





Infectious mononucleosis
General characteristic of a disease
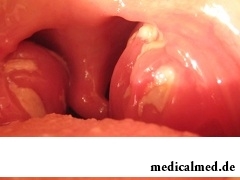 The infectious mononucleosis represents an acute viral disease which causative agent is Epstein-Barre's virus rather steady in external environment.
The infectious mononucleosis represents an acute viral disease which causative agent is Epstein-Barre's virus rather steady in external environment.
Fever, damage of lymph nodes, pharynx, spleen, liver, and also peculiar changes of composition of blood is characteristic of this disease.
The infectious mononucleosis is called sometimes "a potseluyny disease" that is connected with its airborne way of transfer, in particular through kisses, when using the general bed, linen, ware. Places with big density of healthy and sick people - kindergartens, the camp, nursing homes, hostels are favorable for spread of a virus.
As a rule, the clinical picture of an infectious mononucleosis develops at people of young age: the peak of incidence at girls is observed in 14-16 years, and the maximum infectiousness among boys is noted in 16-18 years. At most of people by 25-35 years reveal in antibody blood to this virus.
Symptoms of an infectious mononucleosis
Duration of an incubation interval can vary from 5 to 45 days, however 7-10 days most often last. Disease duration, as a rule, does not exceed two months. The infectious mononucleosis, symptoms can be shown selectively or in a complex, begins with sharp rise in body temperature, swelling of cervical lymph nodes, difficulty of nasal breath and quinsy. These symptoms of a disease in full usually develops by the end of the first week. At the initial stage most of patients has also such symptoms of an infectious mononucleosis as existence in blood of peculiar lymphocytes (atypical mononuklear), and also increase in a liver and spleen.
The disease can begin and gradually: a febricula, small temperature or its absence, moderate inflammatory processes in upper respiratory tracts. At some patients body temperature considerably increases only at the height of a disease, however cases when temperature is absent throughout the entire period of an infectious mononucleosis, are very rare.
Important, very often the first symptom of an infectious mononucleosis is the hyperadenosis, especially cervical. They can be seen or probed – size can vary from the pea size to egg. Suppuration of lymph nodes is not characteristic of this disease.
 Defeat of a stomatopharynx – a constant symptom of an infectious mononucleosis. At patients puffiness and increase in palatine tonsils, defeat of a nasopharyngeal almond is observed that, in turn, causes difficulty of nasal breath, the expressed nose congestion, a voice sdavlennost, the "snoring" breath by a mouth. Back rhinitis therefore allocations from a nose usually are not observed in the period of an exacerbation of a disease is characteristic of an infectious mononucleosis, they appear only after recovery of nasal breath. At patients puffiness of a back wall of a throat which is usually covered with dense slime is noted. During a disease the moderate hyperemia of a pharynx and an insignificant pharyngalgia is observed.
Defeat of a stomatopharynx – a constant symptom of an infectious mononucleosis. At patients puffiness and increase in palatine tonsils, defeat of a nasopharyngeal almond is observed that, in turn, causes difficulty of nasal breath, the expressed nose congestion, a voice sdavlennost, the "snoring" breath by a mouth. Back rhinitis therefore allocations from a nose usually are not observed in the period of an exacerbation of a disease is characteristic of an infectious mononucleosis, they appear only after recovery of nasal breath. At patients puffiness of a back wall of a throat which is usually covered with dense slime is noted. During a disease the moderate hyperemia of a pharynx and an insignificant pharyngalgia is observed.
The infectious mononucleosis at children in 85% of cases is followed by a plaque on nasopharyngeal and palatine tonsils. As a rule, emergence of this symptom (at the beginning or for 3-4 day of a disease) causes a bigger temperature increase and deterioration in the general state.
Increase in a liver and spleen is noted at 97-98% of patients. Change of the sizes of a liver sometimes provokes emergence of yellowness of skin which disappears afterwards together with other displays of a disease. Begun to increase from the first days of a disease and reached the maximum in sizes at 4-10 day, the liver is returned to the normal amount only by the end of the first - the beginning of the second month of a disease.
Quite often symptoms of an infectious mononucleosis are puffiness the century, puffiness of the person, an enanthesis, petechia and a dieback in a mouth.
The disease can be also shown in the form of such disturbances from cardiovascular system as tachycardia, systolic noise, a priglushennost of cordial tones.
The infectious mononucleosis at children is not characterized by a chronic current and a recurrence. Complications at patients are most often caused by activation of microbic flora, and also stratification of a SARS, otitis, pneumonia, bronchitis. Pancreatitis, an orchitis and parotitis are considered as rare complications of a disease. In 80% of cases the infectious mononucleosis completely recovers in 2-3 weeks, only in certain cases changes in blood (existence of atypical mononuklear, a moderate leukocytosis) can remain before half a year. The lethal outcome of the disease is possible only in isolated cases – from a rupture of a spleen, severe defeats of a nervous system, at genetic insufficiency of lymphatic system.
Treatment of an infectious mononucleosis
At the moment specific treatment of an infectious mononucleosis is not developed.
Plentiful drink, bed rest, the diet assuming an exception of fried and fat food, hot spices is recommended to the patient. The symptomatic treatment of an infectious mononucleosis includes reception of vitamins, use of the hyposensibilizing means (reduce sensitivity to allergen), a thaw in a nose, rinsing of a throat and pharynx Iodinolum, Furacilin solution, Tinctura Calendulae, a sage, a camomile, 3% solution of peroxide of hydrogen or other antiseptic agents.
In treatment of an infectious mononucleosis it is reasonable to dig in within 2-3 days in a nose interferon or to apply rectal candles виферон for 5-10 days. Use of natural stimulators of production of interferon – tincture of a magnolia vine, a ginseng, a wolfberry, an arapiya, a sterkuliya is as an alternative possible.
 At an infectious mononucleosis it is recommended to apply not OVIR representing antibacterial, antiviral and immunomodulator. Sulfanamide drugs at this disease are not appointed. Antibiotics can be recommended only in case of accession of secondary microflora. At treatment of a severe form of a disease of short courses corticosteroids, in particular Prednisolonum are applied,
At an infectious mononucleosis it is recommended to apply not OVIR representing antibacterial, antiviral and immunomodulator. Sulfanamide drugs at this disease are not appointed. Antibiotics can be recommended only in case of accession of secondary microflora. At treatment of a severe form of a disease of short courses corticosteroids, in particular Prednisolonum are applied,
The infectious mononucleosis at children does not assume specific treatment. After recovery exercise stresses of athletes and teenagers have to be limited at least for half a year, for the purpose of decrease in risk of traumatization of a spleen.
Prevention of an infectious mononucleosis
The diseased it is necessary or to isolate houses for 2-3 weeks, or to hospitalize according to clinical indications. Disinfection is not required, it is enough to air the room and to regularly do wet cleaning. The patient should give separate ware and necessary objects of leaving.
As the vaccine against an infectious mononucleosis is not developed, active immunization against this disease is not carried out.
Antidepressant Klomipramin causes an orgasm in 5% of patients.

Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. Exists even so-called died away...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often deliver беспоко...
Section: Articles about health
Visit of doctors – business not the most pleasant, and many people do not hurry to undergo necessary planned inspections. Such behavior is extremely thoughtless and improvident. Our health is necessary not only to us: wellbeing of darlings, children, grandsons and aged parents directly depends on as far as we are vigorous and able-bodied. Therefore in time to be inspected – a duty of any modern person. Specialists consider that 7 regular surveys and di are especially necessary for women...
Section: Articles about health
All the known slogan "Protect Men!" arose not from scratch. In a sense, the nature created representatives of strong...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically cystitis 25-30% of women up to 40 years have. With age this indicator raises, besides many do not get to statistics because do not see a doctor. The most sad that after the regular visits to doctors, long reception of antibiotics...
Section: Articles about health
Sometimes it seems that modern society was divided into two camps: representatives of the first are sure that only the woman has to be responsible for contraception, representatives of the second, respectively, are sure that it is destiny of men. Meanwhile the question of contraception has very many aspects – both psychological, and legal and, of course, medical....
Section: Articles about health
The way of life of people promptly changes from year to year: if about ten years ago the personal computer was not in each family...
Section: Articles about health
Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only the food sating an organism but also the medicines curing of many diseases. Unfortunately, having given the use of some of them...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too frequent use of these drugs can lead to allergic reactions, and also overdose, causing poisoning. It happens also that there are no antipyretics simply in the house. In these situations it is pertinent to use it...
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also contain...
Section: Articles about health
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice from 40th years of the last century. Originally antibiotics were called only substances natural (animal, vegetable or микробног...
Section: Articles about health
The popular expression "run from a heart attack" became the motto of the people supporting active lifestyle. Moreover, run became a peculiar fashionable tendency: sales of racetracks and the accompanying goods for run are at permanently high level. Whether really it is possible for one and all people and it is necessary to run to receive the portion of health, a charge of cheerfulness and good mood?...
Section: Articles about health
The pancreas performs two functions in a human body: release of enzymes without which digestion carbohydrate is impossible...
Section: Articles about health
Stability of a hormonal background is one of the most important conditions of preservation of health of the woman. At the same time endocrine system – the thin device extremely sensitive to any external influences. Changes of an image жиз can become the reason of hormonal failure...
Section: Articles about health
Nightmares belong to the most unpleasant frustration. Statistically, they happen at 4% of adults, and almost at 70% of children and teenagers. During a nightmare of people dreams himself in extremely difficult, life-threatening situation. He wakens suddenly, in a condition of a fright, and, as a rule, remembers the dream distinctly. The feeling of depression and alarm does not release throughout the day, creating hindrances for work and normal communication. If such episodes repeat often, can р...
Section: Articles about health
On health of the person physicians know about salutary action of animals long ago. About 7 thousand years ago great Hippocrates рекоменд...
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. The use of sugar in food is based rather on the psychological dependence caused by desire to indulge itself with something tasty, and in дальнейш...
Section: Articles about health
Diseases of joints often begin imperceptibly for the person. The first stages of destruction of the cartilaginous tissue providing soft and free sliding of heads of bones in joint bags proceed slowly and absolutely without serious consequences. Especially unpleasantly for the fact that this process is not connected with advanced age: degradation of joint surfaces is, as a rule, noticeable after 30 years. It means that practically each able-bodied person at any time can face sad results...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions связ...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist...
Section: Articles about health
Condition of lips (their morbidity, outward) – one of indicators of health of the person. The peeling, dryness, pallor, and also cracks in corners of a mouth can be not only the cosmetic shortcoming which arose owing to physical damages and weather conditions but also the satellite of some diseases and disturbances in an organism needing treatment. Let's consider 10 possible reasons of emergence of angular cracks (perleches) in corners of a mouth and ways of their elimination....
Section: Articles about health
What is in our understanding weeds? It plants which are considered to be suitable only for compost pits and feeding жи...
Section: Articles about health
Frosty air, fresh wind and easy snowball at most of Russians are associated with cheerfulness, health and cheerful entertainments on which our winter is so generous. But, unfortunately, cold season sometimes brings also troubles with health. It is not about a season...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs when walking on heels, frequent painful sprains, pain on average and anonymous toes even after small loadings. Usually people with such pathology take off unpleasant effects by means of the anesthetizing pulverizing and ointments, but it does not lead to radical elimination of a problem. Meanwhile, at the known persistence it is possible to strengthen an ankle to the house...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that our country is one of the most "drinking" in the world. At clear understanding of that the use of strong...
Section: Articles about health
One of the useful properties presented to the person by the nature is ability to feel fear. This ability is designed to signal about approach of a dangerous situation and to help to avoid in advance it to keep life. However if the fear is persuasive and not about...
Section: Articles about health
Urogenital candidiasis (milkwoman) – a fungal infection which annoys unpleasant feelings in the field of generative organs, being followed by white curdled allocations, an itch, discomfort during an urination, pain. She is called by Candida fungus – the opportunistic organism living on mucous membranes of an organism....
Section: Articles about health
