





Isoptinum
Application instruction:
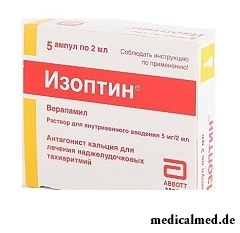 Isoptinum – drug with hypotensive, antiarrhytmic and anti-anginal action.
Isoptinum – drug with hypotensive, antiarrhytmic and anti-anginal action.
Form of release and structure
Isoptinum is released in the following dosage forms:
- Tablets, film coated: white, biconvex, round; on 40 mg – with a text "40" on one of the parties and an engraving in the form of a triangle on another; on 80 mg – with a text of "ISOPTIN 80" on one of the parties both risky for division and a text "KNOLL on another (tablets on 40 and 80 mg: on 10 pieces in blisters, on 2 or 10 blisters in a cardboard pack; on 20 pieces in blisters, on 1 or 5 blisters in a cardboard pack; tablets on 80 mg: on 25 pieces in blisters, on 4 blisters in a cardboard pack);
- Solution for intravenous administration: colourless, transparent (on 2 ml in colourless glass ampoules, on 5, 10 or 50 ampoules in pallets or blisters, on 1 blister or the pallet in a cardboard pack).
Is a part of 1 tablet:
- Active agent: verapamil – 40 or 80 mg (in the form of a hydrochloride);
- Auxiliary components (40/80 mg respectively): a calcium hydrophosphate dihydrate – 70/140 mg; microcrystallic cellulose – 23/46 mg; colloid silicon dioxide – 0,7/1,4 mg; croscarmellose sodium – 1,8/3,6 mg; magnesium stearate – 1,5/3 mg.
Structure of a film cover (40/80 mg respectively): sodium lauryl sulfate – 0,1/0,1 mg; a gipromelloza of 3 MPas – 1,7/2 mg; talc – 4/4,5 mg; macrogoal of 6000 - 2/2,3 mg; titanium dioxide – 1/1,1 mg.
Is a part of 1 ampoule:
- Active agent: verapamil – 5 mg (in the form of a hydrochloride);
- Auxiliary components: Acidum hydrochloricum of 36% – before finishing pH; sodium chloride – 17 mg; water for injections – to 2 ml.
Indications to use
Isoptinum in the form of tablets is appointed for treatment of the following diseases:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Bouveret's supraventricular disease;
- Coronary heart disease, including unstable stenocardia, chronic stable stenocardia (a classical angina of exertion), Printsmetal's stenocardia (stenocardia which is caused by a vasospasm);
- Blinking/atrial flutter which is followed by a tachyarrhythmia (except a syndrome of Launa-Ganonga-Levina (LGL) and Wolf-Parkinson-Whyte (WPW)).
Drug in the form of solution for intravenous administration is used at treatment of supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. Isoptinum is appointed at the following indications:
- Recovery of a sinoatrial rate at Bouveret's supraventricular disease, including states which are connected with existence of additional conduction paths (syndromes of Launa-Ganonga-Levina and Wolf-Parkinson-Whyte);
- Control of frequency of reductions of ventricles during the blinking and an atrial flutter (takhiaritmichesky option), except cases when blinking or an atrial flutter is connected with existence of additional conduction paths (syndromes of Launa-Ganonga-Levina and Wolf-Parkinson-Whyte).
Contraindications
- AV blockade of the II-III degree (except patients with an artificial pacemaker);
- Sick sinus syndrome (a syndrome of "bradycardia tachycardia", except patients with an artificial pacemaker);
- Blinking/atrial flutter in the presence of additional ways of carrying out (a syndrome of Launa-Ganonga-Levina and Wolf-Parkinson-Whyte);
- Age up to 18 years (efficiency and safety of use of drug for this age group of patients are not established);
- Hypersensitivity to drug components.
Additional contraindications to reception of Isoptinum in the form of tablets are:
- Chronic heart failure;
- The acute myocardial infarction complicated by the expressed arterial hypotension, bradycardia and a left ventricular failure;
- Cardiogenic shock;
- Concomitant use with colchicine.
Intravenous administration of Isoptinum is contraindicated in the presence of the following diseases / states:
- Arterial hypotension or cardiogenic shock (except caused by arrhythmia);
- Morganyi-Adams-Stokes's syndrome;
- Sinoauricular block;
- Ventricular tachycardia with the wide QRS complexes (more than 0,12 seconds);
- Chronic heart failure of IIB-III of a stage (except the caused supraventricular tachycardia which is subject to treatment by verapamil);
- Preliminary use of Disopyramidum (within 48 hours);
- Simultaneous intravenous administration of beta adrenoblockers;
- Pregnancy and period of a lactation.
Isoptinum in all medicinal headlights should be applied with care at bradycardia and AV blockade of the I degree.
Inside drug is appointed with care at the expressed functional disturbances of kidneys and a liver, arterial hypotension, diseases concerning neuromuscular transfer including a syndrome of Lambera-Eton, a myasthenia of gravis and muscular dystrophy of Dyushenn.
Intravenous administration is recommended to be carried out with care at patients of advanced age, and also at the following diseases: heart failure, a heavy stenosis of the mouth of an aorta, a myocardial infarction with a left ventricular failure, slight or moderate arterial hypotension, a renal and/or liver failure.
Route of administration and dosage
Isoptinum in the form of tablets is accepted inside, swallowing entirely (it is impossible to chew or rassasyvat) and washing down with water. It is more preferable to accept drug in time or right after meal.
The scheme of use of Isoptinum is defined individually with disease severity and a clinical picture.
For all recommended indications the average daily dose makes 240-480 mg. At long therapy it is not necessary to exceed a daily dose of 480 mg. In the maximum daily dose Isoptinum should be accepted only in the conditions of a hospital.
Initial single dose – 40-80 mg, frequency rate of reception – 3-4 times a day.
Patients with functional disturbances of a liver therapy are recommended to begin 40 mg with a single dose. Frequency rate of reception – 2-3 times a day. Further the doctor selects a dose individually.
Isoptinum in the form of solution for injections can be entered only intravenously.
Introduction needs to be carried out slowly at continuous control of an ECG and arterial pressure for, at least, 2 minutes (at elderly patients – 3 minutes that reduces risk of development of undesirable effects).
Initial dose – 5-10 mg (0,075-0,15 mg/kg of body weight). At the inadequate response to the first introduction in 30 minutes it is possible to enter a repeated dose (10 mg).
Side effects
During therapy development of disturbances from some systems of an organism is possible:
- Alimentary system: pain and feeling of discomfort in a stomach, vomiting, nausea, lock, intestinal impassability; in some cases – tranzitorny increase in a blood plasma of activity of hepatic transaminases and an alkaline phosphatase; seldom – a hyperplasia of gums (morbidity, bleeding, puffiness), increase in appetite, diarrhea;
- Cardiovascular system: the expressed bradycardia, face reddening, an atrioventricular block, the expressed lowering of arterial pressure, emergence of symptoms of heart failure at use of high doses of drug, especially at predisposed patients; heartbeat, tachycardia, stop of a sinus node; seldom – arrhythmia (including trembling and ventricular fibrillation), stenocardia up to development of a myocardial infarction (especially at patients with crushing obstructive defeat of coronary arteries), bradycardia;
- Nervous system: the general weakness, uneasiness, a depression, drowsiness, extrapyramidal disturbances (rigidity of legs or hands, the ataxy shuffling gait, a mask-like face, swallowing difficulty, trembling of brushes and fingers of hands), a headache, dizziness, spasms during administration of drug, a tremor, paresthesias; in rare instances – block, the increased nervous irritability, fatigue;
- Allergic reactions: multiformny exudative erythema, dermahemia of the person, skin rash, itch, Stephens-Johnson's syndrome, bronchospasm;
- Others: increase in body weight; very seldom – arthritis, an agranulocytosis, a tranzitorny blindness at the peak of concentration of drug in blood, asymptomatic thrombocytopenia, a fluid lungs, development of peripheral hypostases, fatigue, a giperprolaktinemiya, a gynecomastia, impotence, a galactorrhoea, muscular weakness, the increased sweating, joint pains, mialgiya.
The majority of the listed side effects are characteristic of all dosage forms of Isoptinum.
Special instructions
Sharply it is impossible to cancel reception of Isoptinum. The dose is recommended to be reduced gradually to full cancellation of therapy.
Intravenous administration of Isoptinum can cause passing lowering of arterial pressure which usually clinically is not shown, but can be followed by development of dizziness.
The circulatory unefficiency (except heavy or caused by arrhythmia) prior to therapy by Isoptinum needs to be compensated by diuretics and cardiac glycosides. At patients with heavy and moderate heart failure during therapy acute progressing of a circulatory unefficiency can be observed.
Solution does not support antimicrobic or bacteriostatic agents and is intended for simultaneous intravenous administration.
Isoptinum keeps stability at least for 24 hours (at its storage at a temperature up to 25 °C in the place protected from light) in the majority of parenteral solutions of large volume. After a fence of a portion of contents of any volume, unused solution should be destroyed immediately.
To avoid disturbance of stability it is not recommended to part Isoptinum with lactate sodium solutions in plastic packages from polyvinylchloride. It is necessary to avoid mixing of solutions of Isoptinum with Amphotericinum In, albumine, a gidralazin a hydrochloride or Trimethoprimum and sulfamethoxazole.
Verapamil the hydrochloride pretsipitirut in any solutions with рН more than 6.
Isoptinum, depending on specific features, can change speed of response, breaking ability to driving and performance of work, requiring special attention.
Medicinal interaction
At simultaneous use of Isoptinum with inhibitors of an isoenzyme CYP3A4 increase in concentration of verapamil in a blood plasma, with CYP3A4 isoenzyme inductors – decrease in its concentration is observed (interaction should be considered at simultaneous use of similar means).
At simultaneous use of Isoptinum with some medicines there can be undesirable effects (Css – average equilibrium concentration of substance in a blood plasma, Cmax – the maximum concentration of substance in a blood plasma, AUC – the area under a pharmacokinetic curve "concentration time", T1/2 – an elimination half-life):
- Prazozinum: increase in its Cmax, T1/2 of Prazozinum does not change;
- Terazozin: increase in its AUC and Cmax;
- Quinidine: reduction of its clearance;
- Theophylline: reduction of its system clearance;
- Carbamazepine: increase in its AUC at patients with steady partial epilepsy;
- Imipraminum: increase in its AUC; on concentration of an active metabolite of Imipraminum – desipramine, Isoptinum of influence does not render;
- Glibenclamidum: increase in its Cmax and AUC;
- Klaritromitsin, erythromycin, телитромицин: increase in concentration of verapamil is possible;
- Rifampicin: reduction of AUC, Cmax and bioavailability of verapamil at intake;
- Doxorubicine: increase in its AUC and Cmax at patients with small-celled cancer of a lung;
- Phenobarbital: increase in clearance of verapamil;
- Buspiron, midazolam: increase in their AUC and Cmax;
- Metoprolol, propranolol: increase in their AUC and Cmax at patients with stenocardia;
- Digitoxin: reduction of its general and extrarenal clearance;
- Digoxin: increase in its Cmax, AUC and Css;
- Cimetidinum: increase in AUC R-enantiomera and S-enantiomera of verapamil with the corresponding decrease in clearance of R-and S-verapamil;
- Cyclosporine: increase in its AUC, Css, Cmax;
- Sirolimus, такролимус, ловастатин: increase in their concentration is possible;
- Atorvastatin: increase in its concentration and AUC is possible;
- Simvastatin, алмотриптан: increase in their AUC and Cmax;
- Sulfinpyrazonum: increase in clearance of verapamil and decrease in its bioavailability;
- The St. John's Wort which is made a hole: reduction of AUC R-enantiomera and S-enantiomera of verapamil with the corresponding decrease in Cmax;
- Grapefruit juice: increase in AUC and Cmax R-enantiomera and S-enantiomera of verapamil (the renal clearance and T1/2 do not change);
- Terazozin, Prazozinum: the additive hypotensive action;
- Diuretics, antihypertensives, vazodilatator: strengthening of hypotensive effect;
- Ritonavir and other antiviral means for treatment of HIV infection: the verapamil metabolism inhibition is possible that can lead to increase in its concentration in a blood plasma (at simultaneous use of a dose of Isoptinum it is necessary to lower);
- Quinidine: strengthening of hypotensive action is possible; at patients with a hypertrophic subaortic stenosis edematization of lungs is possible;
- Carbamazepine: increase in its concentration in a blood plasma; development of the side reactions inherent to carbamazepine (a headache, a diplopia, dizziness or an ataxy) is possible;
- Lithium: increase in its neurotoxicity;
- Rifampicin, Sulfinpyrazonum: reduction of hypotensive effect of verapamil is possible;
- Muscle relaxants: strengthening of their effect is possible;
- Acetylsalicylic acid: increase in bleeding;
- Colchicine: perhaps significant increase in its concentration in blood;
- Ethanol (alcohol): increase in its concentration in a blood plasma;
- Beta adrenoblockers, antiarrhytmic means: mutual strengthening of cardiovascular effects (more considerable urezheniye of heart rate, more expressed AV blockade, strengthening of arterial hypotension and development of symptoms of heart failure).
To the patient accepting Isoptinum, treatment by hypolipidemic means – with GMG-KOA-reduktazy inhibitors (lovastatiny, simvastatiny, atorvastatiny), it is necessary to begin with perhaps lower doses which at therapy continuation gradually increase. If it is necessary to apply Isoptinum at the patients who are already receiving GMG-KOA-reduktazy inhibitors it is necessary to consider the possibility of reduction of a dose of statines and repeated titration of a dose, considering concentration in cholesterol blood serum. Fluvastatin, розувастатин and правастатин under the influence of an isoenzyme of CYP3A4 are not metabolized therefore their interaction with verapamil is least probable.
Terms and storage conditions
To store in the place, unavailable to children, at a temperature: tablets – 15-25 °C, solution for intravenous administration – to 25 °C.
Period of validity – 5 years.
Name of drug
Price
Drugstore
Isoptinum of WEDNESDAY ретард тбл п / about 240 mg No. 30, Abbott Lab.
438 rub.
 Network of the Moscow drugstores of IFC
Network of the Moscow drugstores of IFCIn our intestines are born, millions of bacteria live and die. They can be seen only at strong increase, but if they gathered, then would be located in a usual coffee cup.

It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – in...
Section: Articles about health
The depression not without reason is considered one their main troubles of our century: for scientific and technical progress, acceleration of rate of life and a surplus of information of people it is forced to pay with stresses, negative emotions and weakening of protective forces of an organism. As a result ш...
Section: Articles about health
About 20% of the population of our planet have a hypertension (permanent increase in arterial pressure). This disease has an adverse effect on the standard of living, reduces working capacity, and in the absence of systematic treatment threatens with such complications as a myocardial infarction, a stroke and other heavy illnesses which can result in disability or sudden death. Most of patients for maintenance of pressure at more or less acceptable level accept appointed doctors лекарст...
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. In opinion д...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, pathologies of a thyroid gland in the world more than 500 million people have. Failures in work of this body lead to heavy disbolism, development of heart diseases, vessels, a reproductive and nervous system. In hard cases excessive...
Section: Articles about health
For many spouses the question of planning of a family is one of the main. The problem of the choice of effective and safe contraceptives at the same time comes out on top. Russians still not often resort to operation of a vasectomy extremely popular in the USA, and also in some European and Asian countries. The reason is simple: most of men simply do not possess the complete information about specifics and effects of this procedure. Let's try to meet this lack and to acquaint readers about those...
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. Use...
Section: Articles about health
History of use of an anesthesia during operations contains more than 160 years. Annually in the world hundreds of thousands of surgical interventions during which to patients the substances immersing them in a dream and saving from pain are entered are carried out. Using an anesthesia to these...
Section: Articles about health
Hemorrhoids – extremely widespread disease. Periodically arising inflammations and bleeding of hemorrhoidal nodes cause serious discomfort to nearly fifteen percent of adults. Meanwhile, having a clear idea of the reasons of an exacerbation of an illness and following rules of precaution, it is possible to reduce substantially sharpness of unpleasant feelings and to reduce progressing of a disease....
Section: Articles about health
Among a set of the perfumery and cosmetic goods which are released today the special group is made by the means containing anti-bacterial...
Section: Articles about health
All like to sing. Small children with pleasure are engaged in a vocal, not especially thinking of hit in a melody. Adults most often hesitate, being afraid to show lack of talents in this area, and it is vain: singing is very useful for health....
Section: Articles about health
Each of us repeatedly noticed that the people having the same passport age are sometimes not similar on one-years at all. One at the age of 40-45 years already looks almost an old man, and another and in 60 is young, vigorous and full of life. The matter is that the condition of our health depends not on the number of the lived years, and on degree of safety of an organism. This factor also defines biological age of the person....
Section: Articles about health
Frosty air, fresh wind and easy snowball at most of Russians are associated with cheerfulness, health and cheerful entertainments, on to...
Section: Articles about health
Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Most often - owing to yet not strengthened mentality - children are subject to neurosises. Premises to emergence of such disturbances can become нез...
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make that process of weight loss did not give you an inconvenience, and, on the contrary, brought joy?...
Section: Slideshow
The word "onikhokriptoz" is unfamiliar to most of people, meanwhile quite so physicians call very widespread problem: growing...
Section: Articles about health
Smack in a mouth can arise in the natural way – as a result of lack of morning hygiene or reception of the corresponding food. However in certain cases its existence is a sign of certain pathologies, and allows to reveal an illness at an early stage. In we depend...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly ways of storage and transportation of food ingredients changed, and people of the whole world had an opportunity to regularly use those products about which their grandfathers and grandmothers did not even know....
Section: Articles about health
All got used long ago that, having addressed the plastic surgeon, it is possible to modify natural parameters of a figure or to reduce...
Section: Articles about health
All are familiar with cold, and practically everyone believes that he has sufficient knowledge and experience that correctly to treat it. In practice most of people makes mistakes in attempts to get rid of rhinitis, and divides numerous delusions it....
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number of myths about negative effect which allegedly gluten has on health of the person....
Section: Articles about health
Color of plants is caused by presence at them of certain chemical compounds. Let's talk that various colors mean vegetable...
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. Trainings will help it to become strong and hardy, will improve coordination of movements, and also will exert positive impact on mentality: it...
Section: Articles about health
From sexual contacts each person can test insufficiently strongly expressed sexual desire or lack of satisfaction from time to time. However when it happens regularly, it is an occasion to think about health. Most of people does not hurry to ask similar questions physicians: one consider that they will be able to cope with malfunctions independently, others hesitate to report to strangers about so delicate problems and hope that troubles will stop by itself....
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, can only one of ten of our compatriots brag of a decent condition of an oral cavity. On среднестатистич...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of use of table salt in the therapeutic purposes contains not one century. Applications which do by means of the fabric impregnated with saline solution are considered especially effective. They have antibacterial and antiinflammatory effect, help to heal wounds, exempt fabrics from excess liquid. Hypertonic salt solution of potassium chloride is applied outwardly at many morbid conditions. Let's tell about the most known of them....
Section: Articles about health

