





Vitamin K
Vitamin K – fat-soluble vitamin. This vitamin stocks up in small doses in a liver, has property to collapse on light and in alkaline solutions. Vitamin K in 1935 was discovered by the Danish scientist Henry Damme. For the opening it received the Nobel Prize. Damme found out that vitamin is important for coagulation (blood coagulation) owing to what it also received a letter k.

In the nature vitamins of group K are presented by two forms:
- Vegetable phylloquinone (k1);
- Bacterial менахинон (k2).
Phylloquinone regulates processes of a blood coagulation in an organism, accelerates healing of wounds and stops bleeding. It is extremely necessary for ensuring full activity of cells of a liver. In case of shortage of vegetable phylloquinone production of many components of blood participating in coagulation processes decreases, permeability of capillaries increases.
Disturbance of its absorption in digestive tract owing to disturbances in gepatobiliarny system or because of intestines diseases is the main reason for deficit of phylloquinone at the person.
Shortage of vitamin at small children leads to a hemorrhagic disease.
The alimentary factor does not play an essential role in formation of a vitamin deficiency of group K. It is connected with their prevalence in foodstuff, and also high resistance to heat treatment.
Vitamin K role for an organism
Vitamin K is enzimovitaminy, gormonovitaminy and antioxidant. It is important for a blood coagulation. It is at the moment proved that process of a blood coagulation demands presence of at least 10 active proteins, synthesis 5 of which directly depends on presence at an organism of vitamins of group K.
Vitamin is necessary for a liver for production of a prothrombin (the substance helping formation of blood clots), stops internal bleedings. Besides, vitamin helps to hold calcium as a part of a bone tissue.
Lack of vitamin K of an organism
The only documentary confirmed symptom of shortage of vitamin is the hemorrhage (free bleeding).
In normal conditions deficit of vitamin K at the person is almost impossible as intestines bacteria constantly make it in small amounts which come directly to a blood stream. In addition, vitamin is present at many vegetable products.
Nevertheless, as vitamin K is fat-soluble, for its normal assimilation at intestines there has to be a small amount of fat.
Hypovitaminosis can be caused:
- Disbioz of intestines (for example, after treatment by streptocides and antibiotics);
- Lack of the bile acids necessary for digestion of fat-soluble vitamins (for example, at pathology of biliary tract or a liver);
- Poisoning with antivitamins k (cephalosporins of the third generation, coumarinic anticoagulants).
It is possible to meet a hypovitaminosis at newborns when for the 2-4th days of life bleeding from the umbilical rest, a melena, a metrorrhagia, and appears in especially hard cases – hemorrhage in a liver, adrenal glands, a brain, lungs. It is caused by the fact that at newborns intestines are sterile, that is vitamin K is not synthesized by microflora.
In spite of the fact that women's milk contains not enough this vitamin, breastfeeding is capable to provide the child with maternal factors of coagulation and to reduce risk of development of a hemorrhagic disease of newborns.
Today in most hospitals the newborn right after the birth enter vitamin B a type of injections for deficit prevention.
Excess of vitamin K
Even at excessive reception of vitamin toxic side effects meet extremely seldom.
Administration of vitamin B to a synthetic form can lead to yellowing of eyes and skin, to increase in bilirubin in blood, hemolitic anemia.
Daily need for vitamin K
The adult healthy person needs daily consumption of 120 mkg of vitamin. At dietary food requirement makes from 0,12 to 0,36 mg a day.
Food sources
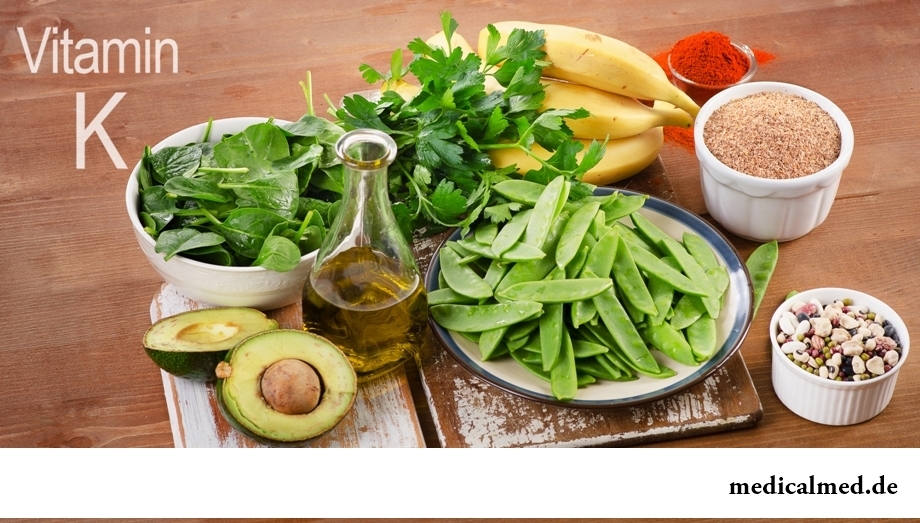
The main food sources of vitamin K are: Bruxelles and cauliflower, salad, spinach, vegetable marrows, oats, cheese, eggs, oil, beet, peas, potatoes, tomatoes, peaches, oranges, wheat, corn, bananas, carrots, fresh parsley, green tea.
In a small amount vitamin contains in nettle leaves, stigmas of corn, cereals, milk, a carrot tops of vegetable, mountain ash fruits, a yarrow.

The drugs containing vitamin K
Medicine as a part of which there is a vitamin is Vikasolum.
Interaction
Excessive reception of calcium is capable to influence vitamin synthesis, worsens its comprehensibility and can cause internal bleeding.
Excessive reception of vitamin E (about 2200 ME a day) reduces digestion of vitamin K from digestive tract.
In our intestines are born, millions of bacteria live and die. They can be seen only at strong increase, but if they gathered, then would be located in a usual coffee cup.

There is an opinion that at low temperatures safety of products is ensured longer and better thanks to what the refrigerator considers...
Section: Articles about health
The medicine promptly develops, and the fact that else quite recently it seemed by miracle can now. We are not surprised any more to the fact that people with artificial joints and extremities can play sports, organ transplantation became a routine, and the latest cancer medicine п...
Section: Articles about health
According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but the minority sees a doctor from them. And in vain - even the insignificant discomfort in the field of generative organs can serve as a symptom of an illness fraught with grave consequences for health. So - after 40 years - it is easy for most widespread disease of the sexual sphere of men to pass the first symptoms of prostatitis (weight in the bottom of a stomach, decrease in a libido), having written off for overfatigue and fatigue. Let's consider...
Section: Articles about health
Health and attractiveness - eternal values, pursuing which people often use the most unusual ingredients and technicians...
Section: Articles about health
Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. There is even a so-called gastronomic tourism which, according to gourmets, not only allows to receive new feelings, but also is capable to show life the friend...
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number of myths about negative effect which allegedly gluten has on health of the person....
Section: Articles about health
Radiological methods of a research are applied in medicine more than hundred years, and thanks to them millions of lives were saved. In m...
Section: Articles about health
An eye of the person daily experiences considerable strain. The problem of preservation of sight is for many years directly connected with a question of supply of tissues of eye enough oxygen and nutrients. This task is carried out by small vessels – capillaries. For holes...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly ways of storage and transportation of food ingredients changed, and people of the whole world had an opportunity to regularly use those products about which their grandfathers and grandmothers did not even know....
Section: Articles about health
Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Nye...
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear are similar, however if the fear is natural protective function of mentality, then the phobia is its deviation. So the person can an ispytyva...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot replace completely modern synthetic drugs, but their use becomes frequent serious help in simplification of a course of many illnesses and improvement of quality of life of chronic patients....
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also contain...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which not only facilitate house work, but also help to keep health of the person? Of course, and we will tell about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Striya (extension) are the defects of skin having an appearance of direct or wavy strips from 1 to 10 cm long and 1-5 mm wide. In most cases at women of a striya are located on a stomach, hips, a breast or buttocks. At athletes they can appear on shoulders and the internal surface of forearms. At initial stages of development of an extension have red or lilac color, but over time their coloring turns pale, and strips become whitish, getting a nacreous shade....
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be study...
Section: Articles about health
The words "disease" and "patient" not without reason come from one root – "pain". As a rule, symptoms of illnesses thoroughly spoil to patients life. However from this rule there are exceptions. Some diseases are shown by signs which can cause even полож...
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some methods of treatment consecrated with "century national experience" can work so on the patient that it will need urgent intervention of physicians....
Section: Articles about health
Quite large number of people adheres to the principles of vegetarian food. But how to be if in a family of vegetarians is д...
Section: Articles about health
The mankind knows that some toxins at intake in the minimum quantities have therapeutic effect from an extreme antiquity. Many substances recognized poisonous are applied in the medical purposes also today, being the main deystvuyushch...
Section: Articles about health
Milk and products of its processing by right occupy one of the main places in a diet of the modern person. They contain proteins, necessary for normal life activity, fats, vitamins and microelements, and are an important part of various medical diets....
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to spread...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include...
Section: Articles about health
Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times medicinal properties of honey and other substances received in the course of beekeeping are known. The fact that all these products are recognized not only national, but also official medicine is especially significant. About influence and routes of administration of bee "drugs" the speech in this article will also go....
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: all эт...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, at the address to doctors seven of each ten patients complain of a headache. Actually it is much more people who are periodically feeling unpleasant feelings such. Many people, apart from a headache the reason for serious fear...
Section: Articles about health
The stroke is one of the most widespread diseases of the person, annually in the world about 6 million cases of this pathology are registered. According to medical statistics, strokes occur almost three times more often than myocardial infarctions. The disease belongs to heavy, and has an unfavourable result: the lethality reaches 40% among women and 25% among men. A considerable part of the patients who endured a stroke cannot be recovered completely. We suggest readers to examine...
Section: Articles about health
