Aortal stenosis
The aortal stenosis, or stenosis of the mouth of an aorta – the inborn or acquired disease which is characterized by narrowing of the taking-out path of a left ventricle in the field of the aortal valve which provokes difficulty of outflow of blood from a left ventricle and also promotes sharp increase of a pressure gradient between an aorta and a ventricle.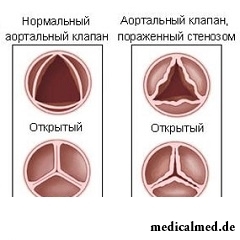
Types and reasons of an aortal stenosis
Distinguish three types of an aortal stenosis:
- valve (inborn or acquired);
- nadklapanny (only inborn);
- subvalvular (inborn or acquired).
Are the main reasons for the acquired aortal stenosis:
- aorta atherosclerosis;
- degenerative changes of valves with their subsequent calcification;
- rheumatic defeat of valve shutters (most common cause of a disease);
- infectious endocarditis.
Rheumatic defeat of valve shutters (rhematoid endocarditis) provokes reduction of shutters of the valve, as a result they become rigid and dense, as is the reason of narrowing of a valve opening. Calcification of the aortal valve which promotes a bigger reduction of mobility of shutters is quite often observed.
At an infectious endocarditis the similar changes leading to development of an aortal stenosis are observed. Often the system lupus erythematosus and a pseudorheumatism become the reasons of formation of a disease.
Atherosclerosis of an aorta is followed by the expressed degenerative processes, a sklerozirovaniye, rigidity and calcification of shutters of a fibrous valve ring that also promote difficulty of outflow of blood from a left ventricle.
Sometimes elderly people have the reason of an aortal stenosis primary and degenerative changes of the valve. This phenomenon received the name "idiopathic calcific stenosis of the mouth of an aorta".
The inborn aortal stenosis results from defects and anomalies of development of the valve. At late stages of a course of a disease the expressed calcification which aggravates the course of a disease joins symptoms of an aortal stenosis.
Thus, at all patients on a certain degree of an aortal stenosis, irrespective of an origin, deformation of the aortal valve and the expressed calcification is observed.
Symptoms of an aortal stenosis
Depending on degree of an aortal stenosis, patients can not feel any discomfort throughout a long time, i.e. for a long time the disease has no symptoms.
At the expressed narrowing of a valve opening patients begin to complain of emergence of attacks of stenocardia, bystry fatigue and weakness at exercise stresses, faints and dizzinesses at bystry change of position of a body, an asthma. In especially hard cases a symptom of an aortal stenosis are suffocation attacks (a fluid lungs or cardiac asthma).
Patients with the isolated stenosis of the mouth of an aorta can have complaints connected with emergence of signs of right ventricular insufficiency (weight in right hypochondrium, hypostases). There are these symptoms of an aortal stenosis at the considerable pulmonary hypertensia caused by defects of the mitral valve in combination with an aortal stenosis.
At the general survey of the patient it observes characteristic pallor of integuments.
Diagnosis of an aortal stenosis
The main methods of tool diagnosis of an aortal stenosis are:
- ECG;
- X-ray analysis;
- Echocardiography;
- Heart catheterization
Treatment of an aortal stenosis
At heavy degree of an aortal stenosis drug treatment is, as a rule, inefficient. The only radical method of treatment is prosthetics of the aortal valve. After manifestation of symptoms of a disease chances to survive without carrying out operation sharply are reduced. On average, patients after manifestation of such symptoms as heartaches, left ventricular failure signs, faints, live no more than five years.
After installation of the diagnosis "the stenosis of the aortal valve" to the patient surely is recommended by preventive measures from an infectious endocarditis.
At an asymptomatic aortal stenosis drug treatment is directed to maintenance of a sinoatrial rate, prevention of an ischemic heart disease and normalization of the ABP.
After emergence of complaints at impossibility of carrying out operation appoint drug treatment. So, in the presence of heart failure by means of medicines try to eliminate stagnation in a small circle of blood circulation by means of reception of diuretics. However their too active use can promote development of an excess diuresis, a hypovolemia and arterial hypotonia. At systolic dysfunction of a left ventricle as symptomatic means appoint Digoxin, especially at a ciliary arrhythmia.
At an aortal stenosis vazodilatator as their use can lead to faints are contraindicated to the patient. However at heavy heart failure careful introduction of Sodium nitroprussidum is allowed.
At an inborn aortal stenosis at children aortal balloon valvuloplasty can be applied. This method allows to lower the maximum transvalve gradient by 65%, however preferential this technique demands repeated operation for 10 years. After carrying out valvuloplasty at patients aortal insufficiency can develop.
The most effective treatment of an aortal stenosis is the surgical method of prosthetics of the valve of an aorta. Prosthetics of the valve of an aorta is shown at heavy degree of an aortal stenosis in the following cases:
- existence of faints, stenocardia or heart failure;
- in combination with coronary shunting;
- in combination with operations on other valves.
The surgical method of treatment of an aortal stenosis significantly improves health of the patient and the forecast of survival. It with success can be seen off even at patients of old age without risk of development of heavy pathologies. For prosthetics use autografts, allogenic prostheses, allotransplants, mechanical prostheses or pork bioprostheses and prostheses from a bull pericardium.
In the aspiration to pull out the patient, doctors often go too far. So, for example, a certain Charles Janszen during the period from 1954 to 1994 endured more than 900 operations on removal of new growths.

Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. In opinion д...
Section: Articles about health
80% of women at least once to lives complained of discomfortable feelings to breasts, consolidations and nagrubaniye. These are mastopathy symptoms. The mastopathy is characterized by change of a ratio between ferruterous and connective tissue tissues of mammary glands. It can bring...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep look youth for many years and what procedures are offered for achievement of this purpose by cosmetologists? And maybe, the only option of rejuvenation is surgery – a blepharoplasty? Let's try to understand this question....
Section: Articles about health
Life activity of one-celled fungi of the sort Candida is a proximate cause of development of candidiasis (milkwoman), it is related...
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. However for nonspecialists this disease remains to not less mysterious, than in the ancient time. Many delusions are connected with epilepsy...
Section: Articles about health
Each woman has preferences in the field of use of those goods which help us to look good, feel young and effective. Besides: selection process of favourite perfume, shampoo or decorative cosmetics already lightens the mood and serves as a peculiar stress medicine. Happens very offensively when the acquired perfumery and cosmetic products not only do not meet our expectations, but also becomes the reason of problems with health. Sources неприятн...
Section: Articles about health
Dogrose – one of the most widespread adornment and medicinal plants growing practically in all territory ours...
Section: Articles about health
All got used long ago that, having addressed the plastic surgeon, it is possible to modify natural parameters of a figure or to minimize the damages put to appearance with ruthless time. Many people (preferential women) worldwide е...
Section: Articles about health
Sometimes it seems that modern society was divided into two camps: representatives of the first are sure that only the woman has to be responsible for contraception, representatives of the second, respectively, are sure that it is destiny of men. Meanwhile the question of contraception has very many aspects – both psychological, and legal and, of course, medical....
Section: Articles about health
Partial and the more so full loss of hearing significantly reduces quality of life. Difficulties with communication lead to loneliness and замкн...
Section: Articles about health
One of the major chemical processes happening in a human body are oxidation reactions. They go with participation of fats and carbohydrates which we receive from food, and the oxygen getting to us from air. A main goal of such reactions is it is received...
Section: Articles about health
Mushrooms - the surprising inhabitants of our planet having a set of wonderful qualities. Thanks to one of them, a mold mushroom of Penicillium notatum, the first natural antibiotic - penicillin was received nearly 80 years ago. The mankind is obliged to this opening by millions of saved lives....
Section: Articles about health
The name of this disease precisely reflects the problem reason: it consists in the bra fastener pressure upon a certain zone...
Section: Articles about health
The pancreas performs two functions in a human body: release of enzymes without which digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, and a producing hormones is impossible. The most important of them - insulin, is the main participant of carbohydrate metabolism, a normal...
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot" were since ancient times used for strengthening of protective forces of an organism, treatment of avitaminosis, anemia and many other diseases. In recent years wide popularity was gained by the national medicines prepared from pinecones. "Fruits" of a coniferous tree contain a huge amount of vitamins, biologically active agents, antioxidants, phytoncides and other useful to...
Section: Articles about health
The metabolism at each person proceeds in own way. However dependence between the speed of this process and disposal from superfluous in...
Section: Articles about health
It is impossible to imagine human life in which there would be no plants. Practically in each apartment and any production room there are window plants, millions of people with pleasure are engaged in gardening and truck farming, many citizens пр...
Section: Articles about health
No, probably, the person who would not have cold. Cold, cough, a headache – these symptoms are known to everyone. The peak of catarrhal diseases is the share of fall. SARS already came to schools and kindergartens, flu slowly makes the way to the cities, in a word, winter close!...
Section: Articles about health
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that a plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and the strengthened reproduction of this microorganism lead to weakening of protection of mucous membranes and their erosive damage. Manifestations not...
Section: Articles about health
On the head of the person about one million hair follicles, or as they are called still, hair bulbs are located. At the time of the birth most of them is in the "sleeping" state, but within several weeks follicles become more active, and from them hair begin to grow. Intensity of this process is individual, and during life it can change. Genetic predisposition, a physical and emotional state, aggressive influence affects the growth rate of hair out of...
Section: Articles about health
Bulimia and anorexia, are heavy deviations of a feeding behavior, become a cause of death of patients much more often than all others...
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far he already helped a significant amount of married couples to become happy parents. Usually to the EKO procedure difficult and very expensive, resort in those...
Section: Articles about health
Doctors claim that the people not so familiar with a dorsodynia occur among adult Russians very seldom. At the same time the vast majority of the patients who are periodically testing this indisposition do not hurry to ask for medical care at all. On the one hand, there is an opinion that feelings of this sort at mature age are nearly natural phenomenon which is not doing serious harm to health. With another – practice of self-treatment various obezbol is eurysynusic...
Section: Articles about health
Bathing in broths of medical flowers and plants (phytobathtub) was eurysynusic since Cleopatra who is a good judge of everything...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of improvement of a condition of the patients at administration of drugs who are not containing active agents, so-called effect of placebo is known long ago. At the end of the 18th century the American doctor Perkins began to treat people the "miracle" sticks made of a spl...
Section: Articles about health
The way of life of people promptly changes from year to year: if about ten years ago the personal computer was not in each family, then today already very few people do without this device. Certainly, and children master the computer at full speed: they not only play on it games, but also study, and write school works, and search for necessary information....
Section: Articles about health