





Osteoma
Osteoma – the high-quality delimited bone new growth proceeding from a bone and consisting of a bone tissue is long and the hemispheres which are slowly growing and having an appearance. Earlier the concept an osteoma irrespective of an origin joined all bone educations (traumatic, blastomatous, inflammatory and neuropathic), however now at all difficulty of differentiation of a tumor from hyperplastic education in medicine above-mentioned growths more an osteoma do not carry to a concept.
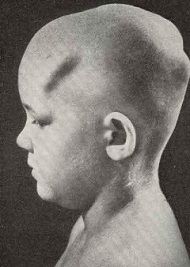 The tumor is formed on bones of a skeleton and often meets on femoral, key, temporal and frontal bones, and also in cavities and an orbit of facial bones. The osteoma of a frontal bone and a wedge-shaped bone often comes from the embryonal cartilaginous rests.
The tumor is formed on bones of a skeleton and often meets on femoral, key, temporal and frontal bones, and also in cavities and an orbit of facial bones. The osteoma of a frontal bone and a wedge-shaped bone often comes from the embryonal cartilaginous rests.
The osteoma which is located over the surface of a bone is called an exostosis, and concluded in spongy substance – enostozy.
Usually tumors meet single (solitary), however also multiple exostoses which represent general diseases meet and belong to ecchondromas. Seldom or never the osteoblastoma proceeding from osteoblasts which costs on border between high-quality new growths and sarcomas (malignancies) meets.
Osteoma reasons
In certain cases, especially at multiple exostoses, the osteoma appears owing to genetic predisposition as with probability the disease is transmitted to 50% to lineal descendants. Are also origins of an osteoma:
Inborn exostoses;
- Injuries;
- Syphilis;
- Gout;
- Rheumatism.
Classification of an osteoma
The osteoma of a bone is divided in the order of a structure into the following types:
Firm which consists of the dense compact substance reminding ivory. This substance does not contain marrow and almost completely does not incorporate Gaversovy channels;
Spongy which consists of porous spongy substance;
Mozgovidny which consists of big wide marrowy cavities.
On genesis of an osteoma also divide into epiphyseal and periosteal exostoses.
Osteoma structure
The osteoma of a bone contains bone plates with the bone little bodies lying among them. These plates are around Gaversovy channels and marrowy space. Depending on above-mentioned types of a tumor the number of Gaversovy channels and size of marrowy space fluctuate. The bone tissue which is a part of an osteoma of a frontal bone often consists of the cartilaginous islands put in a subcortical layer or spongy substance.
Osteoma symptoms
 Often the osteoma develops asymptomatically, and painful feelings appear only when the tumor is an obstacle for the movement of a bone or presses on a nerve. At a tumor arrangement on an upper table of the scull there can be headaches, epileptic seizures and problems with memory. If the osteoma is located in nasal bosoms, then there is a deterioration in sight, and at localization of a tumor around a wedge-shaped bone of a skull disturbance of a hormonal background is observed.
Often the osteoma develops asymptomatically, and painful feelings appear only when the tumor is an obstacle for the movement of a bone or presses on a nerve. At a tumor arrangement on an upper table of the scull there can be headaches, epileptic seizures and problems with memory. If the osteoma is located in nasal bosoms, then there is a deterioration in sight, and at localization of a tumor around a wedge-shaped bone of a skull disturbance of a hormonal background is observed.
Treatment of an osteoma
Originally, based on results of clinicoradiological data, the diagnosis of an osteoma then treatment is appointed is made.
Treatment of an osteoma consists in a radical oncotomy. An operative measure is shown at dysfunctions of bodies, severe pains, a growth inhibition and changes of a shape of bones which result in limitation of mobility and disturbance of a statics of extremities. During operation the surgeon deletes a tumor then carries out a resection of the subject plate of a healthy bone. If the course of a disease is not followed by symptoms and a tumor of the small sizes, then is considered it expedient to conduct dynamic observation.
In Great Britain there is a law according to which the surgeon can refuse to do to the patient operation if he smokes or has excess weight. The person has to refuse addictions, and then, perhaps, he will not need an operative measure.

Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes lying бо...
Section: Articles about health
It is impossible to imagine human life in which there would be no plants. Practically in each apartment and any production room there are window plants, millions of people with pleasure are engaged in gardening and truck farming, many citizens пр...
Section: Articles about health
Olive oil – the product capable to make a powerful contribution to health of the person if it includes it in the diet. The rich vitamin composition of oil does it by a product number one from many diseases including from deadly. Only two tablespoons of oil from olives in day prevent emergence of diseases of vessels and heart, cancer, problems with digestion, presenilation, a depression and many other illnesses which treatment would demand a lot of time and forces. Let's consider on...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and Wuxi...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance of physical, psychological and moral health of the person by means of the complex of procedures including a diet, cleaning of an organism, respiratory упр...
Section: Articles about health
Tick-borne encephalitis – one of the most dangerous viral diseases which causative agents transfer and is given to people by ixodic mites. These are the small blood-sicking insects living in the considerable territory of our country. The person bitten by a tick can catch also erlikhiozy, bartonnelezy, babeziozy, mycoplasmosis and Lyme's disease. As well as encephalitis, these illnesses affect the central nervous system, and as specific antiviral therapy does not exist, the forecast very to a neuta...
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters in any...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – unique body on the structure thanks to which the person obtains about 80% of information on the world around: about a form, color, size, the movement, and also many other parameters of objects or phenomena. But whether much we know about the most valuable body...
Section: Articles about health
The advantage of swimming for the person is so high that this sport is not only the most popular, but also is widely applied in medicine and rehabilitation processes. If you look for for yourself the occupation allowing pleasantly and to spend time, then swimming with advantage – the fact that it is necessary for you. And give learns several facts about swimming....
Section: Slideshow
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutritious...
Section: Articles about health
Epilepsy is one of widespread neurologic diseases. Parents, whose children suffer from this illness, should face rumors and delusions, many of which remained since the Middle Ages....
Section: Articles about health
Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. There is even a so-called gastronomic tourism which, according to gourmets, not only allows to receive new feelings, but also is capable to show life of other people from absolutely unexpected side....
Section: Articles about health
The modern person not always manages to find housing in the environmentally friendly region and such work which would not do harm здо...
Section: Articles about health
History of use of an anesthesia during operations contains more than 160 years. Annually in the world hundreds of thousands of surgical interventions during which to patients the substances immersing them in a dream and saving from pain are entered are carried out. Using an anesthesia to these...
Section: Articles about health
The number of long-livers is very small. One person from 5 thousand lives up to age of 90 years, and the centenary boundary steps over only one of 20 thousand. However, doctors claim that each of us is quite able to affect own destiny. At the same time it is not so much about living as long as possible, how many about an opportunity to keep physical and intellectual activity and to avoid decrepitude. We will also talk about the ways helping to achieve this result today....
Section: Articles about health
Color of plants is caused by presence at them of certain chemical compounds. Let's talk that various colors mean vegetable...
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear are similar, however if the fear is natural protective function of mentality, then the phobia is its deviation. So the person can an ispytyva...
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number of myths about negative effect which allegedly gluten has on health of the person....
Section: Articles about health
The nature does not stand stagnation and monotony. It is known that tissues of a human body atrophy if do not receive necessary loadings...
Section: Articles about health
About influence of fasting days on an organism it is told much – both about advantages, and about shortcomings. It is considered that fasting day in the form of a short-term monodiet is useful, promoting effective removal of slags from an organism whereas irregular, it is excessive п...
Section: Articles about health
The kid who was recently born is surrounded with love of adult family members and their cares without which the baby cannot exist. Some parents consider that gentle attachment and caress are quite enough that the child correctly developed and was happy, but it not so. It is important to know as much as possible about specifics of care of the baby, the reasons of his behavior and possible problems. Only the "able to see" love will provide to the little man that it is necessary for him....
Section: Articles about health
The climax, or menopause is the normal process of the termination of genital function of the woman which is followed serious hormonal...
Section: Articles about health
The technique of acupuncture (acupuncture) is used in the medical purposes more than three and a half millennia. It is eurysynusic and recognized as official medicine in the majority of the developed countries of the world. Influence by fine needles on so-called points...
Section: Articles about health
The cosmetics intended for improvement of a condition of skin, nails and hair are used by each woman. Expenses on regular acquisition of the fashionable widely advertized products of well-known companies for many become very notable and significantly burden the family budget. Meanwhile, there is a number of inexpensive pharmaceutical drugs which can quite be applied in the cosmetic purposes. At the same time the effect of their use is often more noticeable, than result of use of the most expensive...
Section: Articles about health
All got used long ago that, having addressed the plastic surgeon, it is possible to modify natural parameters of a figure or to reduce...
Section: Articles about health
The fatigue, sleep debt, disturbances of food, bad mood, vagaries of the weather – all these circumstances badly affect our appearance. Especially the person suffers: skin becomes flabby, loses healthy color, becomes covered by wrinkles, zones of hypostases and t appear...
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers and cavities), and then small consolidations, the so-called effect of an orange-peel is shown. Changes in a condition of hypodermic cellulose are a consequence of a hormonal imbalance in an organism....
Section: Articles about health
