





Nasal cavity
Short characteristic of a nasal cavity
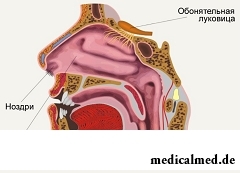 Nasal cavity – the cavity which is the beginning of a respiratory way of the person. It represents the air channel which is in front reported with external environment (through nose openings), and behind – with a nasopharynx. In a nasal cavity olfactor organs are located, and the main functions consist in warming, clarification from foreign particles and moistening of the arriving air.
Nasal cavity – the cavity which is the beginning of a respiratory way of the person. It represents the air channel which is in front reported with external environment (through nose openings), and behind – with a nasopharynx. In a nasal cavity olfactor organs are located, and the main functions consist in warming, clarification from foreign particles and moistening of the arriving air.
Structure of a nasal cavity
Walls of a nasal cavity are formed by skull bones: trellised, frontal, the lacrimal, wedge-shaped, nasal, palatal and maxillary. The nasal cavity from an oral cavity is delimited by a hard and soft palate.
The outside nose is a front part of a nasal cavity, and pair openings behind connect it to a pharyngeal cavity.
The nasal cavity is divided into two half, everyone them whom five walls have: lower, upper, medial, lateral and back. Cavity halves not absolutely symmetric as the partition between them is, as a rule, slightly rejected aside.
The most complex structure at a lateral wall. On it three nasal sinks hang down inside. These sinks serve for department from each other upper, average and lower nasal the course.
In addition to a bone tissue the cartilaginous and webby parts differing in mobility enter a structure of a nasal cavity.
The threshold of a nasal cavity is covered by the flat epithelium which is continuation of an integument from within. In a connective tissue layer under an epithelium roots of setaceous hair and sebaceous glands are put.
Blood supply of a nasal cavity is provided by a front and back trellised and wedge-shaped and palatal artery, and outflow – a wedge-shaped and palatal vein.
Outflow of a lymph from a nasal cavity is carried out in mental and submandibular lymph nodes.
In a structure of a nasal cavity distinguish:
- The upper nasal course which is located only in back department of a nasal cavity. As a rule, it is twice shorter than a half-speed. In it back cells of a sievebone are open;
- The average nasal course located between average and lower sinks. Via the channel in the form of a funnel the average nasal course is reported with front cells of a sievebone and a frontal sinus. This anatomic communication explains transition of inflammatory process to a frontal sinus at cold (frontal sinusitis);
- The lower nasal course passes between a bottom of a nasal cavity and the lower sink. It is reported with an eye-socket through a nasal duct that provides intake of the lacrimal liquid in a nasal cavity. Owing to such structure nasal allocations amplify when crying and, on the contrary, eyes rather often "water" at cold.
Features of a structure of a mucous membrane of a nasal cavity
The mucous membrane of a nasal cavity can be divided into two areas:
- Upper nasal sinks, and also upper part of average nasal sinks and partitions of a nose the olfactory area borrows. This area is covered by the pseudo-multilayer epithelium containing the neurosensory bipolar cells which are responsible for perception of smells;
- Other part of a mucous membrane of a nasal cavity is occupied by respiratory area. It is also covered by a pseudo-multilayer epithelium, but it contains scyphoid cells. These cells emit slime which is necessary for air moistening.
Irrespective of area a plate of a mucous membrane of a nasal cavity rather thin also contains in the structure glands (serous and mucous) and a large amount of elastic fibers.
The nasal cavity submucosa rather thin also contains:
- Adenoid tissue;
- Nervous and vascular textures;
- Glands;
- Mast cells.
The muscular plate of a mucous nasal cavity is developed poorly.
Functions of a nasal cavity
Treat the main functions of a nasal cavity:
- Respiratory. The air inhaled through a nasal cavity makes the arc-shaped way during which it is cleared, warmed and humidified. Warming of the inhaled air is promoted by the numerous blood vessels and thin-walled veins located in a nasal cavity. Besides, the air inhaled through a nose puts pressure upon a mucous membrane of a nasal cavity that leads to excitement of a respiratory reflex and bigger expansion of a thorax, than at a breath through a mouth. Disturbance of nasal breath, as a rule, is reflected in a physical condition of all organism;
- Olfactory. Perception of smells happens thanks to the olfactory epithelium located in epithelial tissue of a nasal cavity;
- Protective. The sneezing arising as irritation of the termination of a trifacial the rough suspended particles which are contained in air provides protection against similar particles. Dacryagogue promotes clarification at inhalation of harmful impurity of air. At the same time the tear flows down not only outside, but also in a nasal cavity via the lacrimonasal channel;
- Resonator. A nasal cavity with an oral cavity, a throat and okolonosovy bosoms serve as the resonator for a voice.
The liver is the heaviest body in our body. Its average weight makes 1,5 kg.

Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times from...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. The statistics of incidence is considered not full as at an initial stage the illness, as a rule, does not cause to the person of special inconveniences, and many having got sick...
Section: Articles about health
For the person who daily since morning gathers for work it is very important to wake up vigorous and ready by day of work. Actually, each of us experiences difficulties with this, at first sight, simple business from time to time. After night rest exert impact on a condition of an organism the weather which collected for several days fatigue, household and office problems, quality of a dream and many other factors....
Section: Articles about health
The list of stereotypes of which, apparently, all know strongly includes following: British surely eat for breakfast овсянк...
Section: Articles about health
Popular joke that there are no healthy people, and is nedoobsledovanny, most of us considers an honest truth, continually it is necessary to hear that all of us are sick hardly from a school bench. It is hard to say, whether so it actually because...
Section: Articles about health
For the help to doctors in the choice of optimal solutions for treatment of various diseases the Cochrane scientific organization (Cochrane) conducts joint researches with representatives of scientific community around the world. The analysis of a series of the conducted researches of the drug Oscillococcinum® relating to group of cold remedies became one of the last methanolyses....
Section: Articles about health
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible on...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste, because of to...
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as are afraid that they can do harm to health of children. What troubles can really trap kids and how to make joint life of a family and domestic animals comfortable and safe?...
Section: Articles about health
All know that self-treatment is dangerous. However absolutely it is almost impossible to do without it. Rate of modern life not on...
Section: Articles about health
Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only the food sating an organism but also the medicines curing of many diseases. Unfortunately, having given the use of some of them...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of use of table salt in the therapeutic purposes contains not one century. Applications which do by means of the fabric impregnated with saline solution are considered especially effective. They have antibacterial and antiinflammatory effect, help to heal wounds, exempt fabrics from excess liquid. Hypertonic salt solution of potassium chloride is applied outwardly at many morbid conditions. Let's tell about the most known of them....
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. Odes...
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. According to nutritionists, the separate use of the carbohydrate and proteinaceous products demanding different conditions of assimilation helps to get rid from Bol...
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far he already helped a significant amount of married couples to become happy parents. Usually to the EKO procedure difficult and very expensive, resort in those situations when all other ways to help couple to bring the child are inefficient. "Conception in a test tube" yields quite good results in cases of infertility of one of partners, existence at the woman of impassability of uterine tubes...
Section: Articles about health
Residents of big cities quite often have a disease which is known as the syndrome of chronic fatigue (SCF) today. This illness...
Section: Articles about health
During foot walks blood moves on vessels more actively and one and all bodies are supplied with a large amount of oxygen. It affects the state of health of the person very positively....
Section: Slideshow
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. In the summer repeatedly the risk increases to ache with some very dangerous illnesses, we also will talk about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in a nevozder...
Section: Articles about health
Among a set of the perfumery and cosmetic goods which are released today the special group is made by the means containing antibacterial components. Such types of gels, shampoos, soaps, creams, lotions and other products are positioned by manufacturers as a panacea...
Section: Articles about health
Impossibility to conceive the child – a trouble of many Russian families. During quite long time was considered that main "culprits" of troubles such are women. Modern physicians claim that the situation is different: about a half of failures in attempts of reproduction are connected with male infertility....
Section: Articles about health
Cold is such painful that each sigh becomes a victory, heat "knocks" down, and the ache in joints forces to think only about...
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? While physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the industry of hairdresser's art a few years ago there was a sensation – methods of hair extension appeared. It would seem, dreams came true...
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create to it healthy immunity since early years. Nevertheless, this important process in life of mother and child can be saddened laktostazy − by a milk delay in a mammary gland. What main reasons for a laktostaz? How not to allow problems with breastfeeding? Let's consider 10 premises resulting in stagnation of milk at the nursing mother....
Section: Articles about health
Small appetite at the child – the complaint which pediatricians should hear practically from each mother. Most often it is carried to разр...
Section: Articles about health
The mankind knows that some toxins at intake in the minimum quantities have therapeutic effect from an extreme antiquity. Many substances recognized poisonous are applied in the medical purposes also today, being the main deystvuyushch...
Section: Articles about health
You heard that laughter prolongs life? Researchers did not manage to establish longevity direct link with sincere fun yet, but several facts confirming beneficial influence of risibility on the state of health are clinically proved....
Section: Articles about health
