





Spinal cord
Spinal cord – the department of the central nervous system of a backbone representing a cord 45 cm long and 1 cm wide.
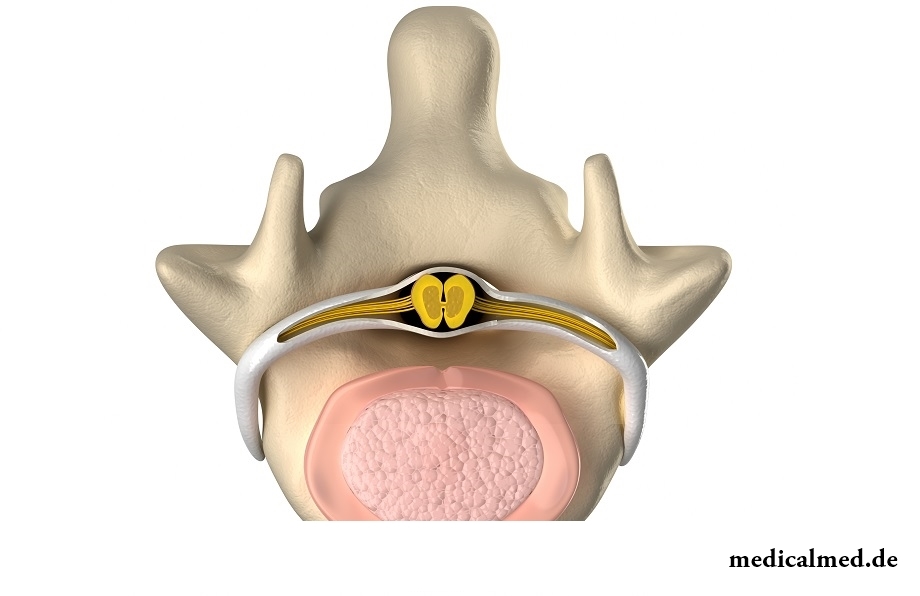
Structure of a spinal cord
The spinal cord in the vertebral channel is located. Behind and in front there are two furrows thanks to which the brain is divided into the right and left half. It is covered with three covers: vascular, web and firm. The space between vascular and web covers is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
In the center of a spinal cord it is possible to see gray matter, on a cut in a form reminding a butterfly. Gray matter consists of motor and internuncial neurons. The periblast of a brain represents white matter of the axons collected in the descending and ascending conduction paths.
In gray matter distinguish two types of horns: lobbies in which there are motor neurons, and back, the location of internuncial neurons.
In a structure of a spinal cord contain 31 segments. From everyone ventral and back roots which, merging, form a spinal nerve last. At an exit from a brain nerves at once break up to roots – back and front. Back roots are formed by means of axons of afferent neurons and they are sent to back horns of gray matter. In this place they form synapses with efferent neurons whose axons form ventral roots of spinal nerves.
In back roots there are spinal nodes in which sensory nervous cells are located.
On the center of a spinal cord there passes the spinal channel. To head muscles, lungs, heart, bodies of a chest cavity and upper extremities nerves depart from segments of an upper chest and cervical part of a brain. Segments of lumbar and chest parts manage abdominal organs and muscles of a trunk. Sacral and nizhnepoyasnichny segments of a brain manage muscles of the lower part of an abdominal cavity and muscles of the lower extremities.
Functions of a spinal cord
Two main functions of a spinal cord are known:
- Conduction;
- Reflex.
Conduction function consists that nervous impulses on the ascending ways of a brain move to a brain, and on the descending ways from a brain to working bodies teams arrive.
Reflex function of a spinal cord is that it allows to carry out the elementary reflexes (knee a reflex, otdergivany hands, bending and extension of upper and lower extremities, etc.).
Under control of a spinal cord only simple motive reflexes are carried out. All other movements, such as walking, run, etc., demand obligatory participation of a brain.
Pathologies of a spinal cord
If to proceed from origins of pathologies of a spinal cord, it is possible to allocate three groups of his diseases:
- Malformations – puerperal or inborn deviations in a brain structure;
- The diseases caused by tumors, neuroinfections, disturbance of spinal blood circulation, hereditary diseases of a nervous system;
- Injuries of a spinal cord to which injuries and fractures, squeezings, concussions, dislocations and hemorrhages belong. They can appear as it is autonomous, and in combination with other factors.
Any diseases of a spinal cord have very serious effects. It is possible to carry injuries of a spinal cord which statistically can be divided into three groups to special type of diseases:
- Road accidents – are the most common cause of injuries of a spinal cord. Driving of motorcycles as there is no back back of sitting protecting a backbone is especially injury-causing.
- Falling from height – can be both accidental, and intentional. Anyway, the risk of injury of a spinal cord is rather high. Often athletes, fans of extreme sports and jumps from height receive injuries in such a way.
- Home and extraordinary accidents. Often they result from descent and falling in the unsuccessful place, falling from a ladder or at ice. Also it is possible to carry knife and bullet wounds and many other cases to this group.
At injuries of a spinal cord first of all conduction function is broken that leads to very deplorable effects. So, for example, injury of a brain to cervical department leads to the fact that functions of a brain remain, but lose bonds with most bodies and muscles of a body that leads to body paralysis. The same frustration arise at damage of peripheral nerves. If sensory nerves are damaged, then sensitivity is broken in certain body parts, and damage of motor nerves breaks the movement of certain muscles.
The majority of nerves have the mixed character, and their damage causes at the same time both impossibility of the movement, and an anesthesia.
Puncture of a spinal cord
The spinal puncture consists in introduction to a subarachnoid space of a special needle. The puncture of a spinal cord in special laboratories where define passability of this body is carried out and measure liquor pressure. The puncture is carried out as in the medical, and diagnostic purposes. It allows to diagnose timely existence of hemorrhage and its intensity, to find inflammatory processes in a meninx, to define the nature of a stroke, to define the changes in character of cerebrospinal liquid signaling about diseases of the central nervous system.
Often the puncture is done for administration of X-ray contrast and medicinal liquids.
In the medical purposes the puncture is carried out for the purpose of extraction of blood or purulent liquid, and also for introduction of antibiotics and antiseptic agents.
Indications to a puncture of a spinal cord:
- Meningoentsefalita;
- Unexpected hemorrhages in a subarachnoid space owing to a rupture of aneurism;
- Cysticercosis;
- Myelites;
- Meningitis;
- Neurosyphilis;
- Craniocereberal injury;
- Liquorrhea;
- Echinococcosis.
Sometimes when carrying out operations on a brain use a puncture of a spinal cord for decrease in parameters of intracranial pressure, and also for simplification of access to malignant new growths.
Caries is the most widespread infectious disease in the world to which even flu cannot compete.

For most of the working people the problem of having a snack is particularly acute enough. Sooner or later there is a question: what is possible quickly for a sja...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and the strengthened reproduction of this microorganism lead to weakening of protection of mucous membranes and their erosive damage. Manifestations not...
Section: Articles about health
Childbirth is the most important event in life of each woman. We are women we give birth to the new little man on this light. Now the tendency to that was outlined, as men want to participate in labor too. But there is a question and whether it is worth allowing the husbands on childbirth?...
Section: Articles about health
Dark circles (bruises) under eyes – a shortcoming with most of which often fight against the help of cosmetics (proofreaders, salons...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of use of table salt in the therapeutic purposes contains not one century. Applications which do by means of the fabric impregnated with saline solution are considered especially effective. They have antibacterial and antiinflammatory effect, help to heal wounds, exempt fabrics from excess liquid. Hypertonic salt solution of potassium chloride is applied outwardly at many morbid conditions. Let's tell about the most known of them....
Section: Articles about health
Striya (extension) are the defects of skin having an appearance of direct or wavy strips from 1 to 10 cm long and 1-5 mm wide. In the majority with...
Section: Articles about health
Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only the food sating an organism but also the medicines curing of many diseases. Unfortunately, having given the use of some of them...
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In certain cases inflammatory process is not limited to discomfort, being followed by emergence of hypostasis, consolidations, temperature increase. At the wrong treatment the acute miositis can lead to a chronic disease or aggravation of other pathologies of a back (vertebral hernia, osteochondrosis) therefore it is important to pay attention to symptoms of an illness in time and to start to...
Section: Articles about health
The sudden heat on all body which is followed by perspiration and a cardiopalmus – the phenomenon familiar to many people. Most often t...
Section: Articles about health
Popular joke that there are no healthy people, and is nedoobsledovanny, most of us considers an honest truth, continually it is necessary to hear that all of us are sick hardly from a school bench. It is hard to say, whether so it actually because...
Section: Articles about health
About influence of fasting days on an organism it is told much – both about advantages, and about shortcomings. It is considered that fasting day in the form of a short-term monodiet is useful, promoting effective removal of slags from an organism whereas irregular, excessively long, spontaneous fasting days lead only to deterioration in health. How to derive benefit from the sparing diet and not to do much harm to itself? Let's consider the main advantages and shortcomings of fasting days and their influence on an org...
Section: Articles about health
Kidneys perform the most important function of clarification of blood from those products of metabolic processes which cannot be used орг...
Section: Articles about health
Among a set of the perfumery and cosmetic goods which are released today the special group is made by the means containing antibacterial components. Such types of gels, shampoos, soaps, creams, lotions and other products are positioned by manufacturers as a panacea...
Section: Articles about health
There is a lot of fans of beer in our country. Statistically, on each average Russian (including women and children) in a year about 60 liters of this drink are consumed. It is not a lot of, as in the Czech Republic or Germany, but figure all the same impressive. There is nothing to rejoice here: despite assurances of producers that beer is absolutely harmless, effects of its active consumption cannot be considered positive in any way. Here only part of that negative impact, which popular нап...
Section: Articles about health
Hemorrhoids – extremely widespread disease. Periodically arising inflammations and bleeding of hemorrhoidal nodes пр...
Section: Articles about health
Tea is loved and use almost everything. This drink has tonic properties, contains the tannins capable to suppress activity of causative organisms. Recently great popularity was gained by teas with vegetable additives. Лечеб...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is valuable medicinal raw materials. A, C and E vitamins, organic acids, tannins, wax, saponins, lipids, mineral salts and essential oils are its part....
Section: Articles about health
The popular expression "run from a heart attack" became the motto of the people supporting active lifestyle. Moreover, run became peculiar...
Section: Articles about health
You are office worker, the driver, the fan of winter sports or do not think of life without bicycle? You lead a slow-moving life and you move on the city only on the car? You have no constant partner and you do not love the protected sex? Attention! You one...
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as are afraid that they can do harm to health of children. What troubles can really trap kids and how to make joint life of a family and domestic animals comfortable and safe?...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs п...
Section: Articles about health
The problem of diagnosis was and remains to one of the most important in medicine. From that, the reason of an indisposition of the patient will be how precisely defined, eventually success of treatment depends. In spite of the fact that the majority of the diagnostic methods applied in about...
Section: Articles about health
The thought that the mass of their body is too big at least once in life visits from 80 to 95% of women. Many women are so obsessed with this idea that constantly try all new and new ways of weight reduction. A considerable part of these techniques is ineffective, and some in general are unsafe for health....
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters in any...
Section: Articles about health
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that the plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those who incorrectly eat smokes and badly brushes teeth. But the paradox is available: at everything the variety of toothpastes existing today...
Section: Articles about health
For many women the word "fat" sounds as a sentence. In aspiration to an ideal figure they try to exclude, first of all, from the menu all dishes containing fats without having at the same time a clear idea of a role of these substances in exchange processes, and of effects for health with which food restrictions of this sort are fraught. For what the human body needs fats and as their deficit in a diet is shown, we also will try to find out....
Section: Articles about health
