





Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism (thyrotoxicosis) – the endocrine syndrome (a clinical state) caused by too active production of thyroid hormones of thyroxine (T3) and triiodothyronine (T4) a thyroid gland. The hormones produced by a thyroid gland are the main coordinators of work of an organism and regulate consumption of heat and production of oxygen. The blood oversaturated by hormones carries them on all bodies, fabrics and systems, causing acceleration of processes.
 The hyperthyroidism standardly is result of various pathologies of a thyroid gland which can be caused as disturbances directly in gland, and in processes which it regulates. The hyperthyroidism on the level of dysfunction of a thyroid gland happens primary (pathology of a thyroid gland), secondary (hypophysis pathology) and tertiary (hypothalamus pathology).
The hyperthyroidism standardly is result of various pathologies of a thyroid gland which can be caused as disturbances directly in gland, and in processes which it regulates. The hyperthyroidism on the level of dysfunction of a thyroid gland happens primary (pathology of a thyroid gland), secondary (hypophysis pathology) and tertiary (hypothalamus pathology).
Persons with autoimmune pathology, genetic predisposition and young women are most often subject to a hyperthyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism symptoms
Symptoms of a hyperthyroidism are caused by acceleration of all processes in an organism and are shown by the strengthened work of systems and human organs. Manifestation of symptoms of a hyperthyroidism depends on weight and duration of a disease, and also on degree of a prevalence of bodies, systems or fabrics. Excess of the hormones produced by a thyroid gland as follows influences a human body:
- Central nervous system. Hypererethism, emotional instability, irritability, causeless concern, fear, fluent speech, sleep disorders, trembling of hands;
- Cardiovascular system. Disturbance of a cordial rhythm – the persistent sinus tachycardia which is badly giving in to treatment, blinking and an atrial flutter. Increase in a gap between values of upper and lower indications of pressure due to increase in systolic and simultaneous decrease in diastolic arterial pressure. Increase of pulse, increase in volume and linear speed of blood circulation. Heart failure;
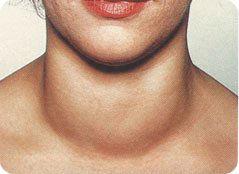
- Ophthalmology. Increase in a palpebral fissure, anteposition, protrusion of an eyeglobe with restriction of its mobility – an exophthalmos. A rare blinking, bifurcation of objects, the century swelled. The raised xerophthalmus, a cornea erosion, gripes in eyes, lachrymation is noted. Total loss of sight can become result of squeezing and dystrophy of an optic nerve;
- Digestive tract. Increase or a loss of appetite, at patients of advanced age – before full refusal of food. Disturbances of digestion and bilification, pristupoobrazny abdominal pains, frequent liquid chair;
- Musculoskeletal system. A thyrocardiac myopathy – a hypotrophy of muscles, the increased muscular fatigue, chronic weakness and trembling of a body and extremities, the broken physical activity, osteoporosis. As a result there are difficulties at long walking, especially on ladders, complexity when carrying weights, development of reversible thyrocardiac muscular paralysis is possible;
- Respiratory organs. Vital capacity of lungs decreases as a result of developments of stagnation and hypostases, persistent short wind forms;
- Sexual sphere. Disturbance of secretion of female and men's gonadotrophins which consequence infertility can be. At men the gynecomastia develops, decrease in a potentiality is observed, women have failures in a menstrual cycle, (the periods irregular, painful, allocations scanty, are followed by a severe headache, the general weakness to faints);
- Metabolism. Metabolism acceleration – reduction of weight, despite the increased appetite, development of thyrogenic diabetes, increase in heat production (the increased temperature, perspiration). As result of the accelerated disintegration of cortisol – insufficiency of adrenal glands. Increase in a liver, at hard cases of a hyperthyroidism – jaundice. Strong thirst, a frequent and plentiful urination (polyuria) owing to disturbance of water exchange. Thinning of skin, hair, nails, early strong gray hair, hypostases of soft tissues.
Hyperthyroidism symptoms at its existence can be absent at people of advanced age – the so-called disguised or hidden hyperthyroidism. Frequent depressions, block, drowsiness, weakness – typical reaction of an organism of elderly people to excess of thyroid hormones. Disturbance of work of cardiovascular system at people of advanced age at a hyperthyroidism is noted much more more often than at young people.
Hyperthyroidism signs
Mark out three severity of a disease which is not depending on the sizes of a thyroid gland which divide on hyperthyroidism symptoms. Easy degree of a hyperthyroidism, signs:
- At suralimentation – decrease in body weight to 5 kg;
- Constant tachycardia, the speeded-up pulse of 80-100 blows/min.;
- Perspiration, even in cool rooms;
- Irritability;
- The laboratory blood analysis on hormones reveals the increased level of contents T3, T4.
Average degree of a hyperthyroidism, signs:
- At suralimentation – decrease in body weight to 10 kg;
- Pathological changes in a myocardium, pulse rate of 100-120 blows/min.;
- Exophthalmos;
- Hyperhidrosis generalized (general);
- Acrimony, excitability, uneasiness, tearfulness, sleep disorders;
- Small trembling of fingers of an outstretched arm – a thyrocardiac tremor.
Severe form of a hyperthyroidism, signs:
- Sharp loss of weight;
- Steady tachycardia, pulse of 120-140 blows/min. and above;
- Explicit disturbance of a cordial rhythm, heart failure;
- Arterial pressure – increase in systolic pressure with simultaneous decrease diastolic;
- Sharply expressed exophthalmos;
- The strong thyrocardiac tremor extending to all body.
The disease on existence of signs of a hyperthyroidism and by results of researches is diagnosed.
 It is necessary to make:
It is necessary to make:
- Blood test on the quantitative content of hormones;
- Ultrasonography and KT of a thyroid gland – for determination of its sizes and existence of nodular educations;
- ECG – for definition of deviations in functioning of cardiovascular system;
- Radio isotope stsintigrafiya – for assessment of functional activity of a thyroid gland and definition of nodular educations.
In case of need appoint a biopsy of nodes. By results of inspection the attending physician draws up hyperthyroidism treatment planning.
Treatment of a hyperthyroidism
In modern medical practice there are several methods of treatment of a hyperthyroidism:
- Medicamentous (conservative) therapy;
- Operational removal of a thyroid gland or its part;
- Radioiodine therapy.
Methods of treatment of a hyperthyroidism are applied separately or is combined. The endocrinologist chooses how to treat the patient, considering his age, the disease which caused a hyperthyroidism and degree of its weight, specific features of an organism and associated diseases. The important role both in treatment of a hyperthyroidism, and in the rehabilitation period, is allocated for a diet and balneotherapy. Once in half a year is recommended a sanatorium course of treatment of a hyperthyroidism with emphasis on cardiovascular diseases.
According to WHO researches the daily half-hour conversation by the mobile phone increases probability of development of a tumor of a brain by 40%.

Small appetite at the child – the complaint which pediatricians should hear practically from each mother. Most often it is carried to разр...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads...
Section: Articles about health
The words "disease" and "patient" not without reason come from one root – "pain". As a rule, symptoms of illnesses thoroughly spoil to patients life. However from this rule there are exceptions. Some diseases are shown by signs which can cause even positive emotions. It is a pity only that the majority of such illnesses are heavy and incurable....
Section: Articles about health
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible on...
Section: Articles about health
History of use of an anesthesia during operations contains more than 160 years. Annually in the world hundreds of thousands of surgical interventions during which to patients the substances immersing them in a dream and saving from pain are entered are carried out. Using an anesthesia to these...
Section: Articles about health
Frosty air, fresh wind and easy snowball at most of Russians are associated with cheerfulness, health and cheerful entertainments on which our winter is so generous. But, unfortunately, cold season sometimes brings also troubles with health. It is not about seasonal colds and frostbites, and about those chronic illnesses which symptoms are shown preferential in the winter....
Section: Articles about health
Dark circles (bruises) under eyes – a shortcoming with most of which often fight against the help of cosmetics (proofreaders, salons...
Section: Articles about health
For the time being the perspective of heart diseases seems to most of people remote and foggy. But sooner or later practically each adult faces extremely unpleasant feelings: sudden stethalgia. To be consoled at this time in a thought of t...
Section: Articles about health
Run - one of the most available and effective ways to revitalize the organism. Knowing about its extraordinary advantage, each of us at least once tried to make jogs, but only the few made these occupations regular. In spite of the fact that in jogging (easy jogging), apparently, there is nothing difficult, the beginning runners often make mistakes which lead to complete cessation of trainings. Let's consider 10 useful tips for beginners who will allow them to make regular п...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: all эт...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of the panic attack is known long ago, but the reasons of its emergence still are up to the end not found out. It is established that more than 30% of people at least once in life become the victims of very unpleasant phenomenon: without everyones on that the reasons they have a feeling of horror, with...
Section: Articles about health
80% of women at least once to lives complained of discomfortable feelings to breasts, consolidations and nagrubaniye. These are mastopathy symptoms. The mastopathy is characterized by change of a ratio between ferruterous and connective tissue tissues of mammary glands. It can lead to formation of cysts (a cystous mastopathy), gland consolidation (a fibrous mastopathy), or a combination of these processes (a fibrous and cystous mastopathy)....
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far it already helped znach...
Section: Articles about health
Mushrooms - the surprising inhabitants of our planet having a set of wonderful qualities. Thanks to one of them, a mold mushroom of Penicillium notatum, the first natural antibiotic - penicillin was received nearly 80 years ago. The mankind is obliged to this opening миллио...
Section: Articles about health
Climax - process of fading of reproductive function of an organism in process of its aging. At women the main sign of its approach is the termination of a menstrual cycle. Officially the menopause is diagnosed when periods are not observed within 12 months. Age changes quite often are followed by emotional failures, disturbance of thermal control and sweating, dizzinesses and headaches, tachycardia and other unpleasant phenomena. This complex of symptoms...
Section: Articles about health
The metabolism at each person proceeds in own way. However dependence between the speed of this process and disposal from superfluous in...
Section: Articles about health
Milk and products of its processing by right occupy one of the main places in a diet of the modern person. They contain proteins, necessary for normal life activity, fats, vitamins and microelements, and are an important part of various medical diets....
Section: Articles about health
The cosmetics intended for improvement of a condition of skin, nails and hair are used by each woman. Expenses on regular acquisition of the fashionable widely advertized products of well-known companies for many become very notable and significantly burden the family budget. Meanwhile, there is a number of inexpensive pharmaceutical drugs which can quite be applied in the cosmetic purposes. At the same time the effect of their use is often more noticeable, than result of use of the most expensive...
Section: Articles about health
All know that self-treatment is dangerous. However absolutely it is almost impossible to do without it. Rate of modern life not on...
Section: Articles about health
Obesity is called a disease of 21 centuries, for the last 100 years the number of the people suffering from excess body weight considerably increased. Statistically, on Earth already about 1,5 billion corpulent people, and 500 million from them have extreme degree of completeness, are negative...
Section: Articles about health
From sexual contacts each person can test insufficiently strongly expressed sexual desire or lack of satisfaction from time to time. However when it happens regularly, it is an occasion to think about health. Most of people does not hurry to ask similar questions physicians: one consider that they will be able to cope with malfunctions independently, others hesitate to report to strangers about so delicate problems and hope that troubles will stop by itself....
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – in...
Section: Articles about health
Subfebrile temperature call fervescence to 38 degrees, and subfebrile condition - existence of such temperature over 3 days, and quite often it happens without the visible reasons. Existence of subfebrile condition - a strong indication of disturbances in an organism which can...
Section: Articles about health
Nightmares belong to the most unpleasant frustration. Statistically, they happen at 4% of adults, and almost at 70% of children and teenagers. During a nightmare of people dreams himself in extremely difficult, life-threatening situation. He wakens suddenly, in a condition of a fright, and, as a rule, remembers the dream distinctly. The feeling of depression and alarm does not release throughout the day, creating hindrances for work and normal communication. If such episodes repeat often, can р...
Section: Articles about health
Cystitis, or inflammation of a mucous membrane of a bladder, this very widespread disease, which, owing to some persons...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, can only one of ten of our compatriots brag of a decent condition of an oral cavity. Six teeth affected with caries are the share of the average Russian. For comparison, this indicator for Europeans almost six times exchanges...
Section: Articles about health
EKO, or extracorporal fertilization - a method of treatment of infertility which became the reason of a set of broken-down copies in due time accused the people working on its creation neither more nor less of rivalry good luck. Already very few people deny the right of a method for existence, and to surprise nobody with "children from a test tube". And nevertheless, a certain magic in the procedure of artificial fertilization is, process of origin of new life is always a secret, and even it р now...
Section: Articles about health
