





First aid at bruises
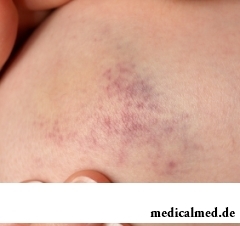 Bruise call the closed injury of fabrics without disturbance of their integrity. The bruise belongs to injuries easy and moderately severe and, as a rule, in such cases enough first-aid treatment though there can be also exceptions. So, severe bruises of the head (brain), internals, eyes, a backbone, thorax and abdominal cavity can constitute health hazard.
Bruise call the closed injury of fabrics without disturbance of their integrity. The bruise belongs to injuries easy and moderately severe and, as a rule, in such cases enough first-aid treatment though there can be also exceptions. So, severe bruises of the head (brain), internals, eyes, a backbone, thorax and abdominal cavity can constitute health hazard.
There is one complexity – directly after a bruise, especially strong, not always perhaps quickly and truly to define weight of an injury. The fact that in the beginning it seemed a bruise, maybe a change or a crack of a bone, both a rupture of internals, and concussion. That is why first aid at bruises has to be given correctly, and in any doubtful cases it is necessary to ask for medical assistance in emergency station or traumatologic department of the nearest hospital.
Symptoms of a bruise
The first and main symptoms of a bruise are pain and a swelling in the injured place. Pain carries intensive, but short-term character, however in process of increase of hypostasis painful feelings renew and amplify that is explained by squeezing of nerve terminations. Pain from a bruise can be very long – it is about weeks, and sometimes and months, depending on an anatomic arrangement of the injured body part.
Emergence of a hematoma – the hypodermic hemorrhage formed as a result of a rupture of vessels is a frequent consequence of a bruise. The hematoma not always should be considered as harmless bruise – hematomas of a brain and internals can be extremely dangerous, situation is aggravated with the fact that their bystry diagnosis is not always possible.
Restriction or dysfunction of an affected body part belongs to late symptoms of a bruise. So, at a severe bruise of a joint often there is absolutely impossible a movement in it, at a bruise of eyes victims often note decrease in sight, etc.
First aid at bruises
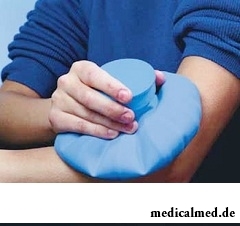 First aid at a bruise is simple – it is necessary to put cold to the affected place and to immobilize it for some time. Cold will help to reduce hypostasis, and respectively and pain, it is necessary to put it as soon as possible. Classical means of first aid in this case is the bubble with ice (bubbles for ice are on sale in drugstores). If it is absent near at hand, it can be replaced with success any other cold subject, for example a water bottle from the refrigerator, a package of the frozen vegetables, the towel moistened with cold water, etc.
First aid at a bruise is simple – it is necessary to put cold to the affected place and to immobilize it for some time. Cold will help to reduce hypostasis, and respectively and pain, it is necessary to put it as soon as possible. Classical means of first aid in this case is the bubble with ice (bubbles for ice are on sale in drugstores). If it is absent near at hand, it can be replaced with success any other cold subject, for example a water bottle from the refrigerator, a package of the frozen vegetables, the towel moistened with cold water, etc.
Imposing of a compressing bandage will be useful. Its purpose consists in prevention of hypostasis and reduction of a possible hematoma too.
In case of a megalgia it is admissible to accept anesthetic, however it is possible to do it only when there is an absolute confidence that the occurred injury – hurt also anything else. In all other cases it is necessary to refrain from reception of analgetics before medical examination, otherwise it is possible to distort symptoms – the injury will be represented easier, than is actually.
If confidence that there was a bruise no, it is necessary to ask for medical assistance in emergency station or a hospital as with a high probability carrying out a X-ray analysis will be required.
Features of first-aid treatment at bruises of various localization
Depending on where the injured place is located, first aid can vary a little.
At an eyeglobe bruise before applying of cold it is necessary to impose approximately sterile (or at least just pure) a bandage and to immediately transport the victim in hospital. The hurt eye quickly swells and is closed and to carry out its diagnosis, having defined precisely character and severity of an injury, only the specialist can. If the severe injury then what will give specialized help earlier, that a high probability to keep all functions of an eye.
First aid at a bruise of the head has to include express diagnosis on existence of possible concussion.
The occurred loss of consciousness after a bruise, even short-term, is a reliable symptom of concussion, however if the loss of consciousness did not occur, it does not mean yet that everything was. Can point the following symptoms to concussion:
- Nausea and/or vomiting soon after the occurred injury;
- Headache, dizziness, sonitus;
- Oxycinesia of eyes;
- Pallor of integuments, perspiration, rushes of blood (feeling of heat in the head, extremities);
- Disorientation in space;
- Block of reactions, answers inattentively, complexity in concentration;
- Temperature increase.
There is a simple test by which it is possible to define quickly and effectively existence of a concussion of the brain: suggest the victim to track a look your finger which you move before his face. If there is no concussion, eyes will smoothly move if is – there will be disturbances of the movement (twitchings, interruption, etc.).
Concussion demands medical intervention. In this case before arrival of the doctor or delivery of the victim to hospital (emergency station) it it is not necessary to leave one as the state can worsen at any time.
At severe bruises of a backbone, thorax and abdominal cavity it is necessary to ask for medical assistance if after the occurred injury any deviation in the state of health appears: disturbance of motive or sensitive function, faintness, weakness, a cold perspiration, a syncope, the complicated breath, an asthma, etc.
There are very curious medical syndromes, for example, persuasive swallowing objects. In a stomach of one patient suffering from this mania 2500 foreign objects were revealed.

It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital in step a toast...
Section: Articles about health
Striya (extension) are the defects of skin having an appearance of direct or wavy strips from 1 to 10 cm long and 1-5 mm wide. In most cases at women of a striya are located on a stomach, hips, a breast or buttocks. At athletes they can appear on shoulders and внутренн...
Section: Articles about health
For the last decades the diabetes mellitus of the second type became really world problem. The number of cases annually increases, and average age of patients for whom the illness is diagnosed, steadily decreases. Specialists consider that one of the main reasons for this trouble is disturbance of a diet. In other words, the huge number of people regularly overeats or excessively is fond of the products causing glucose exchange process failures....
Section: Articles about health
Aging — natural and inevitable process. Over time our skin loses elasticity, on it saggings, a face form теря are formed...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs when walking on heels, frequent painful sprains, pain on average and anonymous toes even after small nagruzo...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of improvement of a condition of the patients at administration of drugs who are not containing active agents, so-called effect of placebo is known long ago. At the end of the 18th century the American doctor Perkins began to treat people the "miracle" sticks made of alloy of steel and brass. Was for several minutes to press such subject enough to a sore point that it became much easier for the patient. Having suspected Perkins of charlatanism, his colleagues tried to repeat "miracle" by means of sticks, steles...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, in Russia about 34% of citizens smoke. Most of consumers of tobacco has problems about health sooner or later...
Section: Articles about health
Energy saving lamps are one of the most popular products of innovative technologies, and there is no wonder: they much more economic also are more long-lasting than usual filament lamps. At the same time there are fears that energy saving bulbs can become the reasons...
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair by means of coloring, or considerably changing it for the purpose of creation of absolutely new image. All know that the gray hair is a sign of the coming old age, so, it is necessary to get rid of it....
Section: Articles about health
Each person supports all life a SARS about 200 times. The peak of incidence falls on cold season, but to get sick from temperatures...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – as a result of sweating, breath, an urination, and its insufficient completion due to various reasons can bring to обезвожив...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of the panic attack is known long ago, but the reasons of its emergence still are up to the end not found out. It is established that more than 30% of people at least once in life become the victims of very unpleasant phenomenon: without everyones on that the reasons they have a feeling of horror which is followed by a cardiopalmus, a shiver and the fever or feeling of sudden heat increased by sweating, breath constraint, dizziness, nausea....
Section: Articles about health
History of cultivation of a buckwheat contains more than five thousand years. Grain which is received from this plant is used for пригото...
Section: Articles about health
Kidneys perform the most important function of clarification of blood from those products of metabolic processes which cannot be used by an organism for obtaining energy and construction of new cells. With the urine produced by kidneys from a body of the person bulk is removed...
Section: Articles about health
Helminthosis is one of the most widespread diseases. Statistically, any species of helminths infected every third inhabitant of the planet. Most of specialists even consider these data strongly underestimated: some uninvited "cohabitants" do not cause the carriers serious troubles, and patients just do not see doctors. The situation is aggravated also with the fact that people know about specifics of similar illnesses very little. At many presence of worms is strong ассоциир...
Section: Articles about health
The person, as well as all other beings living on our planet feels weather changing. It is normal meteosensitivity, not...
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" and "assimilation" of information is strongly slowed down. Especially this problem urgent for persons of age becomes more senior than fifty years. "It is already bad with...
Section: Articles about health
Zone hypostases under eyes - very widespread problem giving to people is a lot of inconvenience. Hypodermic fabric in these parts has very loose structure and almost does not contain collagenic fibers. Besides, the skin covering подглазья constantly is exposed to compression and stretching when the person blinks, blinks, etc. These features also create premises for emergence of the so-called bags which are giving to the face a tired and sickly look, and also visually adding increased...
Section: Articles about health
Venereal diseases in medicine are called the infections which are transmitted preferential sexually, now they are so...
Section: Articles about health
Coffee - the tonic loved by many for the invigorating aroma and deep taste. Having the stimulating effect, coffee increases working capacity, promotes concentration of attention, fights against drowsiness and improves mood. Statistically, about 30% of inhabitants...
Section: Articles about health
On the head of the person about one million hair follicles, or as they are called still, hair bulbs are located. At the time of the birth most of them is in the "sleeping" state, but within several weeks follicles become more active, and from them hair begin to grow. Intensity of this process is individual, and during life it can change. Genetic predisposition, a physical and emotional state, aggressive influence affects the growth rate of hair out of...
Section: Articles about health
You are office worker, the driver, the fan of winter sports or do not think of life without bicycle? You conduct a slow-moving image жизн...
Section: Articles about health
Health and attractiveness - eternal values, pursuing which people often use the most unusual ingredients and technicians. Let's consider 11 most exotic and sometimes not most pleasant Spa procedures to which the person in a pursuit for beauty agrees...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning they laugh and joke, and in the evening cry or are irritated....
Section: Articles about health
When overcomes feeling of hunger, and an opportunity to have dinner fully is absent, having a snack − small on volume comes to the rescue...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor with age forgetfulness and problems with concentration of attention. This disease has the autoimmune nature. Pathological process is expressed in degradation of nervous tissue and destruction of its enveloping layer - a myelin. Multiple damages of the central nervous system which are shown by decrease in sight, bystry fatigue, on become result of development of an illness...
Section: Articles about health
