





Metacarpal bone
The metacarpal bone represents the short tubular bone located on a brush and departing from a wrist in the form of a beam. At the person on each hand up to five metacarpal bones. Each bone consists of the basis, a body and a head. These bones connect joints to bones of a wrist and the basis of the first phalanx of fingers of a hand.
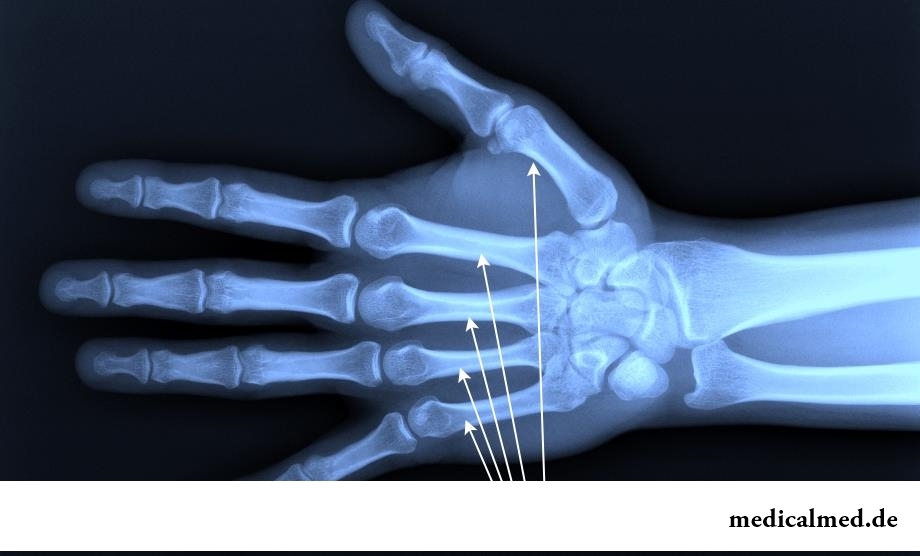
Structure of a metacarpal bone
Metacarpal bones are counted from a thumb of a hand and have the curved form to a brush. In each such bone there are a body and an epiphysis. The body of a metacarpal bone has three surfaces – back, medial and side. Medial and side surfaces are divided by a comb where there is an opening passing in a nutrient canal.
The body of a metacarpal bone is bent in the back, and side surfaces of the basis represent joint platforms which connect adjacent bones. Joint surfaces have the saddle form.
The basis of the third metacarpal bone has a shoot of awl-shaped type. In the bottom of a distal part the head of a metacarpal bone of spherical shape is located. Side surfaces of a head of a metacarpal bone rough.
Each head of a metacarpal bone and its body can be probed through skin on a brush surface. Between metacarpal bones there are interosseous intervals which are called pyastyam.
Injuries of metacarpal bones
The most widespread injuries are fractures of a metacarpal bone, the basis, diaphysis and phalanxes of fingers. Most often the fracture of the first and fifth metacarpal bones meets. The injury can be done by direct stroke about a blunt object.
In rare instances there are fractures of the second, third and fourth metacarpal bones. Usually such change happens because of an injury of a brush or punch about a blunt object.
The fracture of a metacarpal bone at the basis happens several types: intra articulate, extra articulate and cross. Symptoms are pain in the field of a change, hypostasis, impossibility of bending of a finger, and at palpation of the place of a change the pain syndrome amplifies. Bennet's change is called the injury at which there is a splinter of triangular shape, and also dislocation towards a beam bone. The complicated change with dislocation is called Roland's change. The exact diagnosis is established by means of radiological survey.
Treatment of a change of the basis begins with a local anesthesia and imposing of a plaster bandage to the place of a change. At serious damages and existence of splinters surgical intervention is carried out. The plaster bandage is applied five weeks, and after its removal, to the patient physiotherapy exercises and physical therapy are appointed.
Seldom the change of a diaphysis of a metacarpal bone which passes with shift or without shift meets. Symptoms are pain in the field of an injury, strong loading and shift of the first finger of a brush.
Treatment begins with the roentgenogram and overlaying of a plaster bandage from a forearm to the basis of fingers. In certain cases operational treatment and fixing of fingers by means of spokes is required.
The fracture of phalanxes of fingers occurs at strong direct or indirect stroke of a finger. Such change has several types: cross, spiral, splintered, intra articulate and extra articulate. Symptoms are pain, a hand swelling, finger hypostasis, painful feelings at extension of a brush. At the first survey deformation of a finger is observed.
Treatment begins with comparison of splinters of the broken bone and return of normal position of a phalanx. On a finger for 30 days it is imposed plaster steak or the tire. At serious damages the finger is fixed spokes and a bone pin, and then the plaster bandage is applied.
Human bones are stronger than concrete four times.

The person, as well as all other beings living on our planet feels weather changing. It is normal meteosensitivity, not...
Section: Articles about health
The brain of the person is studied not one hundred years, but the quantity of the riddles connected with this body increases rather, than decreases. Perhaps, numerous delusions concerning a structure and functioning of a brain, many are explained by it from...
Section: Articles about health
Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only the food sating an organism but also the medicines curing of many diseases. Unfortunately, the use of some of them got out of fashion long ago, and once favourite plants and vegetables almost ceased to make a contribution to human health. Inclusion of such products in a modern diet − an effective measure of prevention and treatment of diseases which seldom suffered...
Section: Articles about health
Insufficiently strongly expressed sexual desire or lack of satisfaction from sexual contacts can test time from in...
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair by means of coloring, or considerably changing it for the purpose of creation of absolutely new image. All know that the gray hair is a sign приближающ...
Section: Articles about health
Each person has easy indispositions which he transfers "standing", trying not to ask for medical care. Arguments at the same time are adduced same: "it is a trifle, itself will pass", "I have too many important issues", "there are no wish to spend time for doctors", etc. At good shape of health, normal working capacity and lack of suspiciousness dislike for complaints to such problems is quite natural. It is not the most correct, but very widespread type of behavior. I am glad...
Section: Articles about health
EKO, or extracorporal fertilization - a method of treatment of infertility which became the reason of a set broken mines in due time...
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching of oral cavities over health periodically has problems: enamel of teeth darkens under the influence of some products, on it I accumulate...
Section: Articles about health
Almost each of us during life faced dissatisfaction with own body. At such moments, as a rule, we begin to shame ourselves, urgently we go on the most rigid diet promising minus of 10 kg in a week, or we exhaust ourselves in the gym to almost death. As a rule, similar attempts come to an end with a campaign to the refrigerator for jamming of the next stress. Further history repeats itself with individual frequency....
Section: Articles about health
For most of the working people the problem of having a snack is particularly acute enough. Sooner or later there is a question: what is possible quickly for a sja...
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear are similar, however if the fear is natural protective function of mentality, then the phobia is its deviation. So the person can an ispytyva...
Section: Articles about health
Tuberculosis – a serious infectious disease which development is caused by mycobacteria (Koch's bacilli). The illness is known from an extreme antiquity. Long time fight against it was considered as ineffective. Quite often the disease affected the whole families, and mortality from it was very high. It became the reason of emergence of a set of delusions concerning transmissibility and a possibility of treatment of tuberculosis....
Section: Articles about health
For the last decades the diabetes mellitus of the second type became really world problem. Number of cases annually cart...
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot" were since ancient times used for strengthening of protective forces of an organism, treatment of avitaminosis, anemia and many other diseases. In recent years wide п...
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. In the summer repeatedly the risk increases to ache with some very dangerous illnesses, we also will talk about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications to...
Section: Articles about health
It is impossible to imagine human life in which there would be no plants. Practically in each apartment and any production room there are window plants, millions of people with pleasure are engaged in gardening and truck farming, many citizens пр...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism not only the remains of food, but also mass of harmful substances which we with food accepted accumulate. Accepted to accept, and about that to remove them, did not take care. And in it a problem....
Section: Articles about health
Each failure in work of bodies and systems of a human body is, as a rule, shown by the whole complex of symptoms. In particular, N...
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far he already helped a significant amount of married couples to become happy parents. Usually to the EKO procedure difficult and very expensive, resort in those...
Section: Articles about health
What is in our understanding weeds? It plants which are considered to be suitable only for compost pits and feeding of animals. Meanwhile, among the weeds growing literally under legs it is possible to find the mass of the officinal herbs having invaluable advantage for human health. It is possible not only to be treated by most of them, using as broths, tinctures, compresses, but also to accept in food as usual products. Let's consider 8 widespread and often ignored by people...
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. Odes...
Section: Articles about health
Tea is loved and use almost everything. This drink has tonic properties, contains the tannins capable to suppress activity of causative organisms. Recently great popularity was gained by teas with vegetable additives. Лечеб...
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead to decrease in protective forces of an organism, and it becomes vulnerable for a set of diseases. It is wrong to think that the stress is a problem of the present. Life of people and hundred, and one thousand years ago also abounded with problems therefore need of a relaxation understood in ancient times – to some techniques more than one thousand years. The person needs knowledge of how it is possible to relax, this knowledge пригод...
Section: Articles about health
Cold – a state known to everyone which is followed by cold, cough, high temperature, a pharyngalgia. Often перво...
Section: Articles about health
The healthy nutrition is the invariable principle of health and good health for long years of the woman. Nevertheless, in a diet at each stage of life there are the features allowing to support an organism by those substances which are most necessary...
Section: Articles about health
It is difficult to revaluate importance of kidneys for an organism. These bodies not only perform work on purification of blood of decomposition products and removal of excess liquid. They are responsible also for production of some hormones necessary for maintenance of a normality of a bone tissue, and also for a producing red blood cells – erythrocytes....
Section: Articles about health
