





Heart arrhythmia
Heart arrhythmia (arrhythmia cordis; Greek arrhythmia – unevenness, lack of a rhythm, and - – otritsa. rhythmos – a rhythm) – the name combining disturbances of formation of an impulse of excitement or its carrying out on a myocardium is frequent +; it is shown by disturbances of a rhythm of cordial reductions.
Allocate the following types of arrhythmia of heart:
- Respiratory (respiratoria; synonym: Goering a phenomenon) – increase in heart rate at a breath and its reduction at an exhalation; it is caused by change of a tone of a vagus nerve, is a kind of a sinus arrhythmia;
- Ciliary (fibrillaris; synonyms: arrhythmia is full, (устар.) "nonsense of heart") – fibrillation of auricles with a full irregularity of breaks between cordial reductions, and forces of reductions of ventricles of heart;
- Ciliary bradisistolichesky (fibrillaris bradysystolica; synonym: the bradyarrhythmia ciliary) – proceeds with lack of deficit of pulse and reduced or normal rate of cordial reductions;
- Ciliary large and wave – is characterized by existence on an ECG of rather rare and large teeth of atrial fibrillation;
- Ciliary melkovolnovy – is characterized by existence on an ECG of rather small and frequent waves of atrial fibrillation;
- Ciliary paroxysmal (fibrillaris paroxysmalis) – is characterized by a pristupoobrazny current; in intervals between attacks the correct sinoatrial rate is noted;
- Ciliary constant (fibrillaris perpetua) – is characterized by constant atrial fibrillation; usually arises because of an overload or organic lesions of auricles;
- Ciliary takhisistolichesky (fibrillaris tachysystolica; synonym: the tachyarrhythmia ciliary) – is characterized by increase of cordial reductions and is followed by deficit of pulse;
- Ciliary euritmichesky (fibrillaris eurhythmica) – the frequency of reductions of ventricles is in the limits which are norm for the healthy person;
- Paroxysmal (paroxysmalis) – arises and stops suddenly, proceeds against the background of a normal nomotopny heart rhythm or rather constant form of disturbance of a heart rhythm of other character;
- The post-prefix post-conversion (Latin – after + conversio – circular motion) – is observed after recovery of a sinoatrial rate at patients with a ciliary arrhythmia, a Bouveret's disease or an atrial flutter;
- Sinus (sinuosa) – is caused by fluctuations of automatic activity of a sinus and atrial node, usually connected with fluctuations of a tone of a vagus nerve.
In operating time our brain spends the amount of energy equal to the 10 Watts bulb. So the image of a bulb over the head at the time of emergence of an interesting thought is not so far from the truth.

There is an opinion that at low temperatures safety of products is ensured longer and better thanks to what the refrigerator considers...
Section: Articles about health
The chia plant, or the Spanish sage, is from South America. The indigenous people of the continent since ancient times used its seeds in food: small, but very nutritious kernels, in a form the reminding fasolina. Indians knew about useful properties of seeds of a chia, and applied...
Section: Articles about health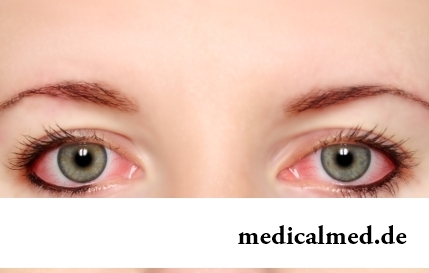
The sclera and mucous membrane of an eye are intensively supplied with blood vessels which problem - to saturate nervous tissues of body with nutrients and oxygen. In a normality vessels are almost not noticeable, however at their expansion (owing to thinning of walls) become visible, painting a sclera in red color. Quite often red eyes - the signal of any trouble in an organism caused as external irritants, allergens, and diseases which need in about...
Section: Articles about health
Each of us repeatedly noticed that the people having the same passport age are sometimes not similar on one-years at all. One...
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutrients and receiving pleasure from process of its satisfaction demonstrates that the organism functions without special from...
Section: Articles about health
The body of the person almost for 60% consists of water. It is so important for normal functioning of an organism that loss of only one and a half percent of liquid already leads to the most unpleasant effects. The problems connected with deficit of water can overtake also the healthiest person if he, for example, spends several hours under the scorching sun, without having taken with themselves drink, but is very simple to correct health in this case. It is much more difficult to minimize effects of other reasons about...
Section: Articles about health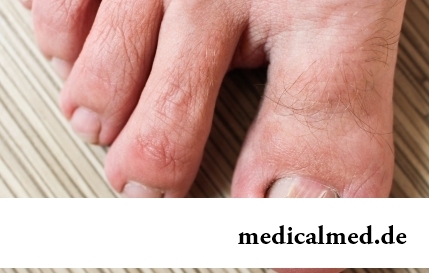
The word "onikhokriptoz" is unfamiliar to most of people, meanwhile quite so physicians call very widespread problem: growing...
Section: Articles about health
All parents are ready to what the baby often and pisat much. Since then, as the absorbing diapers strongly became current, keeping of the kid in dryness does not represent any problems. But if the grown-up kid continues to urinate in panties, parents of a nacha...
Section: Articles about health
There is a lot of fans of beer in our country. Statistically, on each average Russian (including women and children) in a year about 60 liters of this drink are consumed. It is not a lot of, as in the Czech Republic or Germany, but figure all the same impressive. There is nothing to rejoice here: despite assurances of producers that beer is absolutely harmless, effects of its active consumption cannot be considered positive in any way. Here only part of that negative impact, which popular нап...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs п...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
The fatigue, sleep debt, disturbances of food, bad mood, vagaries of the weather – all these circumstances badly affect our appearance. Especially the person suffers: skin becomes flabby, loses healthy color, becomes covered by wrinkles, zones of hypostases and dark circles under eyes appear. It is not always possible to be saved from influence of aggressive factors, but we are quite able to minimize its effects. For this purpose usually apply the cosmetics and procedures helping увлаж...
Section: Articles about health
Life of the modern woman is very difficult. Opportunities to realize itself are wide: it not only education and career, but also most differently...
Section: Articles about health
The Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) are plants or animals (as a rule, agricultural) to whose genotype purposeful changes were made. Opposition of supporters and opponents of inclusion of such organisms in foodstuff всег...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning they laugh and joke, and in the evening cry or are irritated....
Section: Articles about health
All the known slogan "Protect Men!" arose not from scratch. In a sense, the nature created representatives of strong...
Section: Articles about health
(Xerostomia) many people consider feeling of a xerostomia small and easily removable inconvenience. This delusion: the symptom can demonstrate existence of serious diseases. It is worth to remember also that saliva performs important functions...
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to get access to various apparatuses and an opportunity to train under the leadership of the experienced consultant. Many consider fitness the best way of maintenance of physical shape and receiving dynamic loads which the people occupied preferential with brainwork so need. Nevertheless, representations of most of consumers of similar services about специф...
Section: Articles about health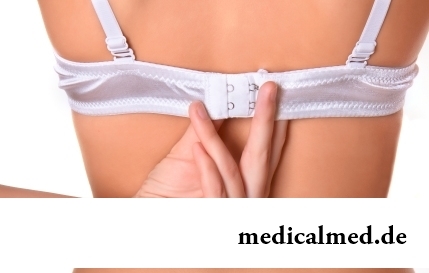
The name of this disease precisely reflects the problem reason: it consists in the bra fastener pressure upon a certain zone...
Section: Articles about health
Urogenital candidiasis (milkwoman) – a fungal infection which annoys unpleasant feelings in the field of generative organs, being followed by white curdled allocations, an itch, discomfort during an urination, pain. She is called by Candida fungus – a mustache...
Section: Articles about health
Each failure in work of bodies and systems of a human body is, as a rule, shown by the whole complex of symptoms. In particular, malfunctions with health often cause emergence of cosmetic defects in the form of rashes on a face. Experienced doctors know that localization of heat-spots usually depends on what disease the patient has....
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it is strong for...
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear are similar, however if the fear is natural protective function of mentality, then the phobia is its deviation. So the person can an ispytyva...
Section: Articles about health
Coffee - the tonic loved by many for the invigorating aroma and deep taste. Having the stimulating effect, coffee increases working capacity, promotes concentration of attention, fights against drowsiness and improves mood. Statistically, about 30% of inhabitants of the planet regularly use coffee, from them more than 8% are "coffee-achievers" - the persons using more than 3 cups of drink a day....
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be study...
Section: Articles about health
The number of long-livers is very small. One person from 5 thousand lives up to age of 90 years, and the centenary boundary steps over only one of 20 thousand. However, doctors claim that each of us is quite able to affect own destiny. At the same time speech to Ida...
Section: Articles about health
To look healthy and means well-groomed not only to be pleasant to people around, but also to feel strong, sure and taken place. Specialists in the field of cosmetology quite often note that not all women are able to look after face skin. Many women incorrectly apply cosmetics, ineptly use various procedures, without having exact information on their real influence and dividing numerous delusions about it. All this not the best...
Section: Articles about health
