





Prolapse of the mitral valve
The mitral valve is presented by the front and back connective tissue shutters having an appearance of flat leaflets. Strong chords (threads) of a shutter fasten to papillary muscles, and papillary muscles are attached to a bottom of a left ventricle of heart. In a phase of relaxation (diastole) of a shutter of the valve cave in down. Blood from the left auricle freely moves to a left ventricle. In a phase of a systole of a shutter of the valve rise, closing an entrance to the left auricle.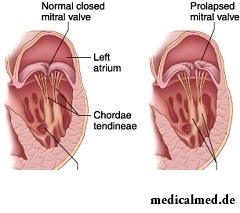
Prolapse of the mitral valve – sagging of shutters (one or both) in an auricle cavity. For the first time this phenomenon was described during emergence of a method of an echocardiography (in the sixties). This pathology can be diagnosed at any age, but most often it is revealed at children is more senior than seven years.
Pathogeny and etiology of a prolapse of the mitral valve
Depending on an origin the prolapse of the mitral valve is divided on idiopathic (primary) and secondary. Primary prolapse arises at a dysplasia of connecting fabric. The dysplasia of connecting fabric leads to change of structure of papillary muscles and the valve, distribution disturbance, the wrong attachment, shortening or lengthening of chords, emergence of additional chords.
The secondary prolapse of the mitral valve usually accompanies and complicates hereditary syndromes (an inborn kontrakturny spider finger, an elastic pseudoxanthoma, a syndrome of Elersa-Danlo-Chernogubova, Marfin's syndrome), and also endocrine pathologies, rheumatic diseases, heart diseases. The secondary prolapse of the valve can develop at the acquired myxomatosis, inflammatory damage of valve structures, a valve and ventricular disproportion.
The prolapse of the mitral valve can develop owing to dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, disturbance of metabolism and deficit of microelements, in particular potassium ions and magnesium
Discrepancy or leaky smykaniye of shutters of the valve is followed by emergence of systolic noise of various intensity. At the same time the mesosystolic clicks arising at an excessive tension of chords are auskultativno registered.
Depending on the size of protrusion of shutters of the valve allocate the following degrees of a prolapse of the mitral valve:
- first degree (from 2 to 3 mm);
- second degree (from 3 to 6 mm);
- third degree (from 6 to 9 mm);
- fourth degree of a prolapse of the mitral valve (more than 9 mm).
Course of this disease usually high-quality, long, favorable. Dysfunction of the device of the valve usually progresses slowly. At one patients throughout all life the state remains stable, and at other patients with age the given pathology of the valve can decrease or disappear.
Symptoms of a prolapse of the mitral valve
Symptoms of a prolapse of the mitral valve depend on expressiveness of vegetative shifts and a connective tissue dysplasia. Patients with this disease most often complain of increased fatigue, heartbeat, dizziness, headaches, the lowered physical effeciency, interruptions in cardiac performance, psychoemotional lability, irritability, a hyperexcitability, pain in heart, uneasiness, hypochiondrial and depressive reactions.
Various displays of a dysplasia of connecting fabric are characteristic of this disease: the reduced body weight, the increased elasticity of skin, hyper mobility of joints, scoliosis, deformation of a thorax, flat-footedness, a myopia, alate shovels. It is also possible to find a nephroptosis, a sandalevidny crack, a peculiar structure of a gall bladder and auricles, a giperterolizm of nipples and eyes. Quite often at a prolapse of the valve observe change of arterial pressure and heart rate.
Diagnosis and treatment of a prolapse of the mitral valve
For diagnosis of a prolapse of the valve use tool and clinical methods. Diagnosis is promoted given the anamnesis, the complaint, by results of a X-ray analysis and ECG, display of a dysplasia of connecting fabric. Diagnostic methods allow to reveal this pathology and to differentiate it from the acquired or inborn insufficiency of the mitral valve, other options of anomalies of development of heart or dysfunction of the valve device. By results of EhoKG it is possible to estimate correctly revealed cordial changes.
Tactics of treatment of a prolapse of the mitral valve depends on degree of a prolapse of shutters of the valve and volume of regurgitation, and also the nature of cardiovascular and psychoemotional disturbances. At this disease it is necessary to pay attention to a sufficient (long) dream. The question of sports activities is usually considered by the attending physician after assessment of indicators of physical fitness. Patients with a prolapse without the expressed regurgitation can lead active lifestyle without any restrictions.
Phytotherapy – an important component in treatment of a prolapse of the valve. This type of treatment consists in reception of the calming (sedative) drugs on the basis of a motherwort, a valerian, a Labrador tea, a hawthorn, a St. John's Wort, a sage. Medicamentous therapy is directed to a symptomatic treatment of displays of a disease.
Sewing up of the struck mitral valve (valvuloplasty) is carried out at the expressed regurgitation and a circulatory unefficiency. At inefficiency of valvuloplasty replacement of the struck valve with an artificial analog is made.
Complications of a prolapse of the mitral valve
Insufficiency of the mitral valve – quite frequent complication of rheumatic damage of heart. The incomplete smykaniye of shutters of the valve and their anatomic defect promote considerable return of blood to an auricle. The patient is disturbed by an asthma, weakness, cough. At development of a similar complication prosthetics of the struck valve is shown.
Complications of a prolapse of the mitral valve can be shown in the form of attacks of arrhythmia and stenocardia. These complications can be followed by disturbance of a cordial rhythm, dizziness, faints.
In the aspiration to pull out the patient, doctors often go too far. So, for example, a certain Charles Janszen during the period from 1954 to 1994 endured more than 900 operations on removal of new growths.

According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. Statistics we get sick...
Section: Articles about health
Stroke (acute disorder of cerebral circulation) – one of the most widespread neurologic diseases. Annually in the world more than 6 million people die of this illness. From the survived patients about 80% become disabled people, and nearly a thirds from them впо...
Section: Articles about health
It is pleasant to state a possibility of improvement of quality of life of people with problems of functioning of secretory system. Efforts of talented inventors created products which will be able to provide normal life activity of clients with moderate degree of a disease, it is essential to facilitate the help to patients with strongly expressed disturbances....
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even at the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching з...
Section: Articles about health
The stroke is one of the most widespread diseases of the person, annually in the world about 6 million cases of this pathology are registered. According to medical statistics, strokes occur almost three times more often than myocardial infarctions. Disease otno...
Section: Articles about health
The climax, or menopause is the normal process of the termination of genital function of the woman which is followed by serious hormonal changes in an organism. Usually the menopause begins at the age of 50-55 years, but characteristics of this process are very individual. Factors of earlier approach of a climax are irregular sex life, numerous abortions, addictions, existence of endocrine, autoimmune and gynecologic diseases, frequent stresses and excessive hobby of diets...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant but which is not exhausting, motive...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning...
Section: Articles about health
The number of long-livers is very small. One person from 5 thousand lives up to age of 90 years, and the centenary boundary steps over only one of 20 thousand. However, doctors claim that each of us is quite able to affect own destiny. At the same time it is not so much about living as long as possible, how many about an opportunity to keep physical and intellectual activity and to avoid decrepitude. We will also talk about the ways helping to achieve this result today....
Section: Articles about health
The problem of diagnosis was and remains to one of the most important in medicine. From that, the reason недо will be how precisely defined...
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. The use of sugar in food is based rather on the psychological dependence caused by desire to indulge itself with something tasty, and in дальнейш...
Section: Articles about health
All are familiar with cold, and practically everyone believes that he has sufficient knowledge and experience that correctly to treat it. In practice most of people makes mistakes in attempts to get rid of rhinitis, and divides numerous delusions it....
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need to the visa...
Section: Articles about health
One of the useful properties presented to the person by the nature is ability to feel fear. This ability is designed to signal about approach of a dangerous situation and to help to avoid in advance it to keep life. However if the fear is persuasive and not about...
Section: Articles about health
The endocrine system carries out extremely important role in a human body, practically all processes of life activity are regulated by it. Closed glands (hemadens) produce special biologically active agents – hormones which then get to a blood channel and are transferred to bodies addressees, or as they are called still, to target organs. Frustration of this mechanism are fraught with development of serious chronic pathologies....
Section: Articles about health
Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes lying бо...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste, because of to...
Section: Articles about health
Life activity of one-celled fungi of the sort Candida, related to yeast is a proximate cause of development of candidiasis (milkwoman). Normal these microorganisms are a part of the microflora living in an oral cavity and intestines of most of people and also in a female genital tract. The pathological phenomena are observed when fungi begin to breed too violently. At the same time there is an inflammatory process affecting mucous membranes and which is shown very nepr...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of improvement of a condition of the patients at administration of drugs who are not containing active agents, so-called effect of placebo is known...
Section: Articles about health
The next flu epidemic leads to the next panic, from year to year we give in on these manipulations: professionally alarming voice of the announcer in news, reports with calculation of the died patients, an interview with people in white dressing gowns and advertizing of anti-influenza means ра...
Section: Articles about health
All know that self-treatment is dangerous. However absolutely it is almost impossible to do without it. Rate of modern life does not allow to handle each small trouble to the doctor and information on ways of independent delivery of health care is quite available. Means, all of us have only one: to learn to give this help competently and in those limits in which it is possible for the person who does not have vocational education....
Section: Articles about health
Tea is loved and use almost everything. This drink has tonic properties, contains the tannins capable podavlit...
Section: Articles about health
Life expectancy in various regions of Earth is not identical. Social stability, economic wellbeing, availability and level of medical care, household comfort, literacy of the population in the field of observance sanitary гигиен exert impact on it...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – unique body on the structure thanks to which the person obtains about 80% of information on the world around: about a form, color, size, the movement, and also many other parameters of objects or phenomena. But whether much we know about the most valuable sense body which, according to the scientist Sechenov, provides us about one thousand various feelings a minute? Let's consider 10 most surprising facts about eyes and sight....
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs п...
Section: Articles about health
All parents are ready to what the baby often and pisat much. Since then, as the absorbing diapers strongly became current, keeping of the kid in dryness does not represent any problems. But if the grown-up kid continues to urinate in panties, parents of a nacha...
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number of myths about negative effect which allegedly gluten has on health of the person....
Section: Articles about health
