





Achalasia
Gullet achalasia – the disease which is characterized by lack of reflex disclosure of the cardia when swallowing. The disease is followed by decrease in a tone of chest department of a gullet and disturbance of a vermicular movement of intestines.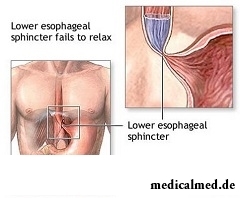
For the first time the disease was described in 1672. Statistically, a disease 1 person from 100 thousand has. Most often the achalasia of a gullet meets at the age of 40-50 years. The gullet achalasia at children – quite unusual occurrence also makes about 3,9% among all cases of diseases. Women, as a rule, have this disease several times more often than men.
The most common causes of development of an achalasia
The exact reason promoting developing of an achalasia of a gullet is unknown. Infectious diseases, an outside prelum of a gullet, inflammatory processes, malignancies, infiltrative defeats, etc. belong to the most frequent reasons.
The achalasia of a gullet is most often diagnosed for children after five-year age. On emergence of the first symptoms, as a rule, nobody turns special attention therefore diagnose a disease with delay. The most common symptoms of an achalasia of a gullet at children are the dysphagy and vomiting right after meal.
The most characteristic symptoms of an achalasia
The dysphagy is the most important symptom of an achalasia. The dysphagy practically occurs at all patients with this disease. As a rule, the time interval between manifestation of the first symptoms of a disease and time of the address to the doctor varies within 1-10 years.
Symptom of an achalasia, the second for frequency, is regurgitation of the remains of food without impurity of an acid gastric juice and bile as a result of stagnation of contents in a gullet. It leads to the fact that patients often test at night attacks of suffocation or cough.
Also heartburn and thorax pains belong to symptoms of an achalasia. Pains are preferential localized behind a breast, have the squeezing or squeezing character and often give to a back, a mandible or a neck. Happens, in the presence of heartburn instead of a gullet achalasia make to the patient the wrong diagnosis, for example, a gastroesophagal reflux. However heartburn at an achalasia does not arise after meal and does not cease at use of antiacid drugs.
Gullet achalasia complications
The achalasia of a gullet leads to irreversible changes in nervous and other systems of an organism.
The most widespread complications of a disease are:
- purulent pericardis;
- planocellular cancer of a gullet;
- gullet bezoara;
- flaking of a submucosal layer of a gullet;
- damage of lungs;
- volume formations of a neck;
- gullet varicosity;
- diverticulum of distal department of a gullet;
- pneumopericardium, etc.
At it is long the existing achalasia the gullet is inclined to extend significantly that leads to thinning of its walls therefore there are above described complications of a disease.
Approximately at 85% of patients with an achalasia essential decrease in body weight is noted.
Diagnosis of an achalasia of a gullet
At different stages of an achalasia there is only an obstruction of the cardia with insignificant dilatation of proximal department. In process of progressing of a disease on X-ray it is possible to see characteristic signs: an esophagectasia, in a lower part clinical narrowing on a small extent with coronoid expansion on site the narrowed department. In spite of the fact that the clinical picture of a disease is quite characteristic, often at patients aged after 50 years it can be confused with gullet cancer, especially at its early stages.
The greatest advantage in diagnosis of an achalasia is rendered by an ezofagoskopiya. Confirmation of clinical displays of an achalasia is studying of motive function of a gullet. In a gullet low pressure with dilatation of its gleam and lack of a vermicular movement after swallowing is found. Throughout a gullet after swallowing there is a rise in pressure. During swallowing the ezofagealny sphincter does not reveal that gives the chance with an accuracy to speak about the diagnosis of an achalasia.
At some patients disturbance of a vermicular movement of a gullet passes into a diffusion spasm, and in response to the act of swallowing there are repeated strong spasms.
Treatment of an achalasia
The achalasia of a gullet will very badly respond to drug treatment. Drug treatment of an achalasia is applied unless to relief of symptoms of a disease. To the patient appoint a sparing diet, sedatives, complexes of vitamins, antispastik. As a rule, medicamentous therapy gives only temporary relief.
The forced expansion of the cardia is possible due to use of the mechanical, pneumatic or hydrostatic dilatator. The greatest distribution was gained by pneumatic dilatators as the safest.
Under radiological control enter the probe with a cylinder on the end into a stomach. In a stomach gleam the cylinder is inflated by air and extended outside. It allows to expand a gullet gleam. Ruptures of a wall of a gullet or mucous can arise when using the elastic dilatator approximately in 1% of cases whereas when using mechanical the percent increases to 6. Approximately in 80% of cases dilatation renders positive effect and successfully saves the patient from burdensome symptoms of an achalasia.
If dilatation does not yield a positive take, surgical treatment of an achalasia can be applied. The most widespread modern operational method of treatment of an achalasia of a gullet is bilateral cardiomyotomy. Operation consists of a longitudinal section of muscular layers of distal department of a gullet. Sometimes there is enough only a front cardiomyotomy.
After this operation about 90% of patients recover. Unsatisfactory results are connected preferential with scarring in the remote terms. This operation is most a procedure of choice of treatment of an achalasia of a gullet at children at the started stages.
In Great Britain there is a law according to which the surgeon can refuse to do to the patient operation if he smokes or has excess weight. The person has to refuse addictions, and then, perhaps, he will not need an operative measure.

Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times from...
Section: Articles about health
Very often as a source of the infection which caused a disease serves our house - the place which a priori has to be safe. However disease-producing bacteria can perfectly feel not only in insanitary conditions, but also in our apartment if not осущ...
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead to decrease in protective forces of an organism, and it becomes vulnerable for a set of diseases. It is wrong to think that the stress is a problem of the present. Life of people and hundred, and one thousand years ago also abounded with problems therefore need of a relaxation understood in ancient times – to some techniques more than one thousand years. The person needs knowledge of how it is possible to relax, this knowledge пригод...
Section: Articles about health
For residents of the countries of Southeast Asia various algas are an obligatory component of a daily diet. Their priest...
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching of oral cavities over health periodically has problems: enamel of teeth darkens under the influence of some products, on it I accumulate...
Section: Articles about health
The technique of acupuncture (acupuncture) is used in the medical purposes more than three and a half millennia. It is eurysynusic and recognized as official medicine in the majority of the developed countries of the world. Influence by fine needles on so-called points of acupuncture contributes to normalization of a metabolism and hormonal background, activates protective forces of an organism, has anesthetic and antiinflammatory effect, stabilizes a condition of mentality....
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutritious...
Section: Articles about health
Modern footwear is extremely various. It stopped being only protection for legs long ago. Today shoes, boots, barefoot persons choose not so much proceeding from their convenience and functionality how many being guided by outward, brand and an opportunity to add with it...
Section: Articles about health
A little more than a century ago goat milk was a traditional food stuff of most of Russians. Unfortunately, today on tables of our compatriots it appears extremely seldom. The reason that the use of so useful product practically came to naught, not only in very modest volumes of its production and, respectively, rather high cost. Potential consumers are just insufficiently informed on unique properties of goat milk and that advantage which...
Section: Articles about health
Heart disease and blood vessels lead to disturbance of blood supply of bodies and fabrics that involves failures in their works...
Section: Articles about health
On health of the person physicians know about salutary action of animals long ago. About 7 thousand years ago great Hippocrates recommended to the patients riding walks for strengthening of a nervous system and increase in vitality....
Section: Articles about health
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice from 40th years of the last century. Originally antibiotics were called only substances natural (animal, vegetable or microbic) origins, but over time this concept extended, and it includes also semi-synthetic and completely artificial antibacterial drugs....
Section: Articles about health
Practice of hypnotic impact on consciousness of the person contains about two millennia. During this time scientists were in time a lot of things узн...
Section: Articles about health
Such trouble as the milkwoman's attack, at least once in life happened almost to each woman. Prevalence of a disease is explained by the fact that the causative agent of an illness belongs to the so-called opportunistic microflora living on mucous an obol...
Section: Articles about health
Aging — natural and inevitable process. Over time our skin loses elasticity, on it saggings are formed, the face form loses former clearness. The procedure of nitevy lifting (nitevy tightening) can successfully solve this problem. In order that it is better to get acquainted with this popular procedure, we will tell you 6 cognitive facts about it....
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing optimum set...
Section: Articles about health
The popular expression "run from a heart attack" became the motto of the people supporting active lifestyle. Moreover, run became a peculiar fashionable tendency: sales of racetracks and the accompanying goods for run are at permanently high level. Really...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow
Hemorrhoids – extremely widespread disease. Periodically arising inflammations and bleeding of hemorrhoidal nodes пр...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – as a result of sweating, breath, an urination, and its insufficient completion due to various reasons can bring to обезвожив...
Section: Articles about health
Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes the bed patient, and remains in such state for a long time. It extremely suppresses both the most injured, and all its house which life considerably changes....
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" also "assimilation"...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. The statistics of incidence is considered not full as at an initial stage the illness, as a rule, does not cause to the person of special inconveniences, and many having got sick...
Section: Articles about health
Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary to minimize. There is a number of rules, following to which will help or to avoid absolutely infection with flu or a SARS, or to have an illness benign and without essential complications. About ways of prevention of seasonal infections the speech in this article will also go....
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: all эт...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often deliver беспоко...
Section: Articles about health
The name of this disease precisely reflects the problem reason: it consists in the bra fastener pressure upon a certain zone of a back. At the same time one of vertebrae of chest department of a backbone is as if blocked and loses mobility, and the loading falling on it is distributed on the next vertebrae. At 70-80% of women local pains in a backbone point on which the fastener of the often put most on bra presses result....
Section: Articles about health
