





Appendicitis
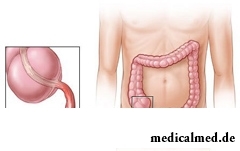
Appendicitis – an inflammation of the worm-shaped shoot called by an appendix. It is the small blind appendage of a colon located on border of a small and large intestine. Because of anatomic features the appendix quite often inflames – the acute appendicitis is the most frequent surgical disease.
There is it so often that in the thirties the last century in Germany the proposal to delete an appendix to children at early children's age, in the form of a preventive measure for fight against appendicitis was made. Those years was considered that the appendix represents atavism, absolutely useless anatomic education without which it is quite possible to do. However results of an experiment were depressing: at those children to whom at early age removed a worm-shaped shoot the severe form of an immunodeficiency developed afterwards.
The acute appendicitis at rejection of urgent medical measures is dangerous that it leads to suppuration and a rupture of the inflamed worm-shaped shoot, with spillage of pus and distribution of an inflammation on a peritoneum – peritonitis, a dangerous complication which can lead to a lethal outcome develops.
Appendicitis reasons
Believe that obstruction of a gleam of a worm-shaped shoot is the main reason for appendicitis. It can happen because of an appendix excess, and also as a result of mechanical obturation, at hit in a gleam of fecal stones or foreign bodys. Hit of foreign bodys in an appendix – one of the frequent reasons of development of appendicitis in children, and appendicitis is more often caused in adults by fecal stones. One more mechanism of an inflammation of an appendix, this emergence of ulcers on his mucous membrane, as a rule, as a result of the postponed viral infection.
Appendicitis symptoms
The main symptom of appendicitis is suddenly appeared abdominal pain. The following is characteristic of a pain syndrome at an acute appendicitis:
- Initially pain is localized in epigastric area;
- In 6-8 hours pain moves to the right ileal area (Kokhera-Volkovich's symptom, or a symptom of movement of pains);
- Further pain accepts diffuse character;
- Pain is constant, there can be periods of strengthening and easing of pain, but the bezbolevy periods are absent;
- Pain amplifies at the movement therefore patients with an acute appendicitis often move, holding the right side of a stomach with hands that is one of characteristic an appendicitis symptom;
- Sharp pain testifies to a purulent inflammation of a worm-shaped shoot (an appendix empyema);
- Remitting at an acute appendicitis – an adverse sign as the beginning of a sphacelism and death of nerve terminations can be the cause of it.
 In addition to a pain syndrome, symptoms of appendicitis are appetite loss, nausea, single vomiting, a chair delay, increase of an urination is possible.
In addition to a pain syndrome, symptoms of appendicitis are appetite loss, nausea, single vomiting, a chair delay, increase of an urination is possible.
Appendicitis usually does not cause sharp deterioration in the general state in adults, in any case before development of peritonitis. Perhaps slight increase of temperature, to subfebrile figures (37-37,5 °C). Adult patients can have a simple appendicitis and destructive. At a destructive current all symptoms are more brightly expressed, pain more considerable and the general state suffers.
Appendicitis at children proceeds much more violently, the inflammation progresses quickly, and peritonitis develops much quicker. At appendicitis at children severe pain in a stomach can have diffuse character at once, the general symptoms are brightly expressed: severe nausea, repeated vomiting, fever. Appendicitis at children practically always proceeds as destructive appendicitis at adults.
Diagnosis of appendicitis
In a classical form the disease does not cause difficulty with diagnosis which is put on the basis of characteristic symptoms of appendicitis. The following tests help to specify the diagnosis:
- Morbidity in the right ileal area at a stomach palpation;
- Morbidity in the right ileal area at easy effleurage (Razdolsky's symptom);
- Strengthening of pain at sharp hand otnyatiya after pressing of a front abdominal wall (impty Shchetkina-Blyumberg);
- Strengthening of pain at position of the patient lying on the left side (Sitkovsky's symptom);
- The palpation is much more painful at a prone position on the left side (Bartomye-Michelson's symptom);
- Strengthening of pain at a raising of the straightened right leg in a dorsal decubitus (Obraztsov's symptom);
- Strengthening of pain in the right ileal area at the movement by a hand from an upper part of a stomach to the right ileal area through the tense shirt (Voskresensky's symptom);
- Morbidity in the right ileal area at pushes fingers in the left ileal area (a symptom of Rovzinga).
These symptoms of appendicitis have important diagnostic value. However in certain cases, at the abnormal provision of a worm-shaped shoot, the clinical picture can be greased, and some of the described signs can be negative. Also there can be symptoms, uncharacteristic for appendicitis, for example, diarrhea.
Any signs of an acute abdomen have to guard concerning an appendicitis attack therefore, as a rule, the specifying diagnosis is carried out already to operation time (a diagnostic laparotomy) as the delay can lead to heavy complications, life-threatening. Because of difficulties in diagnosis abnormal forms of an acute appendicitis become much more often the reason of a lethal outcome.
Treatment of appendicitis
Treatment consists in surgical removal of appendicitis.
At suspicion of an acute appendicitis of the patient it is necessary to lay and provide it rest before arrival of an ambulance crew. Transportation in hospital also happens in a prone position. It is forbidden to give enemas and accept laxative, food, water, reception of the anesthetizing drugs, because of the subsequent difficulties in carrying out diagnosis is also undesirable.
Removal of appendicitis should be carried out as soon as possible to avoid a rupture of a worm-shaped shoot and development of peritonitis. To reduce probability of infection during removal of appendicitis, before operation enter antibacterial agents. Antibiotics are appointed also in the postoperative period.
Removal of appendicitis is carried out under the general anesthesia, in certain cases at thin patients use of local anesthesia is possible.
Now at a simple form of appendicitis prefer the laparoscopic operations which are not demanding abdominal section. In this case the endoscopic tool is entered into an abdominal cavity through a small puncture in fabrics. Removal of appendicitis allows to avoid this way an operational injury and to reduce the recovery period many times. The risk of development of postoperative complications during removal of appendicitis by a laparoscopic method is minimum.
Four segments of dark chocolate contain about two hundred calories. So if you do not want to recover, better not to eat it is more than two segments in days.

Water with a lemon - idle time in preparation drink which supporters of a healthy lifestyle already managed to appreciate. Upo...
Section: Articles about health
The summer of this year in Russia was very ambiguous. Regions suffered from a merciless heat, from pouring rains, the hail from time to time dropped out, then there was again a heat which alternated with rainfall again. Many people suffer from such sharp changes of weather...
Section: Articles about health
Each woman has preferences in the field of use of those goods which help us to look good, feel young and effective. Besides: selection process of favourite perfume, shampoo or decorative cosmetics already lightens the mood and serves as a peculiar stress medicine. Happens very offensively when the acquired perfumery and cosmetic products not only do not meet our expectations, but also becomes the reason of problems with health. Sources неприятн...
Section: Articles about health
Residents of big cities quite often have a disease which is known as the syndrome of chronic fatigue (SCF) today. This illness...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs when walking on heels, frequent painful sprains, pain on average and anonymous toes even after small nagruzo...
Section: Articles about health
A little more than a century ago goat milk was a traditional food stuff of most of Russians. Unfortunately, today on tables of our compatriots it appears extremely seldom. The reason that the use of so useful product practically came to naught, not only in very modest volumes of its production and, respectively, rather high cost. Potential consumers are just insufficiently informed on unique properties of goat milk and that advantage which...
Section: Articles about health
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) – one of those drugs which are known literally to all. It is available in each home first-aid kit...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease физич...
Section: Articles about health
History of use of an anesthesia during operations contains more than 160 years. Annually in the world hundreds of thousands of surgical interventions during which to patients the substances immersing them in a dream and saving from pain are entered are carried out. Using an anesthesia many myths and delusions are still connected. It is worth getting acquainted with the most widespread of them....
Section: Articles about health
Household skills which to us so diligently imparted in the childhood it appears, not always bring only benefit. According to result...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste, because of to...
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as are afraid that they can do harm to health of children. What troubles can really trap kids and how to make joint life of a family and domestic animals comfortable and safe?...
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" also "assimilation"...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which is felt by the kid, to...
Section: Articles about health
The cosmetics intended for improvement of a condition of skin, nails and hair are used by each woman. Expenses on regular acquisition of the fashionable widely advertized products of well-known companies for many become very notable and significantly burden the family budget. Meanwhile, there is a number of inexpensive pharmaceutical drugs which can quite be applied in the cosmetic purposes. At the same time the effect of their use is often more noticeable, than result of use of the most expensive...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it are...
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair by means of coloring, or considerably changing it for the purpose of creation of absolutely new image. All know that the gray hair is a sign приближающ...
Section: Articles about health
Diseases of joints often begin imperceptibly for the person. The first stages of destruction of the cartilaginous tissue providing soft and free sliding of heads of bones in joint bags proceed slowly and absolutely without serious consequences. Especially unpleasantly for the fact that this process is not connected with advanced age: degradation of joint surfaces is, as a rule, noticeable after 30 years. It means that practically each able-bodied person at any time can face sad results...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot on...
Section: Articles about health
Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. The fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding in a family and various illnesses immediately affect a condition of hair and skin. And to look safe and attractive so хоч...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too frequent use of these drugs can lead to allergic reactions, and also overdose, causing poisoning. It happens also that there are no antipyretics simply in the house. In these situations it is pertinent to use it...
Section: Articles about health
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible on...
Section: Articles about health
80% of women at least once to lives complained of discomfortable feelings to breasts, consolidations and nagrubaniye. These are mastopathy symptoms. The mastopathy is characterized by change of a ratio between ferruterous and connective tissue tissues of mammary glands. It can bring...
Section: Articles about health
Work of a brain is extremely complex and in many respects is not studied yet. It is confirmed also by the features of thought processes which are shown when the person sleeps. Let's tell about some of them....
Section: Articles about health
Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on is called...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. A contribution of drugs to rescue of people from...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
