Fracture of base of the skull
The fracture of base of the skull represents the hardest injury which is followed by a fracture of one or several  bones entering foundation of brain department of a skull – occipital, temporal, trellised, wedge-shaped.
bones entering foundation of brain department of a skull – occipital, temporal, trellised, wedge-shaped.
Similar damages statistically meet seldom, making only 4% of number of severe craniocereberal injuries, and voznikayutchashche vseg result of a car accident, falling from the big height, and also strong blows in a nose or a mandible.
The fracture of base of the skull is followed by damage of covers of a brain that causes the expiration of cerebrospinal fluid (liquor) through nasal and oral cavities, an eye-socket, a tympanic cavity. In most cases it leads to emergence of a posttravmaticheskoypnevmotsefaliya - to infection of intracranial contents due to penetration of activators.
Anatomy of a fracture of base of the skull
Fractures of base of the skull are subdivided a napovrezhdeniya of front and back parts of its basis. Injuries of temporal, occipital and back parts of wedge-shaped bones belong to the first type of changes. To the second - fractures of trellised and wedge-shaped bones. The most widespread of them is the fracture of a temporal bone (more than in 75% of cases), depending on an arrangement of the line of damage of rather longitudinal axis of a pyramid of a temporal bone can be cross, longitudinal and mixed.
Fractures of an occipital bone are accompanied by high risk of damage of large blood vessels, nerves and a spinal cord. Damages of cranial nerves are fraught with paralysis of oculomotor and facial nerves or a hearing loss owing to an eighth cranial nerve injury.
Symptoms of a fracture of base of the skull are:
- Bleeding from ears or a nose;
- The expiration of liquor from ears (отоликворея) or a nose (риноликворея);
- Accumulation of blood allocations in a drum cavity;
- Symptom of "points" (so-called, "eyes of a raccoon") - an okologlaznichny ecchymoma;
- Symptom of Bettla-ekhimoz in the field of a mastoid of a temporal bone;
- Vomiting, nystagmus, hearing disorder;
- Vision disorders - in case of jamming by the broken bones of an optic nerve;
- Disturbances of the vital functions: hemodynamics, breath.
Effects of a fracture of base of the skull
The fracture of base of the skull is a most dangerous injury, pernicious both for head, and for a spinal cord as the base of skull is the combining link of all central nervous system of the person. Effects of a fracture of base of the skull can be various, beginning from a small rachiocampsis, frequent 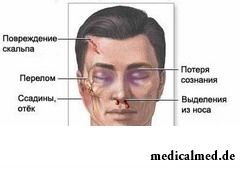 headaches, the increase in arterial pressure which is not giving in to control, finishing with meningitis, encephalitis, full paralysis of a body or death.
headaches, the increase in arterial pressure which is not giving in to control, finishing with meningitis, encephalitis, full paralysis of a body or death.
Quality of life of the victim who transferred a fracture of base of the skull depends on character and weight of a craniocereberal injury, existence of infection of a meninx, the accompanying pathologies.
Treatment of a fracture of base of the skull
Patients have to perform treatment of a fracture of base of the skull in neurosurgical department of hospital. Distinguish conservative and operational methods of treatment. The leading role in a conservative method of treatment is occupied by prevention of intracranial complications for what at once after arrival of the patient in a hospital intravenous, intramuscular, endolumbar or subarachnoidal administration of drugs antibiotics of a broad spectrum of activity is appointed.
In cases of emergence of the pressed getting defeats of a side and front parabasal sine, multisplintered change of a front cranial pole conservative treatment is senseless. Surgical methods also treat a recurrence of an intracranial purulent complication, назальнаяликворея. However in each separate case the decision on need of surgical intervention is made by the experienced neurosurgeon.
Was considered earlier that yawning enriches an organism with oxygen. However this opinion was disproved. Scientists proved that yawning, the person cools a brain and improves its working capacity.

According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but sees a doctor from them меньшинс...
Section: Articles about health
The naturopathy sometimes moves as the new direction of medicine, something like fashionable hobby, and there is nothing farther from the truth. This most ancient direction, the word "naturopathy" is translated as "treatment by the nature", and, no doubt, treatment приро...
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. In the summer repeatedly the risk increases to ache with some very dangerous illnesses, we also will talk about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit and...
Section: Articles about health
Heart disease and blood vessels lead to disturbance of blood supply of bodies and fabrics that involves failures in their work, deterioration in health of the person, decrease in its working capacity and standard of living. Annually such perishes from pathologies more...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads, to slopes of ravines, on heathlands. Also several cultural versions different from wild plants are removed by larger and juicy root crops....
Section: Articles about health
To look healthy and means well-groomed not only to be pleasant to people around, but also to feel strong, sure and taken place. To Spa...
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be studied already up and down, and each person, at least once by it had (and the number of such people in our country aims at 100%), a dolzha...
Section: Articles about health
Tuberculosis – a serious infectious disease which development is caused by mycobacteria (Koch's bacilli). The illness is known from an extreme antiquity. Long time fight against it was considered as ineffective. Quite often the disease affected the whole families, and mortality from it was very high. It became the reason of emergence of a set of delusions concerning transmissibility and a possibility of treatment of tuberculosis....
Section: Articles about health
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) – one of those drugs which are known literally to all. It is available in each home first-aid kit...
Section: Articles about health
Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Most often - owing to yet not strengthened mentality - children are subject to neurosises. Premises to emergence of such disturbances can become нез...
Section: Articles about health
The advantage of swimming for the person is so high that this sport is not only the most popular, but also is widely applied in medicine and rehabilitation processes. If you look for for yourself the occupation allowing pleasantly and to spend time, then swimming with advantage – the fact that it is necessary for you. And give learns several facts about swimming....
Section: Slideshow
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people упот...
Section: Articles about health
History of cultivation of a buckwheat contains more than five thousand years. Grain which is received from this plant is used for preparation of porridges, soups, baked puddings and puddings, do flour which is one of the main ingredients of the noodles popular in of it...
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot" were since ancient times used for strengthening of protective forces of an organism, treatment of avitaminosis, anemia and many other diseases. In recent years wide popularity was gained by the national medicines prepared from pinecones. "Fruits" of a coniferous tree contain a huge amount of vitamins, biologically active agents, antioxidants, phytoncides and other useful to...
Section: Articles about health
Each of us faces from time to time that other people need the immediate help. We react to it on-raznomu:...
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as are afraid that they can do harm to health of children. What troubles can really trap kids and how to make with...
Section: Articles about health
The list of stereotypes of which, apparently, all know strongly includes following: British surely eat porridge for breakfast. Perhaps, not all modern residents of Britain arrive quite so, but for those from them which continue to follow this tradition, it is possible to be glad sincerely: oat flakes are a product which regular use not only helps the person to keep force and beauty long. Porridge in a special way influences an organism, protecting it from seriousness...
Section: Articles about health
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice with 4...
Section: Articles about health
Bathing in broths of medical flowers and plants (phytobathtub) was eurysynusic since Cleopatra who is a good judge in all that concerns beauty and health. And today phytobathtubs is the simple and available means allowing not only to remove nervous N...
Section: Articles about health
About influence of fasting days on an organism it is told much – both about advantages, and about shortcomings. It is considered that fasting day in the form of a short-term monodiet is useful, promoting effective removal of slags from an organism whereas irregular, excessively long, spontaneous fasting days lead only to deterioration in health. How to derive benefit from the sparing diet and not to do much harm to itself? Let's consider the main advantages and shortcomings of fasting days and their influence on an org...
Section: Articles about health
We present to yours the TOP of the medicamentous means exerting the stimulating impact on a potentiality, i.e. on ability of a muzhcha...
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create to it healthy immunity since early years. Nevertheless, this important process in life of mother and child can be saddened laktostazy − by a delay of milts...
Section: Articles about health
(Xerostomia) many people consider feeling of a xerostomia small and easily removable inconvenience. This delusion: the symptom can demonstrate existence of serious diseases. It is worth to remember also that saliva performs important functions in an organism: clears the surface of teeth of a food plaque, growth of pathogenic microorganisms oppresses, normalizes acid-base balance, liquefies food and helps to split the carbohydrates which are contained in it. Chronic deficit слюн...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access appeared with...
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In certain cases inflammatory process is not limited to discomfort, being followed by emergence of hypostasis, consolidations, increase температ...
Section: Articles about health
All the known slogan "Protect Men!" arose not from scratch. In a sense, the nature created men much less adapted for vital disorders, than it seems at first sight. Statistically, men are ill more often, than women, have the majority of illnesses heavier and earlier die. The situation is aggravated with the fact that our fathers, husbands, brothers and sons are not always inclined to care for the health. Partly it happens because of unwillingness of t...
Section: Articles about health