





Fluid lungs
Short characteristic of a disease
 Fluid lungs – heavy, in many cases the deadly complication of a number of cardiovascular diseases connected with sweating of serous and hemorrhagic liquid in alveoluses of lungs.
Fluid lungs – heavy, in many cases the deadly complication of a number of cardiovascular diseases connected with sweating of serous and hemorrhagic liquid in alveoluses of lungs.
There is a membranogenny, hydrostatic fluid lungs which differ on the origin.
Depending on the disease which led to hypostasis it is possible to allocate a cardial and toxic fluid lungs.
Emergence reasons
The main reasons for a fluid lungs – stagnation in a small circle of blood circulation or toxic destruction of vessels of lungs. Often hypostasis arises at the same diseases, as bronchial asthma: the cardiosclerosis is atherosclerotic, heart disease, a myocardial infarction, a hypertension (cardial hypostasis). In these cases hypostasis represents the most severe form of cardiac asthma.
The reason of a fluid lungs toxic – a poisoning with barbiturates, alcohol, poisons, nitric oxides, carbonyls of metals, arsenic, and also a burn, a diabetic or hepatic coma, uraemia.
The reason of a fluid lungs membranogenny – primary increase in permeability of pulmonary capillaries arising at various diseases.
The reason of a fluid lungs hydrostatic – increase in intra capillary hydrostatic capillary pressure of blood to 7-10mm.rt.st., causing an exit of a liquid part of blood in excess quantity who cannot be brought in lymphatic ways.
Fluid lungs symptoms, diagnosis
In view of the fact that the attack develops quickly, its diagnosing happens at a survey stage, on the basis of the observed symptoms. It is important to understand quickly a situation, to give acute management at a fluid lungs, to begin therapy in order to avoid repeated attacks, otherwise the person can die within several minutes of suffocation.
The disease suddenly, develops at night when the patient sleeps or in the afternoon when he experiences nervousness or makes physical effort. Often initial symptoms of a fluid lungs are expressed in a frequent tussiculation, increase in lungs of wet rattles, discoloration of the person. The patient feels severe suffocation, the pressing pain, constraint in breasts, its breath sharply becomes frequent and even at distance is heard the bubbling rattles. Everything the becoming frequent cough is followed by plentiful allocation of a foamy pink or light phlegm. If the state very heavy, foam can go also from a nose. The complicated breath and an exhalation, swelling of cervical veins, a cold clammy sweat, cyanosis of skin are added to these symptoms.
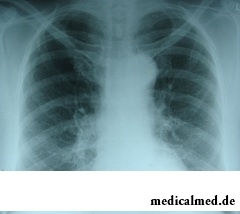
As the attack develops, when listening lungs wet mixed rattles over various sites of lungs are defined, breath in these sites or is weakened, or at all is absent. If during an attack their expanded roots, focal large shadows with indistinct contours are to conduct X-ray inspection characteristic symptoms of a fluid lungs (at the same time transparency of pulmonary fields is lowered).
Also sharp increase of pulse is noted, it is frequent to 140-160 уд / minute, sudden bradycardia is sometimes observed.
Level of arterial pressure is not an important symptom of a fluid lungs – it depends on initial level (to an attack) and can be a miscellaneous.
Usual symptoms of hypostasis of a toxic origin are supplemented with signs of a basic disease or destructive process: burn disease, coma, injury of upper airways, etc.
Treatment of a fluid lungs
Very important before performing full therapy to give acute management at a fluid lungs:
- to watch that the person who has an attack was in a semi-sitting or sitting position.
- From upper respiratory tracts to suck away slime.
- If supertension to carry out bloodletting: adult 200-300ml, to children 100-200ml.
- To carry out by vapors of alcohol inhalation. For children use 30% alcohol, for adults – 70%.
- To impose a plait on legs for half an hour or hour.
- To enter 2 ml of solution of camphor of 20% under skin.
- To carry out an oxygenotherapy (administration of oxygen to oxygen respiratory tracts by means of an oxygen cushion).
 In stationary conditions acute management at a fluid lungs consists in administration of cardiac glycosides, performing bloodletting if before it did not carry out (with the lowered pressure, a collapse, a heart attack bloodletting is contraindicated), continuation of an oxygenotherapy, introduction of Lasixum or Novuritum.
In stationary conditions acute management at a fluid lungs consists in administration of cardiac glycosides, performing bloodletting if before it did not carry out (with the lowered pressure, a collapse, a heart attack bloodletting is contraindicated), continuation of an oxygenotherapy, introduction of Lasixum or Novuritum.
After carrying out acute management and stabilization of a condition of the partner, carry out treatment of a fluid lungs which has to be directed to reduction of action or full elimination of the reasons of an attack. Having reduced inflow of blood to lungs (bloodletting, plaits, diuretics), appoint the drugs facilitating cardiac performance, reducing peripheric vascular resistance, improving process of exchange in a myocardium.
Also in the course of treatment of a fluid lungs hold a number of the events directed to consolidation of capillary alveolar membranes, constant supply of oxygen. It is important to improve an emotional condition of the patient, to bring him out of a stress which often and provokes an attack. For this purpose as treatment of a fluid lungs successfully use soothing drugs. Except the cumulative calming effect these means reduce vascular spasms, inflow of blood to lungs, facilitate cardiac performance, reduce an asthma, penetration of liquid of fabrics through a capillary alveolar membrane, reduce intensity of processes of exchange (that allows to transfer easier a lack of oxygen).
Frequent such sedative which long ago is successfully applied in treatment of a fluid lungs is morphine. Its 1% enter solution intravenously in volume 1-1,5ml. In certain cases it allows to eliminate hypostasis completely.
Prevention of a disease
The prevention of an attack consists in timely treatment of states and diseases which can provoke an attack, in observance of safety rules on productions with use of harmful toxics.
During sneezing our organism completely stops working. Even heart stops.

In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if no more эфф strongly took roots...
Section: Articles about health
What is in our understanding weeds? It plants which are considered to be suitable only for compost pits and feeding of animals. Meanwhile, among the weeds growing literally under legs it is possible to find the mass of the officinal herbs possessing invaluable Paul...
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make that process of weight loss did not give you an inconvenience, and, on the contrary, brought joy?...
Section: Slideshow
Reactive pancreatitis - the disease which is characterized by inflammatory process in a pancreas which arises more often everything...
Section: Articles about health
About influence of fasting days on an organism it is told much – both about advantages, and about shortcomings. It is considered that fasting day in the form of a short-term monodiet is useful, promoting effective removal of slags from an organism whereas irregular, it is excessive п...
Section: Articles about health
One of the major chemical processes happening in a human body are oxidation reactions. They go with participation of fats and carbohydrates which we receive from food, and the oxygen getting to us from air. A main goal of such reactions is obtaining the energy necessary for life activity. Unfortunately, as a result of these processes dangerous by-products – so-called free radicals are allocated. To minimize harm which they can cause to the person neo...
Section: Articles about health
The dietology, as well as other sciences, does not stand still. Food stuffs are exposed to comprehensive study, and scientists receive new and...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly changed спо...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep look youth for many years and what procedures are offered for achievement of this purpose by cosmetologists? And maybe, the only option of rejuvenation is surgery – a blepharoplasty? Let's try to understand this question....
Section: Articles about health
Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times from...
Section: Articles about health
Childbirth is the most important event in life of each woman. We are women we give birth to the new little man on this light. Now the tendency to that was outlined, as men want to participate in labor too. But there is a question and whether it is worth allowing the husband...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of the panic attack is known long ago, but the reasons of its emergence still are up to the end not found out. It is established that more than 30% of people at least once in life become the victims of very unpleasant phenomenon: without everyones on that the reasons they have a feeling of horror which is followed by a cardiopalmus, a shiver and the fever or feeling of sudden heat increased by sweating, breath constraint, dizziness, nausea....
Section: Articles about health
All like to sing. Small children with pleasure are engaged in a vocal, not especially thinking of hit in a melody. Adults most often...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. A contribution of drugs to rescue of people from...
Section: Articles about health
The chia plant, or the Spanish sage, is from South America. The indigenous people of the continent since ancient times used its seeds in food: small, but very nutritious kernels, in a form the reminding fasolina. Indians knew about useful properties of seeds of a chia, and applied them to maintenance of vitality and increase in endurance before serious exercise stresses....
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create since early years...
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as are afraid that they can do harm to health of children. What troubles can really trap kids and how to make with...
Section: Articles about health
Dark circles (bruises) under eyes – a shortcoming with most of which often fight against the help of cosmetics (proofreaders, saloon procedures and so forth), eliminating only its visibility. However, according to doctors, skin around eyes – the indicator of many disturbances in an organism. To reveal them at early stages, without having disguised bruise, and having addressed its reasons – a task of each person who is regularly finding under with own eyes dark stains. Early detection and elimination of the disease lying in wasps...
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? So far physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the bet industry...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes the bed patient, and remains in such state for a long time. It extremely suppresses both the most injured, and all its house which life considerably changes....
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also contain...
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. The use of sugar in food is based rather on the psychological dependence caused by desire to indulge itself with something tasty, and in дальнейш...
Section: Articles about health
Zone hypostases under eyes - very widespread problem giving to people is a lot of inconvenience. Hypodermic fabric in these parts has very loose structure and almost does not contain collagenic fibers. Besides, the skin covering подглазья constantly is exposed to compression and stretching when the person blinks, blinks, etc. These features also create premises for emergence of the so-called bags which are giving to the face a tired and sickly look, and also visually adding increased...
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair with the help about...
Section: Articles about health
Each person knows that fervescence is an illness sign. However too low temperature (hypothermia), especially also can demonstrate existence of diseases when it is observed long enough. Such state is dangerous those...
Section: Articles about health
The person, as well as all other beings living on our planet feels weather changing. It is the normal meteosensitivity which is not causing to healthy people of special troubles. Meteodependence, on the contrary, is the morbid condition which is characterized by an exacerbation of chronic illnesses at change of air temperature, differences of atmospheric pressure, wind strengthening, magnetic storms and other "surprises" on which the nature is so generous. The people suffering from meteodependence have to з...
Section: Articles about health
