





Ulitis
What is an ulitis
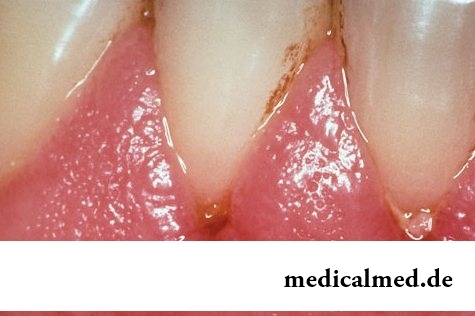
The official medical statistics demonstrates that more than 70% of the population of our country in a varying degree suffer from bleeding of gums. One of the most common causes of such state is the ulitis – the inflammatory disease which is followed by hypostasis and bleeding of gums. The ulitis at children and adults arises owing to activity of bacteria which active reproduction leads to emergence of irritation and development of inflammatory process. In the absence of treatment the disease progresses and causes more serious effects, for example, the periodontal disease fraught with loss and denture treatment.
The most probable cause of emergence of an ulitis – an unsatisfactory condition of an oral cavity, non-compliance with elementary rules of hygiene. Besides, the disease is provoked by some drugs, low immunity, malocclusion and mechanical injuries of gums. Regardless of the reasons for which the ulitis appeared treatment of a disease has to begin as soon as possible. Urgency of medical actions it is connected both with danger of development of a periodontal disease, and with the fact that the ulitis can be only a sign of a general disease (avitaminosis, a diabetes mellitus, herpes, an allergy, a leukopenia). Respectively, the reason of an inflammation of gums will be established quicker, the chance to avoid serious consequences is higher.
Ulitis – disease symptoms
Manifestations of an ulitis depend on a disease form. Today the catarral ulitis which has the following symptoms is most widespread:
- unpleasant feelings in gingivas;
- smell from a mouth;
- decrease in sensitivity of flavoring receptors;
- bleeding of gums during toothbrushing or meal;
- gingiva hypostasis;
- the increased maintenance of a dental plaque.
This form of a disease is characterized by existence of the periods of an aggravation and remission. The general condition of patients changes slightly, however, during an aggravation the catarral ulitis can cause feeling of an indisposition and subfebrile temperature. Let's note also that the acute catarral ulitis which symptoms are shown during the periods of eruption and change of teeth differs in pronounced symptoms of a disease, but will well respond to treatment. The chronic form is more dangerous as inflammation symptoms are practically absent, so – treatment begins already when bacteria lead to development of a periodontal disease and other diseases of an oral cavity.
Hypertrophic ulitis – chronic inflammatory process which snips off frontal sites of both jaws and nearby soft tissues. In certain cases the hypertrophic ulitis at children is the only early symptom of disturbances of endocrine system and diseases of blood therefore it is worth treating its manifestations with all possible gravity. Characteristic signs of this form are:
- essential increase in the sizes of a gingiva;
- the itch, bleeding and pain amplifying at meal;
- unpleasant smell from a mouth;
- existence of a plaque, strongly accrete with teeth.
At easy forms of an ulitis symptoms are expressed poorly. Patients practically do not show complaints or complain only not unusual increase in a gingiva. The pronounced signs of an inflammation which are followed by severe pains are characteristic of average and heavy forms.
The ulocace (ulcer and necrotic ulitis) – is a consequence of an undertreated catarral form. Are characteristic of the initial stages of a disease: itch, hypostasis of gums, easy bleeding. Then the ulocace leads to emergence of the necroses and ulcerations covered with a gray or dirty-green plaque. Patients feel severe pain at meal, a putrefactive smell from a mouth, complain of the raised department of viscous saliva and a sleep disorder.
Ulitis – treatment of a disease
As the catarral ulitis most often is a consequence of acute infectious diseases (scarlet fever, measles, a mononucleosis, diphtheria), initial actions come down to identification of the reason of the main disease. Local therapy assumes anesthesia of a gingiva, prevention of consecutive infections, reduction of puffiness of fabrics. The catarral ulitis at children is treated by means of steroid antiinflammatory drugs, vitamin and mineral complexes and vegetable phenolic connections. The last differ in soft action, are non-toxical and have no heavy side effects therefore them are widely used at children's and teenage age.
Treatment of a hypertrophic ulitis depends on degree of manifestation of symptoms and a clinical picture of an inflammation. In most cases involvement of specialists from other fields of medicine is required (for example, the psychoneurologist if the ulitis is connected with reception of anticonvulsant drugs, or the endocrinologist if the disease develops against the background of hormonal disturbances). Also the doctor has to take care of elimination of local adverse factors – low-quality orthodontic devices, anomaly of a bite, tooth deposits, bad seals. At the diagnosis a hypertrophic ulitis treatment is based on elimination of an inflammation and the exudative phenomena. Antiinflammatory therapy is for this purpose carried out, hygienic means and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used. Besides, natural antibacterial drugs and astringents of a plant origin – a sage, yarrow herbs, broth from nettle leaves are recommended to patients.
The ulcer and necrotic ulitis is characterized by a necrosis of fabrics and penetration of an inflammation into a connecting basis of a gingiva therefore the plan of medical actions is formed taking into account weight of clinical disease, age of the patient, a pathogeny of a disease and results of a bacteriological research. The patient appoints plentiful drink, a diet, protein-rich and vitamins, antihistamines. The started ulocace can demand operational surgical intervention.
The 74-year-old resident of Australia James Harrison became blood donor about 1000 times. It has a rare blood group which antibodies help to survive the newborn with a severe form of anemia. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.

Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects on...
Section: Articles about health
Quite large number of people adheres to the principles of vegetarian food. But how to be if in a family of vegetarians there are children? Whether it is possible to eat also it the same as to parents, or after all the children's organism is not adapted for the use only раст...
Section: Articles about health
Milk and products of its processing by right occupy one of the main places in a diet of the modern person. They contain proteins, necessary for normal life activity, fats, vitamins and microelements, and are an important part of various medical diets....
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications to...
Section: Articles about health
Dark circles (bruises) under eyes – a shortcoming with most of which often fight against the help of cosmetics (proofreaders, saloon procedures and so forth), eliminating only its visibility. However, according to doctors, skin around eyes – the indicator of many disturbances in an organism...
Section: Articles about health
Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. There is even a so-called gastronomic tourism which, according to gourmets, not only allows to receive new feelings, but also is capable to show life of other people from absolutely unexpected side....
Section: Articles about health
Stability of a hormonal background is one of the most important conditions of preservation of health of the woman. At the same time endocrine system –...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance of physical, psychological and moral health of the person by means of the complex of procedures including a diet, cleaning of an organism, respiratory упр...
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, not too modest, and excessively curvy shapes become the reason of sincere discomfort sometimes. Except psychological problems, the big bust sometimes creates also quite notable malfunctions with health: his owner can feel muscular dorsodynias, feeling of constant fatigue and difficulty of breath. Over time excess loading leads to development of diseases позвоночн...
Section: Articles about health
Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. Fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding...
Section: Articles about health
The way of life of people promptly changes from year to year: if about ten years ago the personal computer was not in each family, then today already very few people do without this device. Certainly, and children master the computer at full speed: they not only I play...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, a sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease in physical and intellectual activity and a number of other symptoms reducing quality of life. Abstinence can be strong: an essential part of attempts comes to an end leaving off smoking failure, and people are returned to the use of cigars...
Section: Articles about health
Venereal diseases in medicine are called the infections which are transmitted preferential sexually, now they are so...
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. Trainings will help it to become strong and hardy, will improve coordination of movements, and also will exert positive impact on mentality: it...
Section: Articles about health
Each woman has preferences in the field of use of those goods which help us to look good, feel young and effective. Besides: selection process of favourite perfume, shampoo or decorative cosmetics already lightens the mood and serves as a peculiar stress medicine. Happens very offensively when the acquired perfumery and cosmetic products not only do not meet our expectations, but also becomes the reason of problems with health. Sources неприятн...
Section: Articles about health
What will only not be thought up by persons interested to have a beautiful figure. Here the last innovation – for weight loss needs to be eaten greasy food. Give ра...
Section: Slideshow
Today about 30 diseases, sexually transmitted are known. Wide circulation of these illnesses is extremely promoted by the dual attitude towards them: on the one hand, most of people know about "shameful" diseases and not a stirrup very little...
Section: Articles about health
The winter swimming in open reservoirs called in our country by "winter swimming" – officially recognized sport and one of the most extreme ways of a hardening of an organism. This occupation has an old story and adherents in many countries. The international competitions in winter heats on open water, and every two years – the World Cup are annually held. Despite huge popularity and the proved advantage for health, winter swimming is still surrounded with hardy delusions. Ра...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need to the visa...
Section: Articles about health
The metabolism at each person proceeds in own way. However between the speed of this process and disposal of excess weight after all all have a dependence. Unfortunately, the people inclined to try on itself numerous "miracle" diets, not always at...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and the strengthened reproduction of this microorganism lead to weakening of protection of mucous membranes and their erosive damage. Displays of an illness seriously reduce quality of life: patients regularly test attacks of severe pain, heartburn, nausea. On this background also psychoemotional malfunctions develop: a kidney-vetch, as a rule, shows an acrimony, ча...
Section: Articles about health
Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes lying бо...
Section: Articles about health
The body of the person almost for 60% consists of water. It is so important for normal functioning of an organism that loss of only one and a half percent of liquid already leads to the most unpleasant effects. The problems connected with deficit of water can overtake and...
Section: Articles about health
On the head of the person about one million hair follicles, or as they are called still, hair bulbs are located. At the time of the birth most of them is in the "sleeping" state, but within several weeks follicles become more active, and from them hair begin to grow. Intensity of this process is individual, and during life it can change. Genetic predisposition, a physical and emotional state, aggressive influence affects the growth rate of hair out of...
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutritious...
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also a receptacle for a spinal cord, that is why malfunctions with a backbone are so dangerous. To treat rachis diseases very difficult and long...
Section: Articles about health
Long time antibiotics were considered as a panacea from all diseases and were appointed even at insignificant symptoms of an infection. Even now not everyone knows in what force of antibiotics how and when they should be accepted. Let's discredit 7 popular myths about such drugs....
Section: Articles about health
