





Anesthesia I
Anesthesia I (anesthesia; an-– otritsa. a prefix + Greek aisthesis – feeling, feeling) – lack of painful, temperature, tactile and other sensitivity.
Allocate the following types of anesthesia:
- Dissociated (dissociata) – is characterized by lack of temperature and painful sensitivity at preservation proprioceptive or on the contrary;
- Hysterical (hysterica) – occurs at patients with hysteria, is characterized by lack of organic lesions of receptors, conduction paths and the centers of a nervous system; as a rule, extends to areas of a body which borders do not correspond to zones of an innervation of certain nerves or roots;
- Radicular (radicularis) – total anesthesia in a zone of an innervation of a certain back root of a spinal cord;
- Leprose (leprosa) – occurs at patients with a leprosy, arises because of specific damage of skin receptors; it is characterized by consecutive easing and loss at first temperature, then painful and, at last, tactile sensitivity at long preservation of proprioceptive;
- Partial (partialis) – is characterized by lack of one or several types of sensitivity at preservation of the others;
- Segmented (segmentalis) – the total or dissociated anesthesia in a zone of an innervation of a certain segment of a spinal cord;
- Total (totalis) – is characterized by lack of all types of sensitivity;
- Traumatic (traumatica) – arises because of damage of the centers of a nervous system and/or sensory nerves.
The well-known drug "Viagra" was initially developed for treatment of an arterial hypertension.

Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. To a Torah...
Section: Articles about health
Striya (extension) are the defects of skin having an appearance of direct or wavy strips from 1 to 10 cm long and 1-5 mm wide. In most cases at women of a striya are located on a stomach, hips, a breast or buttocks. At athletes they can appear on shoulders and внутренн...
Section: Articles about health
History of cultivation of a buckwheat contains more than five thousand years. Grain which is received from this plant is used for preparation of porridges, soups, baked puddings and puddings, do flour which is one of the main ingredients of the noodles popular in many countries of it. Buckwheat dishes are useful and tasty, they are perfectly combined with meat, milk, eggs, mushrooms, fruit and vegetables....
Section: Articles about health
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) – one of those drugs which are known literally to all. It is available in each home first-aid kit...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and the strengthened reproduction of this microorganism lead to weakening of protection of mucous membranes and their erosive damage. Manifestations not...
Section: Articles about health
The naturopathy sometimes moves as the new direction of medicine, something like fashionable hobby, and there is nothing farther from the truth. This most ancient direction, the word "naturopathy" is translated as "treatment by the nature", and, no doubt, treatment by natural gifts was the first and only, available to the person in ancient times. Despite modern achievements of medicine, the naturopathy remains urgent and today, anyway the person - a part of the nature, and природн...
Section: Articles about health
Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. Exists even so-called died away...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing an optimum set of nutrients, and which is best adapted in order that the baby normally developed and it was protected from harmful fa...
Section: Articles about health
Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary to minimize. There is a number of rules, following to which will help or to avoid absolutely infection with flu or a SARS, or to have an illness benign and without essential complications. About ways of prevention of seasonal infections the speech in this article will also go....
Section: Articles about health
The stroke is one of the most widespread diseases of the person, annually in the world about 6 million cases эт are registered...
Section: Articles about health
Tick-borne encephalitis – one of the most dangerous viral diseases which causative agents transfer and is given to people by ixodic mites. These are the small blood-sicking insects living in the considerable territory of our country. The person bitten by a tick can catch...
Section: Articles about health
Life of the modern woman is very difficult. Opportunities to realize itself are wide: it not only education and career, but also the most various hobbies from sport before needlework. It is not less important to build private life, paying an attention maximum to children, the husband, parents, friends. For all these affairs there is catastrophically not enough time therefore each of us tries to cut down as far as possible its expenses on necessary, but not the most fascinating housework. With it we are successfully helped by means...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot replace completely modern synthetic drugs, but their use becomes frequent serious help in simplification of a course of many illnesses and improvement of quality of life of chronic patients....
Section: Articles about health
According to World Health Organization, every third inhabitant of Earth has excess weight, and every tenth suffers ожирен...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
The mankind knows that some toxins at intake in the minimum quantities have therapeutic effect from an extreme antiquity. Many substances recognized poisonous are applied in the medical purposes also today, being the main operating components of the medicines which are officially produced by pharmaceutical industry. Let's tell only about the most known of them....
Section: Articles about health
Each woman has preferences in the field of use of those goods which help us to look good, feel се...
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. Summer...
Section: Articles about health
To look healthy and means well-groomed not only to be pleasant to people around, but also to feel strong, sure and taken place. Specialists in the field of cosmetology quite often note that not all women are able to look after face skin. Many women incorrectly apply cosmetics, ineptly use various procedures, without having exact information on their real influence and dividing numerous delusions about it. All this not the best...
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even at the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching з...
Section: Articles about health
Run - one of the most available and effective ways to revitalize the organism. Knowing about its extraordinary advantage, each of us at least once tried to make jogs, but only the few made these occupations regular. In spite of the fact that in jogging (easy an ozdor...
Section: Articles about health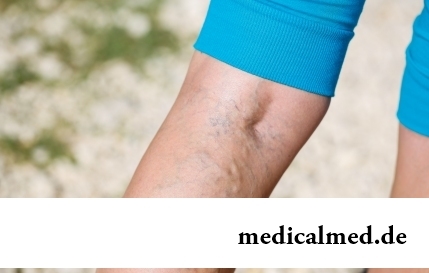
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As a rule, the varicosis affects preferential superficial vessels, and is shown by characteristic cosmetic defects. The deep vein thrombosis as this illness at the initial stages can imperceptibly proceed is represented much more dangerous, and in the started cases threatens with serious danger – thrombosis. This state, when the blood clot formed...
Section: Articles about health
Each person knows that fervescence is an illness sign. However about existence of diseases can to suite...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it receive only useful substances, necessary vitamins and microelements. In this case there will be no problems with digestion, with лишн...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance of physical, psychological and moral health of the person by means of the complex of procedures including a diet, cleaning of an organism, breathing exercises, massage, and in case of a disease - and medicinal therapy. The healers practicing Ayurveda assign very important part to spices, and at the heart of Ayurvedic drugs, as a rule, there are they. It is considered that spices not of t...
Section: Articles about health


