





Hypogonadism
General characteristic of a disease
The hypogonadism at men is the disease caused by deficit of hormones androgens in an organism. Depending on an etiology of a disease it is accepted to distinguish primary hypogonadism and a secondary form of a disease (it – a hypogonadotropic hypogonadism). Primary form of a disease which is characterized by the increased level of gonadotropic hormones in an organism is quite often called a hyper gonadotropic hypogonadism.
Pathology takes the leading place on prevalence among the male diseases caused by functional insufficiency of gonads.
Primary hypogonadism at men
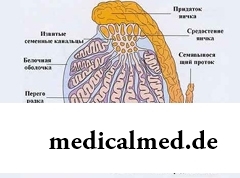
Primary hypogonadism can be inborn. The disease is demonstrated by testicular insufficiency of testicles or their total absence (anorchism). Pathology is shown during the pre-natal period. The boy is born with a penis whose sizes there is much less norm, and also with an underdeveloped scrotum.
Further symptoms of primary hypogonadism of an inborn form appear at teenage age. Young men with primary hypogonadism have so-called "eunuchoid" type of a skeleton, excess body weight, gynecomastia signs (increase in a breast), small degree of pilosis.
Inborn primary hypogonadism – the frequent phenomenon at Klaynfelter, Reyfenstein, Shereshevsky-Turner, Nunan and Del Castillo's genetic syndromes.
Men can also have acquired primary hypogonadism. This form of a disease is the most widespread and occurs on average at every fifth man with the diagnosed infertility.
The acquired primary hypogonadism develops as a result of an inflammation of seminal glands at:
- orchitis (inflammation of testicles),
- vesiculitis (inflammation of seed bubbles),
- to differentita (inflammation of seed cords),
- epididymite (inflammation of appendages of testicles),
- infectious parotitis (mumps),
- to chicken pox.
The provocative factor of the acquired primary hypogonadism finds possible also a cryptorchism (not omission of testicles in a scrotum). Injuries or radiation injury of testicles can provoke functional insufficiency of gonads of the man.
Also idiopathic form of primary hypogonadism at men with the obscure etiology of a disease is possible.
At the acquired primary hypogonadism at teenage age there is no formation of secondary sexual characteristics. At adult men the disease leads to increase in body weight, decrease in a libido, disturbances of an erection and spermatogenesis, to reduction of expressiveness of male sexual characters and development of infertility.
Secondary hypogonadism at men
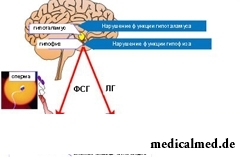
The secondary or hypogonadotropic hypogonadism can also be inborn. It develops at disturbances of secretion of hormones a hypophysis and a hypothalamus. The secondary hypogonadism accompanies the following genetic diseases:
- Paskualini's syndrome,
- Meddok's syndrome,
- Pradera-Willie's syndrome.
Development of a hypogonadotropic hypogonadism - also not a rarity at cranyopharyngiomas (brain epithelium tumors).
The acquired secondary hypogonadism develops as a result of complications of inflammatory processes in a brain. Meningitis, an arachnoiditis, an encephalomeningitis, encephalitis, etc. can provoke them.
At them not only function of gonads suffers, but also there are other pathologies of gipotalamo-pituitary system: disturbances of secretion of a thyroid gland, thermal control, weight and linear growth.
Diagnosis of a hypogonadism at men
Inborn primary hypogonadism is diagnosed if at the newborn boy testicles at a palpation are not probed. Are applied to confirmation of the diagnosis by ultrasonography of bodies of a small pelvis and a hormonal blood analysis.
Characteristic symptoms of a disease are testosterone indicators below norm, the high level of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones at primary hypogonadism and deficit is higher than the specified hormones at a hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
In diagnosis of a secondary hypogonadism at men KT, MPT, and also a brain electroencephalography are applied.
For clarification of the reasons of a hypogonadism of primary or secondary form genetic differential diagnosis of pathology is carried out.
Treatment of a hypogonadism at men
In treatment of a hypogonadism replacement therapy is applied by male sex hormones. At lifelong continuous administration of drugs, since teenage age, at the boy secondary sexual characteristics form. In most cases it is possible to keep sexual function also.
Treatment of the hypogonadism provoked by a cryptorchism, preferential surgical. The recommended age of an operative measure - 1-1,5 years. The provision of a neopushcheny small egg in belly space is higher, the earlier there are irreversible processes in fabrics of seminal glands. They lead to the acquired primary hypogonadism and infertility.
Treatment of a hypogonadism of a hypogonadotropic form consists in therapy of a basic disease. Surgical or beam treatment of a hypogonadism is carried out at brain tumors.
The strategy of replaceable treatment of a hypogonadism of a secondary form depends on extent of disturbances of production of hormones gipotalamo-pituitary system and age of the patient.
If there is no need to keep spermoobrazuyushchy function of the patient, treatment of a hypogonadism of a hypogonadotropic form is carried out by means of testosterone.
At young men and boys of teenage age the short course of testosteronovy therapy is applied, and for normalization of a spermatogenesis at a hypogonadotropic hypogonadism drugs of gonadotropic hormones are used.
Antidepressant Klomipramin causes an orgasm in 5% of patients.

Life of the modern woman is very difficult. Opportunities to realize itself are wide: it not only education and career, but also most differently...
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn – whether you have or your relatives problems....
Section: Articles about health
Musicotherapy – a treatment method which caused and causes a set of a controversy concerning its efficiency. However the facts are relentless: during the numerous researches curative impact of music on an organism was scientifically confirmed. Since then in a number of the countries the technique is included complex therapy of diseases of cardiovascular and respiratory system, dorsodynias and a backbone, psychosomatic disturbances and many other illnesses. The musicotherapy in a pedi is especially widely applied...
Section: Articles about health
Household skills which to us so diligently imparted in the childhood it appears, not always bring only benefit. According to result...
Section: Articles about health
It seems, quite recently you brought the baby from maternity hospital, but time flew by, and here it is already going to join the first in life children's collective. How to prepare the child for visit of a garden? What needs to teach him to facilitate process адап...
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications of the end of the twentieth century. Researches were conducted since 1984, including placebo - controlled effects. In total clinical tests of Mildronate were carried out for more than thirty years....
Section: Articles about health
Each person has easy indispositions which he transfers "standing", trying not to ask for medical care. Argu...
Section: Articles about health
Life expectancy in various regions of Earth is not identical. Social stability, economic wellbeing, availability and level of medical care, household comfort, literacy of the population in the field of observance sanitary гигиен exert impact on it...
Section: Articles about health
Dark circles (bruises) under eyes – a shortcoming with most of which often fight against the help of cosmetics (proofreaders, saloon procedures and so forth), eliminating only its visibility. However, according to doctors, skin around eyes – the indicator of many disturbances in an organism. To reveal them at early stages, without having disguised bruise, and having addressed its reasons – a task of each person who is regularly finding under with own eyes dark stains. Early detection and elimination of the disease lying in wasps...
Section: Articles about health
All know that self-treatment is dangerous. However absolutely it is almost impossible to do without it. Rate of modern life not on...
Section: Articles about health
Vitamin complexes belong to the most popular drugs, probably, in our country there is no person who was not hearing about advantage of vitamins and never their accepting. The more vitamins, the better, we consider and as it appeared, cruelly we are mistaken. So l...
Section: Articles about health
Subfebrile temperature call fervescence to 38 degrees, and subfebrile condition - existence of such temperature over 3 days, and quite often it happens without the visible reasons. Existence of subfebrile condition - a strong indication of disturbances in an organism which can be caused by various reasons: disease, stresses, hormonal failures. Despite the seeming inoffensiveness it is a state at which people often continue to lead a usual life, often is a sign of many of a zabolev...
Section: Articles about health
Mushrooms - the surprising inhabitants of our planet having a set of wonderful qualities. Thanks to one of them, a mold mushroom of Penici...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance of physical, psychological and moral health of the person by means of the complex of procedures including a diet, cleaning of an organism, respiratory упр...
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. According to nutritionists, the separate use of the carbohydrate and proteinaceous products demanding different conditions of assimilation helps to get rid of diseases of digestive tract and serves as prophylactic from a diabetes mellitus, arthritis, food allergies, cholelithiasis and many other frustration. The essence of salutary effect of a method consists in most Kacha...
Section: Articles about health
For the time being the perspective of heart diseases seems to most of people remote and foggy. But sooner or later практичес...
Section: Articles about health
One of the major chemical processes happening in a human body are oxidation reactions. They go with participation of fats and carbohydrates which we receive from food, and the oxygen getting to us from air. A main goal of such reactions is it is received...
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. In the summer repeatedly the risk increases to ache with some very dangerous illnesses, we also will talk about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it is strong for...
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to get access to various apparatuses and an opportunity to train under the leadership of the experienced consultant. Many consider fitness on...
Section: Articles about health
Among a set of the perfumery and cosmetic goods which are released today the special group is made by the means containing antibacterial components. Such types of gels, shampoos, soaps, creams, lotions and other products are positioned by manufacturers as a panacea from all diseases caused by pathogenic microorganisms. The unlimited and uncontrolled use of similar means becomes result of trustfulness of the buyers hypnotized by persuasive advertizing sometimes. Many spetsial...
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. Odes...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. A contribution of drugs to rescue of people from...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one of the most ancient methods of disposal of the most different diseases. Bathtubs, souls, wrappings and inhalations, in combination with water reception inside help to improve a condition of the patients suffering from disturbances of work of a musculoskeletal system, bodies of digestive tract, cardiovascular, nervous, respiratory and secretory system, skin and endocrine п...
Section: Articles about health
What is in our understanding weeds? It plants which are considered to be suitable only for compost pits and feeding жи...
Section: Articles about health
Epilepsy is one of widespread neurologic diseases. Parents, whose children suffer from this illness, should face rumors and delusions, many of which remained since the Middle Ages....
Section: Articles about health
Each of us faces from time to time that other people need the immediate help. We react to it differently: one at once call doctors and police, others rush to victims and try to save them independently. Some pass by at all … Certainly, desire to help the neighbor who got into trouble, quite naturally for any decent person. However not everyone understands that to work in a similar situation, being guided by exclusively good...
Section: Articles about health
