





First aid at changes
Change – a widespread type of injuries at which there is a disturbance of integrity of a bone. Changes divide into full and partial (cracks), and also on closed when integuments remain whole, and opened – when in the place of a change there is a gaping wound formed by bone fragments.
The change is a serious injury and always demands medical intervention therefore in all cases when there is a suspicion of a fracture, it is necessary to ask for medical care. The purpose of pre-medical first aid at changes is ensuring rest of the injured area (not to allow injury of muscles and sinews), whenever possible pain relief and the fastest delivery of the victim in hospital, for rendering the qualified medical care.
Symptoms of a fracture
The main symptoms of the happened fracture is the megalgia, hypostasis and pathological mobility in the injured area. Exist also accessory signs which depend on a look and localization of a change, but to suspect a change, it is enough of three main, and sometimes even one – severe pain. The matter is that hypostasis is not always noticeable to an inexperienced eye. For example, it is difficult to be found in people of a dense constitution, and in some cases it can be and not too expressed. As for pathological mobility, it also can be not always found, for example, if the change is located close to a joint.
The doctor after carrying out a X-ray analysis will be able precisely to define existence of a change, and for first-aid treatment true will consider a fracture any injury of a bone which is followed by the severe pain amplifying in attempt of the movement. If afterwards it turns out that the injury is less serious, for example, a bruise or dislocation, and first aid as is given at a change, it will not do any harm to the victim whereas underestimation of weight of an injury can lead to very serious complications.
Measures for first-aid treatment at changes
First aid at a change consists in an immobilization, i.e. giving of an immovability of the injured part of a body, and the fastest delivery of the victim in medical institution. When carrying out an immobilization it is important to follow the general rules:
- It is not necessary to try to give to the injured bone the correct form. It can lead to painful shock, and also to an additional (secondary) injury of soft and solid tissues;
- If a change open the broken-off sites of a bone are also visible, it is not necessary to try "to move" them in soft tissues. At splintered changes it is not necessary to try delete, to set splinters. It is necessary to make an immobilization in such situation in which there is an affected site at the time of first-aid treatment;
- It is impossible to transport the victim with multiple injuries, including multiple fractures, and also with spinal fractures and a basin. First aid at changes of this kind is given on site, and in hospital the ambulance is engaged in delivery;
- At an intensive pain syndrome it is possible to give to the victim anesthetic. Paracetamol, Analginum or any other anesthetic of non-prescription dispensing will approach;
- In cold season it is necessary to watch that the victim did not overcool, including that the injured extremity did not overcool. For this purpose on it it is possible to outline something from warm clothes or a blanket, and injured to give to drink hot tea (if there is such opportunity).
Rules of an immobilization at various changes
 Before transportation of the victim in hospital the struck area needs to be recorded that the movements in this site did not aggravate an injury.
Before transportation of the victim in hospital the struck area needs to be recorded that the movements in this site did not aggravate an injury.
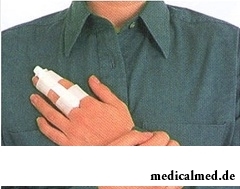
Fractures of fingers of hands and legs:
At fractures of fingers of hands or legs for an immobilization it is enough to bandage the injured finger to next.
Fractures of extremities:
At fractures of extremities impose the tire. Shin can make of any improvised material which is rather strong to hold an extremity in a motionless state.
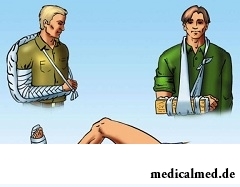 It is necessary to impose the tire, following the following rules:
It is necessary to impose the tire, following the following rules:
- The tire is installed so that to fix not less than two joints – located above and lower than the place of a change;
- Between the tire and skin there shall be a fabric layer;
- The tire has to be strongly fixed, is inadmissible that it dangled since in this case instead of means of an immobilization it turns into the accessory injuring factor.
Fractures of edges:
At fractures of edges the victim needs to apply a pressure, compressing bandage a thorax which purpose to put sufficient pressure in order that the person breathed more at the expense of stomach muscles - it is and will provide fixing, and will reduce pain as at breath the thorax moves. It is not necessary to talk to the victim as the speech also leads to morbidity strengthening.
Spinal fractures and basin:
At spinal fractures and a basin, and also multiple fractures, injured it is not necessary to move, do it the people having sufficient qualification have to. However if such opportunity is absent to give first aid at changes of this kind it is necessary to make a stretcher with the firm basis, observing the maximum precaution, to shift the victim to them. Under knees it is necessary to put the roller from fabric (it is possible to use the curtailed clothes) then to record the patient on a stretcher by means of wide bandage or the fabric replacing them and to transport, without allowing sharp movements.
First aid at open changes
First aid at open changes in general consists of the same measures, as at closed, however in this case it is necessary to stop bleeding as big blood loss is more dangerous, than the most difficult change. For a stop of bleeding it is necessary to apply a bandage, and in case of need burn down (see. "First aid at bleedings"). It is desirable to process a surface of a wound an antiseptic agent (alcohol, iodine), but it is not necessary to delete fabric scraps, splinters, etc. from a wound.
Antidepressant Klomipramin causes an orgasm in 5% of patients.
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. One...
Section: Articles about health
History of cultivation of a buckwheat contains more than five thousand years. Grain which is received from this plant is used for preparation of porridges, soups, baked puddings and puddings, do flour which is one of the main ingredients of the noodles popular in of it...
Section: Articles about health
Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times medicinal properties of honey and other substances received in the course of beekeeping are known. The fact that all these products are recognized not only national, but also official medicine is especially significant. About influence and routes of administration of bee "drugs" the speech in this article will also go....
Section: Articles about health
All the known slogan "Protect Men!" arose not from scratch. In a sense, the nature created representatives of strong...
Section: Articles about health
All are familiar with cold, and practically everyone believes that he has sufficient knowledge and experience that correctly to treat it. In practice most of people makes mistakes in attempts to get rid of rhinitis, and divides numerous delusions it....
Section: Articles about health
The technique of acupuncture (acupuncture) is used in the medical purposes more than three and a half millennia. It is eurysynusic and recognized as official medicine in the majority of the developed countries of the world. Influence by fine needles on so-called points of acupuncture contributes to normalization of a metabolism and hormonal background, activates protective forces of an organism, has anesthetic and antiinflammatory effect, stabilizes a condition of mentality....
Section: Articles about health
Doctors claim that the people not so familiar with a dorsodynia occur among adult Russians very seldom. At the same time подавляющ...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
The body of the person almost for 60% consists of water. It is so important for normal functioning of an organism that loss of only one and a half percent of liquid already leads to the most unpleasant effects. The problems connected with deficit of water can overtake also the healthiest person if he, for example, spends several hours under the scorching sun, without having taken with themselves drink, but is very simple to correct health in this case. It is much more difficult to minimize effects of other reasons about...
Section: Articles about health
They say that to ensure health and longevity of people it is obliged. Really, at competent approach to these questions, we will pass...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste, because of to...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep look youth for many years and what procedures are offered for achievement of this purpose by cosmetologists? And maybe, the only option of rejuvenation is surgery – a blepharoplasty? Let's try to understand this question....
Section: Articles about health
Tick-borne encephalitis – one of the most dangerous viral diseases which causative agents transfer and is given to people by ixodic mites. Эт...
Section: Articles about health
The thought that the mass of their body is too big at least once in life visits from 80 to 95% of women. Many women are so obsessed with this idea that constantly try all new and new ways of weight reduction. Considerable part of these method...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance of physical, psychological and moral health of the person by means of the complex of procedures including a diet, cleaning of an organism, breathing exercises, massage, and in case of a disease - and medicinal therapy. The healers practicing Ayurveda assign very important part to spices, and at the heart of Ayurvedic drugs, as a rule, there are they. It is considered that spices not of t...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing optimum set...
Section: Articles about health
Any person who faced a disease knows that treatment costs expensive. It belongs also to consultations of qualified specialists, and to the diagnostic procedures which are not included in the list of obligatory medical services. Question of cost of medicinal Wednesday...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often give trouble, serving as the reason of a headache, an acrimony, sleep disorders, and in certain cases and the states close to a depression. How to get rid of undesirable satellites of a disease if near at hand there are no antiallergic...
Section: Articles about health
For residents of the countries of Southeast Asia various algas are an obligatory component of a daily diet. Their priest...
Section: Articles about health
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) – one of those drugs which are known literally to all. It is available in each home first-aid kit, and many accept it at the first signs of an indisposition, often without having a fair idea of properties and a therapeutic eff...
Section: Articles about health
Coffee - the tonic loved by many for the invigorating aroma and deep taste. Having the stimulating effect, coffee increases working capacity, promotes concentration of attention, fights against drowsiness and improves mood. Statistically, about 30% of inhabitants of the planet regularly use coffee, from them more than 8% are "coffee-achievers" - the persons using more than 3 cups of drink a day....
Section: Articles about health
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice with 4...
Section: Articles about health
Epilepsy is one of widespread neurologic diseases. Parents, whose children suffer from this illness, should face rumors and delusions, many of which remained since the Middle Ages....
Section: Articles about health
The sclera and mucous membrane of an eye are intensively supplied with blood vessels which problem - to saturate nervous tissues of body with nutrients and oxygen. In a normality vessels are almost not noticeable, however at their expansion (owing to thinning of walls) become visible, painting a sclera in red color. Quite often red eyes - the signal of any trouble in an organism caused as external irritants, allergens, and diseases which need in about...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant but which is not exhausting, motive...
Section: Articles about health
Diapers for adults – individual one-time means of hygiene which in some situations is irreplaceable and from such situations any person is not insured. Though nobody perceives need of their use with enthusiasm, however without it to a sra...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is valuable medicinal raw materials. A, C and E vitamins, organic acids, tannins, wax, saponins, lipids, mineral salts and essential oils are its part....
Section: Articles about health
