





Skull
The skull represents the bone framework consisting of 23 bones and protecting a brain from damages. The skull has 8 steam rooms and 7 unpaired bones.
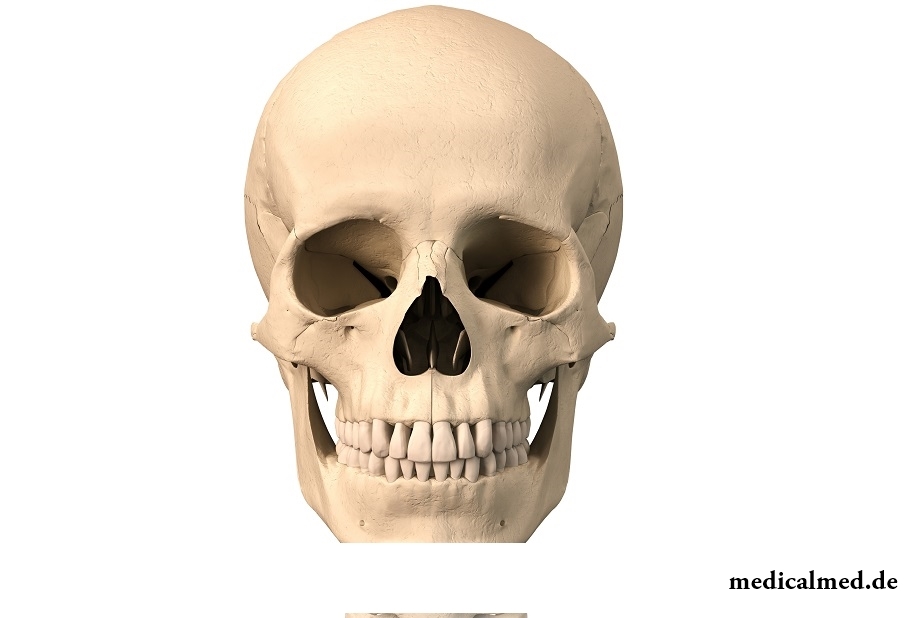
Structure of a skull of the person
The skull of the person belongs to bone system and a musculoskeletal system. The skull is subdivided into two main departments – front and brain. Departments of a skull of the person carry out a certain role and exert impact on all organism.
The front department of a skull of the person consists of steam rooms (an upper jaw, a nasal bone, the lower nasal sink, a palatal bone, malar and lacrimal bones) and unpaired (a sievebone, a share, a mandible, a hypoglossal bone) bones. The front department of a skull exerts impact on sense bodys, breath and digestion.
Unpaired bones have the areas filled with air which connect to a nasal cavity. Air areas allow a skull to be strong, and also they provide thermal isolation for sense bodys. Wedge-shaped, trellised, frontal, pair, temporal bones and an upper jaw belong to air-vessels.
The special role is carried out by the arc-shaped hypoglossal bone which is located between a throat and a mandible, and also connects to skull bones by means of ligaments and muscles. This bone forms a body and pair horns from which awl-shaped shoots of temporal bones depart. Connections between bones are fibrous.
Upper bones of a skull of the person flat also consist of plates with bone substance, and in cells of bone substance there is marrow and blood vessels. Some bones of a skull of the person have roughnesses which correspond to crinkles and furrows of a brain.
The brain department of a skull of the person consists from unpaired (occipital, wedge-shaped and frontal) and steam rooms (parietal and temporal) bones. The brain department which has volume about 1500 cm ³ is a protective bone framework for a brain. This department is located over front department.
The pneumatic frontal bone consists of two cheshuy and a nasal part. In a frontal bone the forehead and frontal hillocks which form walls of eye-sockets, a nasal cavity, temporal poles and parts of a front pole forms. The parietal bone creates calvarias, and also in it there is a parietal hillock. The occipital bone forms a base of skull, the arch and a cranial pole which consists of 4 parts which are located in occipital openings. The pneumatic wedge-shaped bone consists of a body which has a gipofizny pole with a hypophysis.
Difficult pair bone is the pneumatic temporal bone which creates a calvaria and contains acoustic organs. The pneumatic temporal bone forms a pyramid in which the drum cavity and an inner ear is placed.
Bones of a skull of the person are connected among themselves by seams. On front department of a bone adjoin by means of flat and equal seams, and scales of temporal and parietal bones, forming a seam of scaly type connect seams. A parietal and frontal bone connect to the help of a coronal seam, and two parietal bones are connected by a sagittal seam. On site children have connections of sagittal and coronal seams a big fontanel, that is connecting fabric which did not become bone yet. Occipital and parietal bones connect a lyambdovidny seam, and on crossing of lyambdovidny and sagittal seams the small fontanel is formed.
Age features of formation of a skull
The major role in formation of a skull of the person is played by a brain, sense bodys and masseters. In the course of a growing the structure of a skull of the person changes.
At the newborn of a bone of a skull are filled with connecting fabric. Usually at babies six fontanels which are closed by connecting plates – wedge-shaped and mastoidal type are formed. The skull of the newborn is elastic and his form can change therefore the fruit passes through patrimonial ways without injuries of a brain. Transition of connecting fabric to a bone tissue happens at 2-year age when fontanels are completely closed.
Structure of a skull of the adult and child various. Development of a skull takes place in several main stages:
- From the birth up to 7 years is a stage of uniform and vigorous growth. During the period from one to three years a back part of a skull actively forms. By three years with the advent of milk teeth and development of chewing function in the child the facial skull and its basis forms. By the end of the first period the skull gets length which is similar to the adult's length.
- From 7 to 13 years is the period of slow growth of a calvaria. By 13 years the cavity of a calvaria reaches 1300 cm ³.
- After 14 years to mature age is the period of active growth of frontal and front departments of a brain. During this period sexual distinctions are strenuously shown. At boys the skull is extended in length, and at girls its rotundity remains. Total capacity of a skull men have 1500 cm ³ and 1340 cm ³ at women. The male skull during this period gains the expressed relief, and at women it remains to more smoothed.
- Advanced age is the period of change of a skull connected with aging of an organism, dedentition, reduction of chewing function and change of masseters. If at the person during this period teeth dropped out, then the jaw stops being massive, elasticity and durability of a skull decreases.
Functions of a skull
The skull of the person as complex bone body, performs several main functions:
- serves as a bone framework for a brain and sense bodys, and its bone educations are protective cells for the nasal courses and eye-sockets;
- bones of a skull connect mimic muscles, muscles of a neck and masseters;
- participates in process of the speech, and jaws and pneumatic bosoms are intended for formation of sounds;
- plays an important role in the alimentary system, in particular, the jaw is intended for implementation of chewing function and restriction of an oral cavity.
Injuries of a skull and their treatment
Injuries of a skull can lead to serious violations of functioning of a human body – to paralysis, mental disorders, disturbances of the speech and memory. Treat the main injuries of a skull: a change of the arch of the closed and open type, a fracture of base of the skull, a craniocereberal injury with a concussion of the brain.
The change of a calvaria is shown in the form of a hematoma of a hair part of the head of the person, disturbances of consciousness, loss of memory and breath disturbance. The person who got this injury should be laid on a plain surface and to apply a bandage the head. At unconsciousness of the patient it is necessary to put a back on a stretcher in half-turn positions, and under one side of a trunk to enclose a pillow or the roller. At disturbances of breath the artificial respiration is carried out, then the victim is brought to medical institution for performing medical examination.
The fracture of base of the skull can be shown in the form of bleedings from a nose and ears, dizzinesses and a headache, a loss of consciousness. At damage of a base of skull the victim should exempt respiratory tracts and an oral cavity from cerebrospinal fluid and blood, and at disturbances of breath to carry out an artificial respiration.
The concussion of the brain is shown at a craniocereberal injury. Symptoms are the loss of consciousness, dizziness and a headache, nausea, vomiting, increase of pulse, pallor of the person, weakness. At a serious bruise of a brain of people can faint at several o'clock. In hard cases functioning of cardiovascular and respiratory systems is broken. The victim should make immediately an indirect cardiac massage and an artificial respiration, and to apply a bandage a surface of a wound, then to hospitalize the patient.
In the presence of intracranial educations the craniotrypesis is carried out.
The craniotrypesis represents surgery with formation of an opening in a skull bone. The purpose of a craniotrypesis is achievement of the injured area in which there is a hematoma or other malignancies.
There are several ways of a craniotrypesis – decompressive with a resection of a temporal bone and opening of a meninx (at dislocation of marrow); osteoplastic with cutting out of several soft tissues and bones; resection with removal of a part of a bone of a skull (for a decompression and surgical treatment of brain wounds).
The stomach of the person not bad copes with foreign objects and without medical intervention. It is known that the gastric juice is capable to dissolve even coins.

Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times from...
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. The statistics of incidence is considered not full as at an initial stage the illness, as a rule, does not cause to the person of special inconveniences, and many diseased sees doctors not at once. The cataract is not only one of the most widespread ophthalmologic illnesses, but also the reason of a half of cases of loss of sight....
Section: Articles about health
Any person who faced a disease knows that treatment costs expensive. It belongs also to consultations qualified the specialist...
Section: Articles about health
Helminthosis is one of the most widespread diseases. Statistically, any species of helminths infected every third inhabitant of the planet. Most of specialists even consider these data strongly underestimated: some uninvited "cohabitants" of N...
Section: Articles about health
Musicotherapy – a treatment method which caused and causes a set of a controversy concerning its efficiency. However the facts are relentless: during the numerous researches curative impact of music on an organism was scientifically confirmed. Since then in a number of the countries the technique is included complex therapy of diseases of cardiovascular and respiratory system, dorsodynias and a backbone, psychosomatic disturbances and many other illnesses. The musicotherapy in a pedi is especially widely applied...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that our country is one of the most "drinking" in the world. At clear understanding of that the use of strong...
Section: Articles about health
From sexual contacts each person can test insufficiently strongly expressed sexual desire or lack of satisfaction from time to time. However when it happens regularly, it is an occasion to think about health. Most of people does not hurry an obrashcha...
Section: Articles about health
Tuberculosis – a serious infectious disease which development is caused by mycobacteria (Koch's bacilli). The illness is known from an extreme antiquity. Long time fight against it was considered as ineffective. Quite often the disease affected the whole families, and mortality from it was very high. It became the reason of emergence of a set of delusions concerning transmissibility and a possibility of treatment of tuberculosis....
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as about...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which is felt by the kid, to...
Section: Articles about health
Urogenital candidiasis (milkwoman) – a fungal infection which annoys unpleasant feelings in the field of generative organs, being followed by white curdled allocations, an itch, discomfort during an urination, pain. She is called by Candida fungus – the opportunistic organism living on mucous membranes of an organism....
Section: Articles about health
Transfusion of donor blood has almost century history. In spite of the fact that this procedure is quite usual for many people, itself п...
Section: Articles about health
History of use of an anesthesia during operations contains more than 160 years. Annually in the world hundreds of thousands of surgical interventions during which to patients the substances immersing them in a dream and saving from pain are entered are carried out. Using an anesthesia to these...
Section: Articles about health
With age in a human body harmful substances collect. We receive them with food and water, at inhalation of the contaminated air, reception of medicines, use of household chemicals and cosmetics. A considerable part of toxins accumulates in a liver which main function is continuous purification of blood. This body begins to knock as any got littered filter, and efficiency of its work decreases....
Section: Articles about health
We present to yours the TOP of the medicamentous means exerting the stimulating impact on a potentiality, i.e. on ability of a muzhcha...
Section: Articles about health
Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary to minimize. There is a number of rules, following to which will help or to avoid absolutely infection with flu or a SARS, or to have an illness...
Section: Articles about health
Childbirth is the most important event in life of each woman. We are women we give birth to the new little man on this light. Now the tendency to that was outlined, as men want to participate in labor too. But there is a question and whether it is worth allowing the husbands on childbirth?...
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In большинс...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, at the address to doctors seven of each ten patients complain of a headache. Actually it is much more people who are periodically feeling unpleasant feelings such. Many people, apart from a headache the reason for serious fear...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even at the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching з...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
For many spouses the question of planning of a family is one of the main. The problem of the choice of effective and safe contraceptives at the same time comes out on top. Russians still not often resort to operation of a vasectomy extremely popular in the USA, and also in some European and Asian countries. The reason is simple: most of men simply do not possess the complete information about specifics and effects of this procedure. Let's try to meet this lack and to acquaint readers about those...
Section: Articles about health
Each woman has preferences in the field of use of those goods which help us to look good, feel се...
Section: Articles about health
The word "onikhokriptoz" is unfamiliar to most of people, meanwhile quite so physicians call very widespread problem: the growing of edge of a nail into surrounding fabrics causing inflammatory process. Usually the illness affects thumbs of legs, and is followed покр...
Section: Articles about health
Producers of milk mixes for children assure: mixes are ideally balanced and adapted for needs of babies. If mother should raise artificially the kid owing to serious problems with health, to do nothing – it is necessary to feed with substitutes of milk. However pediatricians note that not seldom women without good reasons refuse feeding of the child a breast and pass to milk mixes. Common causes of such decision – the aspiration to leave quicker...
Section: Articles about health
