





Trachea
Trachea – the important part of respiratory tracts connecting a throat to bronchial tubes. On this body air together with necessary amount of oxygen comes to lungs.
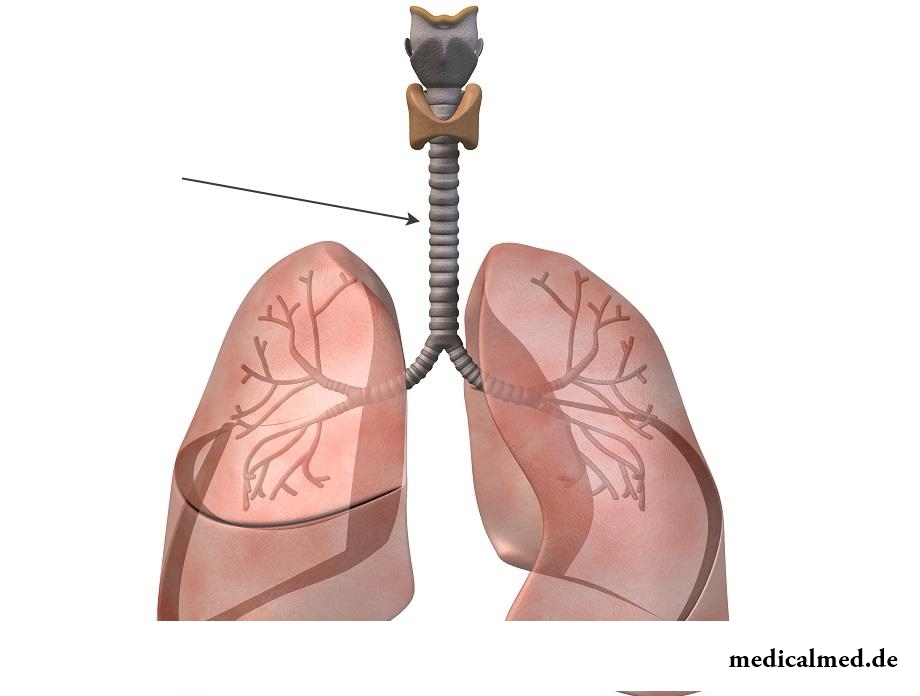
The trachea looks as tubular hollow body, from 8,5 to 15 centimeters long, depending on organism physiology.
The trachea from a cricoid at the level of the sixth cervical vertebra begins. A third of a tube is at the level of cervical department of a backbone, other part is located in chest department. It comes to an end at the level of the fifth chest vertebra where it is divided into two bronchial tubes. In front of a cervical part of a trachea there is a part of a thyroid gland, and behind the gullet adjoins to a tracheal tube. On each side tracheas there passes the neurovascular bunch including fibers of a vagus nerve, carotid arteries and internal jugular veins.
Trachea structure
If to consider a trachea structure in cross section, it becomes visible that it consists of four layers:
- Mucous membrane. Represents the ciliate multilayer epithelium lying on a basal membrane. As a part of an epithelium there are stem cells and scyphoid which emit slime in small amounts. Also there are incretion cells making noradrenaline and serotonin.
- Submucosal layer. Represents friable, fibrous connecting fabric. In this layer the set of the small vessels and nerve fibrils which are responsible for blood supply and regulation is located.
- Cartilaginous part. This layer of a structure of a trachea consists of the hyaline incomplete cartilages occupying two thirds of a part of all circle of a tracheal tube. Among themselves these cartilages connect by means of ring sheaves. At the person the number of cartilages fluctuates from 16 to 20. Behind there is a webby wall adjoining to a gullet that allows not to interfere with the respiratory process when passing food.
- Extima. It is presented in the form of the thin connecting cover covering an outside part of a tube.
Apparently, a trachea structure quite simple, however it performs the vital functions for an organism.
Functions of a trachea
The main function of a trachea is carrying out air to lungs. Nevertheless, the number of functions on it is not limited.
The mucous membrane of body is covered with the ciliate epithelium moving towards an oral cavity and a throat, and scyphoid cells emit slime. Thus, at hit together with air in a trachea of small foreign bodys, for example, of parts of dust, they are enveloped by slime and by means of cilia force the way in a throat and pass into a throat. From there is a protective function of a trachea.
It is known that warming and clarification of air happens in a nasal cavity, but partially this role is carried out also by a trachea. In addition, it should be noted resonator function of a trachea as it pushes air to phonatory bands.
Trachea pathologies
Conditionally pathologies can be divided into malformations, damages, diseases and cancer of a trachea.
Treat malformations:
- Agenesia – rare defect at which the trachea comes to an end blindly, without being reported with bronchial tubes. Given rise with this defect are almost impractical.
- Stenosis. Can be occlusive (in case of existence of an obstacle in a tube) or compression (as a result of pressure upon a trachea of abnormal vessels or a tumor). In most cases the stenosis successfully is eliminated by means of surgical intervention.
- Fistulas. Meet quite seldom. Can be incomplete (to come to an end blindly), or full (to open on skin of a neck and in a trachea).
- Cysts. Have the favorable forecast of treatment. An operative measure is necessary.
- Diverticulums and the expansions of a trachea caused as a result of inborn weakness of a muscle tone of its wall.
Injuries of a trachea can be open and closed. Gaps owing to injuries of a breast, neck, a trachea intubation belong to the closed damages. Chipped and cut, chipped, gunshot wounds belong to open damages.
From diseases are most widespread:
- Trachea inflammation. Can be in a chronic or acute form. As a rule, the inflammation of a trachea is combined with bronchitis. The chronic inflammation of a trachea often is a symptom of a scleroma, tuberculosis. Mushrooms of Aspergillus, Candida, Actinomyces can cause an inflammation of a trachea.
- The acquired stenoses. Distinguish primary, secondary and compression. Primary stenoses can result from a tracheostomy and a long intubation of a trachea. Also physical (beam damages, a burn) mechanical or chemical injuries can be the cause of stenoses.
- The acquired fistulas. As a rule, they are a consequence traumatized or a consequence of various pathological processes in a trachea and nearby bodies. For example, they can result from break of peritracheal lymph nodes at tuberculosis, openings or suppurations of an inborn cyst of a mediastinum, at disintegration of a tumor of a gullet or trachea.
- Amyloidosis – multiple submucosal deposits of amyloid in the form of tumorous educations or flat plaques. The amyloidosis leads to narrowing of a gleam of a trachea.
- Tumors. Tumors happen primary and secondary. Primary tumors proceed from a trachea wall, and secondary – result of germination of the next bodies malignant tumors. Distinguish more than 20 types of benign and malignant tumors. At children the percent of benign tumors outweighs (papillomas, fibromas, hemangiomas). At adults the frequency of benign and malignant tumors is approximately identical. The most often found malignant tumors are adenoid and cystous cancer of a trachea, planocellular cancer of a trachea, sarcoma, a gemangiperitsitoma. All species of crayfish of a trachea gradually sprout its wall and go beyond its limits.
Trachea intubation
The intubation represents introduction to a trachea of a special tube. This manipulation has a number of technical difficulties which, nevertheless, with surpluses are compensated by its advantages when rendering acute management to the patient who is in critical condition.
The intubation of a trachea provides:
- Easy carrying out the managed or assisted breast;
- Passability of respiratory tracts;
- The best conditions for prevention of a fluid lungs;
- Possibility of aspiration from a trachea and bronchial tubes;
In addition, the intubation excludes probability of asphyxia at a spasm of phonatory bands, retractions of language, aspiration of foreign bodys, a detritis, blood, emetic masses, slime.
The procedure is carried out according to the following indications:
- Terminal state;
- Acute respiratory insufficiency;
- Fluid lungs;
- Obturation of a trachea;
- The serious poisoning which is followed by breath disturbance.
It is forbidden to do an intubation at:
- Any pathological changes of a front part of a skull;
- Inflammatory diseases of a neck;
- Any damages of cervical department of a backbone.
According to WHO researches the daily half-hour conversation by the mobile phone increases probability of development of a tumor of a brain by 40%.

Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in a nevozder...
Section: Articles about health
The medicine promptly develops, and the fact that else quite recently it seemed by miracle can now. We are not surprised any more to the fact that people with artificial joints and extremities can play sports, organ transplantation became a routine, and the latest cancer medicine п...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include it in the diet, having given preference "to safer" to vegetable fats. Meanwhile, the last researches showed that harm of butter for health is strongly exaggerated. But the product has a number of unique properties, to...
Section: Articles about health
We present to yours the TOP of the medicamentous means exerting the stimulating impact on a potentiality, i.e. on ability of a muzhcha...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it receive only useful substances, necessary vitamins and microelements. In this case there will be no problems with digestion, with лишн...
Section: Articles about health
Osteoporosis this general disease which main sign is decrease in density of a bone tissue. On distribution width it takes the fourth place among noninfectious diseases. The illness develops at mature age more often: in our country about a third of women and a quarter of men suffers from it 50 years are more senior....
Section: Articles about health
The chia plant, or the Spanish sage, is from South America. The indigenous people of the continent since ancient times used in food it семена:...
Section: Articles about health
Tuberculosis – a serious infectious disease which development is caused by mycobacteria (Koch's bacilli). The illness is known from an extreme antiquity. Long time fight against it was considered as ineffective. Quite often the disease affected the whole families, and mortality from it was very much...
Section: Articles about health
Venereal diseases in medicine are called the infections which are transmitted preferential sexually, now they and are called - infections, sexually transmitted, or STD. Among them is also life-threatening. In spite of the fact that the majority of diseases such will respond to treatment, they are widespread everywhere, and there is no tendency to decrease in incidence. Besides, some of them promptly look younger: statistically, a third of young people at the age of 16-22 years of a str...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing optimum set...
Section: Articles about health
Quite large number of people adheres to the principles of vegetarian food. But how to be if in a family of vegetarians there are children? Whether it is possible to eat also it the same as to parents, or after all the children's organism is not adapted for the use only раст...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which not only facilitate house work, but also help to keep health of the person? Of course, and we will tell about them today....
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? So far physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the bet industry...
Section: Articles about health
It is impossible to imagine human life in which there would be no plants. Practically in each apartment and any production room there are window plants, millions of people with pleasure are engaged in gardening and truck farming, many citizens пр...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot replace completely modern synthetic drugs, but their use becomes frequent serious help in simplification of a course of many illnesses and improvement of quality of life of chronic patients....
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor about age...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
The summer of this year in Russia was very ambiguous. Regions suffered from a merciless heat, from pouring rains, the hail from time to time dropped out, then there was again a heat which alternated with rainfall again. Many people suffer from such sharp changes of weather. Even flu epidemics and a SARS were recorded....
Section: Articles about health
For many spouses the question of planning of a family is one of the main. The choice problem effect at the same time comes out on top...
Section: Articles about health
Any person who faced a disease knows that treatment costs expensive. It belongs also to consultations of qualified specialists, and to the diagnostic procedures which are not included in the list of obligatory medical services. Question of cost of medicinal Wednesday...
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications of the end of the twentieth century. Researches were conducted since 1984, including placebo - controlled effects. In total clinical tests of Mildronate were carried out for more than thirty years....
Section: Articles about health
We live during an advertizing era. Daily each person receives a solid portion of persuasive councils about what to eat to be здо...
Section: Articles about health
The body of the person almost for 60% consists of water. It is so important for normal functioning of an organism that loss of only one and a half percent of liquid already leads to the most unpleasant effects. The problems connected with deficit of water can overtake and...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist of iodine more than for 65%. The lack of iodine leads to decrease in production of hormones and, as a result, development of a hypothyroidism. The long condition of deficit can become a source of problems of the cardiovascular, bone, digestive SI...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of hypnotic impact on consciousness of the person contains about two millennia. During this time scientists were in time a lot of things узн...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one of the most ancient methods of disposal of the most different diseases. Bathtubs, souls, wrappings and inhalations, in combination with reception of water vnut...
Section: Articles about health
According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but the minority sees a doctor from them. And in vain - even the insignificant discomfort in the field of generative organs can serve as a symptom of an illness fraught with grave consequences for health. So - after 40 years - it is easy for most widespread disease of the sexual sphere of men to pass the first symptoms of prostatitis (weight in the bottom of a stomach, decrease in a libido), having written off for overfatigue and fatigue. Let's consider...
Section: Articles about health
