





Backbone
Backbone – a body of an axial skeleton of an organism. The structure of a backbone is ideally adapted for performance of basic function. Besides, the backbone is an elaborate receptacle of a spinal cord, nervous roots.
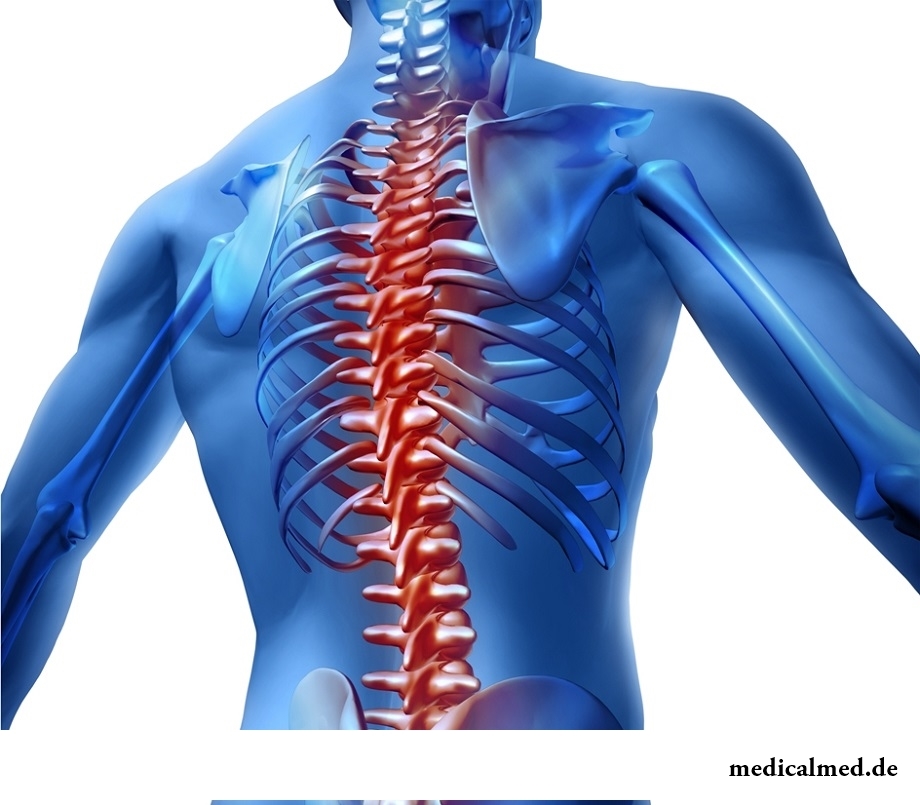
The rachis is formed by 24 vertebrae and intervertebral disks. Intervertebral disks are biological shock-absorbers which extinguish the loadings which are constantly perceived by a backbone tie vertebras among themselves, and also play a role of semi-joints, providing the small volume of movements within one segment.
Departments of a backbone
There are five departments of a backbone:
- cervical (contains 7 vertebrae);
- chest (12 vertebrae);
- lumbar (5 vertebrae);
- sacral (5 vertebrae);
- coccygeal department of a backbone (3-5 vertebrae).
Backbone bends
The rachis has bends: lordoses – the departments curved forward (cervical, lumbar), a kyphosis – the departments curved back (chest, sacral).
Vertebra structure
Vertebrae are the bones creating a rachis. A front cylindrical part of each vertebra is called a body. The body of a vertebra maintains the main axial loading. Behind from a body the semi-ring handle of a vertebra having several shoots is located. The body and a handle of a vertebra limit a pozvonkovy opening. The openings of all vertebrae located one above another create the vertebral channel. In the channel of a backbone the spinal cord, nervous roots, blood vessels, a fatty tissue are located.
7 shoots depart from a handle of each vertebra: acantha (unpaired) and pair upper joint, lower joint and cross shoots. Cross and acanthas provide an attachment of sheaves and muscles, and joint shoots take part in formation of facet joints of a backbone.
Backbone ligaments
In addition to bodies and handles of vertebrae, sheaves participate in formation of the vertebral channel. The large role is played a back longitudinal, and also yellow sheaf. The back longitudinal sheaf has an appearance of a tyazh, connects bodies of all vertebrae behind. The yellow ligament of a backbone connects arches of the next vertebrae. She received the name thanks to the yellow pigment which is a part. At damage of intervertebral disks, joints these sheaves compensate pathological mobility (instability) of vertebrae, at the same time there is a hypertrophy of sheaves. As a result of this process the gleam of the vertebral channel decreases, then even small hernias and bone outgrowths squeeze a spinal cord, roots.
Intervertebral disk
The intervertebral disk is the flat formation of rounded shape located between the next vertebrae. Structure of an intervertebral disk quite difficult. In the center of a disk the pulpozny kernel having elastic properties and which is carrying out a role of the shock-absorber of vertical loading is located. Around a pulpozny kernel the multilayer fibrous ring holding the pulpozny kernel in the center and also interfering the shift of vertebrae is located. The intervertebral disk of the adult has no vessels, his cartilage eats thanks to diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from vessels of bodies of vertebrae. For this reason the majority of drugs do not get into a disk cartilage. Treatment of a backbone at many diseases is complicated by it.
Intervertebral joints
Intervertebral, or facet, joints connect the next vertebrae and are located from two parties from a pozvonkovy handle symmetrically. Joint shoots of the next vertebrae go to each other, the terminations of shoots are covered with a joint cartilage. The cartilage has a slippery smooth surface thanks to what friction between bones which form a joint significantly decreases. The ends of joint shoots are surrounded with the tight joint capsule. Cells of a joint bag produce synovial fluid. It is necessary for food and lubricant of a joint cartilage.
Intervertebral openings
Intervertebral openings are located in side departments of a backbone, are formed by bodies, legs, and also joint shoots of the next vertebrae. Through intervertebral openings there are veins and nerves, and arteries, krovosnabzhayushchy structures of a backbone enter. Between pair of vertebras two openings are located.
Backbone hernia
Backbone hernia, or hernia nuclei pulposi, represents the shift of the pulpozny kernel located in an intervertebral disk with a rupture of a fibrous ring. Most often this pathology arises in lumbosacral department, is much more rare – in cervical, chest departments. Clinical signs of hernia of a backbone are the local pain in a projection of the damaged disk amplifying at loading, irradiating in a buttock and also on the back surface of a hip, numbness, a pricking in a zone of an innervation of the damaged roots, disturbance of sensitivity in the lower extremities, and also dysfunction of pelvic bodies. At localization of hernia in cervical department the pain irradiating on an upper extremity, dizziness, arterial hypertension, numbness of fingers of hands is characteristic. At defeat of chest department there is constant pain during the work in forced situation which is localized in chest department of a backbone. Treatment of a hernia nuclei pulposi consists in system antiinflammatory therapy (NPVS), and also operational treatment. Indications to operational treatment of a backbone at this pathology are neurologic disturbances and a pain syndrome, resistant to conservative therapy. Operational treatment consists in intralaminarny microsurgical removal of hernia of a disk. Also actively the direction of endoscopic removal of a hernia nuclei pulposi develops.
Spinal fracture
Spinal fracture is a disturbance of anatomic integrity of bones of a backbone under the influence of force provoking the sharp excessive flexion movements in a rachis, or directly at influence of the injuring agent. On the mechanism of damage distinguish such types of spinal fracture: compression, flexion дистракционный, rotational spinal fracture. Symptoms of spinal fracture depend on damage localization. Characteristic signs is pain, numbness, muscular spasms, change of a vermicular movement of intestines, paralyzes (this symptom indicates injury of a spinal cord). The diagnosis is made on the basis of data of X-ray inspection, computer tomography, magnetic and resonant tomography of a backbone. Treatment of spinal fracture can be conservative (the special holding corsets) or operational (it is necessary at spinal fractures with shift). At treatment of compression changes the vertebroplastika and a kifoplastika is applied.
The educated person is less subject to brain diseases. Intellectual activity promotes formation of the additional fabric compensating sick.

Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects on...
Section: Articles about health
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice from 40th years of the last century. Originally antibiotics were called only substances natural (animal, vegetable or микробног...
Section: Articles about health
Cold – a state known to everyone which is followed by cold, cough, high temperature, a pharyngalgia. Often the first that we begin to do in hope again to become healthy – to accept medicines which are not always harmless whereas it is easy to facilitate displays of a disease by means of natural means. They not only softly eliminate disease symptoms, but also enrich the weakened organism with useful substances. We present you 8 drinks which are successfully used for...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need to the visa...
Section: Articles about health
About influence of fasting days on an organism it is told much – both about advantages, and about shortcomings. It is considered that fasting day in the form of a short-term monodiet is useful, promoting effective removal of slags from an organism whereas irregular, it is excessive п...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. The statistics of incidence is considered not full as at an initial stage the illness, as a rule, does not cause to the person of special inconveniences, and many diseased sees doctors not at once. The cataract is not only one of the most widespread ophthalmologic illnesses, but also the reason of a half of cases of loss of sight....
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, in Russia about 34% of citizens smoke. Most of consumers of tobacco has problems about health sooner or later...
Section: Articles about health
Household skills which to us so diligently imparted in the childhood it appears, not always bring only benefit. According to results of the last researches, some habits which for a long time were considered useful and even necessary can become...
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. Trainings will help it to become strong and hardy, will improve coordination of movements, and also will exert positive impact on mentality: it will become more collected and purposeful....
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence ег...
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create to it healthy immunity since early years. Nevertheless, this important process in life of mother and child can be saddened laktostazy − by a delay of milts...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, a sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease in physical and intellectual activity and a number of other symptoms reducing quality of life. Abstinence can be strong: an essential part of attempts comes to an end leaving off smoking failure, and people are returned to the use of cigars...
Section: Articles about health
On the head of the person about one million hair follicles, or as they are called still, hair bulbs are located. At the moment he is born...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
Quite large number of people adheres to the principles of vegetarian food. But how to be if in a family of vegetarians there are children? Whether it is possible to eat also it the same as to parents, or after all the children's organism is not adapted for the use of exclusively vegetable food? Let's try to understand....
Section: Articles about health
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As...
Section: Articles about health
The problem of diagnosis was and remains to one of the most important in medicine. From that, the reason of an indisposition of the patient will be how precisely defined, eventually success of treatment depends. In spite of the fact that the majority of the diagnostic methods applied in about...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which tests the kid when it absorbs maternal milk. Besides, getting into a human body, sugar strengthens production of "happiness hormones" which all of us so need. And still life of sweet teeth seldom happens cloudless: their too big loss...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
The words "disease" and "patient" not without reason come from one root – "pain". As a rule, symptoms of illnesses thoroughly spoil to patients life. However from this rule there are exceptions. Some diseases are shown by signs which can cause even positive emotions. It is a pity only that the majority of such illnesses are heavy and incurable....
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to receive to a toast...
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair by means of coloring, or considerably changing it for the purpose of creation of absolutely new image. All know that the gray hair is a sign приближающ...
Section: Articles about health
When overcomes feeling of hunger, and an opportunity to have dinner fully is absent, having a snack − the meals, small on volume, stabilizing sugar level in blood comes to the rescue. The relation of nutritionists to having a snack more often negative, but only because as snack people choose the most caloric products with the increased amount of "bystry" carbohydrates: cookies, rolls, chips, candies. Nevertheless, the advantage of having a snack is obvious to weight loss: the person avoids strong feeling of hunger...
Section: Articles about health
Energy saving lamps are one of the most popular products of innovative technologies, and there is no wonder: they much эк...
Section: Articles about health
The business lady, the become mother, it is necessary to solve an array of problems. But of them is main: how to combine the beloved child and work? What traps trap the working mother and how she needs to behave?...
Section: Slideshow
Today about 30 diseases, sexually transmitted are known. Wide circulation of these illnesses is extremely promoted by the dual attitude towards them: on the one hand, most of people know about "shameful" diseases very little and do not aim at receiving detailed and reliable information, considering that such problems personally will never concern them. With another – there are delusions about STD which instill unreasonable confidence that troubles such...
Section: Articles about health
