform to these requirements....
Section: Articles about health
Scientists have no unambiguous opinion on a proximate cause of emergence of a carcinoma cutaneum today. Are precisely established only фа...
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. According to nutritionists, the separate use of the carbohydrate and proteinaceous products demanding different conditions of assimilation helps to get rid from Bol...
Section: Articles about health
With age in a human body harmful substances collect. We receive them with food and water, at inhalation of the contaminated air, reception of medicines, use of household chemicals and cosmetics. A considerable part of toxins accumulates in a liver which main function is continuous purification of blood. This body begins to knock as any got littered filter, and efficiency of its work decreases....
Section: Articles about health
Popular joke that there are no healthy people, and is nedoobsledovanny, most of us considers an honest truth, and put that...
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create to it healthy immunity since early years. Nevertheless, this important process in life of mother and child can be saddened laktostazy − by a delay of milts...
Section: Articles about health
History of mankind contains several tens of epidemics whose emergence was compared by eyewitnesses and historians to doomsday. The most terrible of them claimed the lives of millions of people, having made even the whole people to the person of the earth. What they − the diseases striking terror? Whether it managed to the person to find treatment, or he is still powerless before forces of nature?...
Section: Articles about health
