





Shock
General information
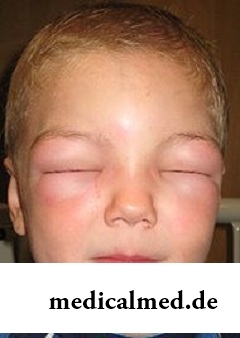 Shock is a response of an organism to action of external aggressive irritants which can be followed by disturbances of blood circulation, a metabolism, nervous system, breath, other vital functions of an organism.
Shock is a response of an organism to action of external aggressive irritants which can be followed by disturbances of blood circulation, a metabolism, nervous system, breath, other vital functions of an organism.
There are such reasons of shock:
1. The injuries got owing to mechanical or chemical influence: burns, gaps, disturbance of fabrics, separations of extremities, influence of current (traumatic shock);
2. The loss of blood accompanying an injury in large numbers (hemorrhagic shock);
3. Transfusion to the patient of incompatible blood in large volume;
4. Hit of allergens on sensibilized Wednesday (acute anaphylaxis);
5. Necrosis extensive liver, intestines, kidneys, heart; ischemia.
It is possible to diagnose shock for the person who transferred a shock or an injury proceeding from the following signs:
- concern;
- the obscured consciousness with tachycardia;
- reduced arterial pressure;
- the broken breath
- the reduced volume of the emitted urine;
- integuments cold and wet, marble or it is pale - cyanochroic color
Clinical picture of shock
The clinical picture of shock differs depending on weight of influence of external irritants. For the correct assessment of a condition of the person who transferred shock and assistance at shock, it is necessary to distinguish several stages of this state:
1. Shock of 1 degree. At the person consciousness remains, he makes contact though reactions are slowed slightly down. Pulse indicators – 90-100 blows, systolic pressure – 90 mm;
2. Shock 2 degrees. Reactions at the person are slowed also down, but he in consciousness, correctly answers the asked questions, talks a vocal murmur. The speeded-up shallow breathing, frequent pulse (140 beats per minute), pressure is observed arterial it is lowered to 90-80 mm hg. The forecast at such shock serious, a state demands urgent holding antishock procedures;
3. Shock 3 degrees. At the person reactions are slowed down, he does not feel pain and is adynamic. The patient slowly and in a whisper talks, can not answer questions in general, or is terse. Consciousness can be absent completely. Integuments are pale, with the expressed Crocq's disease, are covered then. Pulse at the victim hardly noticeable, is probed only on femoral and sleepy arteries (usually 130-180 уд. / mines). Also shallow and frequent breathing is observed. Venous central pressure can be below zero or zero, and systolic pressure – lower than 70 mm hg.
4. Shock 4 degrees is the terminal state of an organism which is expressed often in irreversible pathological changes – a hypoxia of fabrics, acidosis, intoxication. A condition of the patient at such form of shock extremely heavy and the forecast practically always negative. At the victim heart is not listened, he unconscious also breathes superficially with whimpers and spasms. There is no reaction to pain, pupils are expanded. At the same time arterial pressure – 50 mm hg, can also not be defined in general. Pulse is also hardly noticeable and is felt only on the main arteries. Integuments of the person - gray, with the characteristic marble drawing and spots similar on cadaveric, pointing to the general decrease in a krovenapolneniye.
Types of shock
The depressed case is classified depending on shock origins. So, it is possible to allocate:
- Vascular shock (septic, neurogenic, acute anaphylaxis);
- Hypovolemic (angidremichesky and hemorrhagic shock);
- Cardiogenic shock;
- Painful shock (burn, traumatic shock).
Vascular shock is the shock caused by vasodepression. Its subspecies: the septic, neurogenic, acute anaphylaxis is states with a different pathogeny. Septic shock arises owing to infection of the person with a bacterial infection (sepsis, peritonitis, a sphacelism). Neurogenic shock is most often shown after an injury back or a myelencephalon. The acute anaphylaxis is the allergic reaction proceeding in a severe form which arises within the first 2-25 min. after hit of allergen in an organism. The substances capable to cause an acute anaphylaxis are drugs of plasma and plasma proteins, X-ray contrast and anesthetics, other medicines.
Hypovolemic shock is caused by acute shortage of the circulating blood, secondary decrease in emission of heart, decrease in venous return to heart. There is this depressed case at dehydration, plasma loss (angidremichesky shock) and a loss of blood - hemorrhagic shock.
Cardiogenic shock – the critical condition of heart and vessels which is characterized by high mortality (from 50 to 90%), and coming owing to serious violation of blood circulation. At cardiogenic shock the brain due to the lack of blood supply (the broken cardiac performance, the expanded vessels incapable to hold blood), suffers a sharp shortage of oxygen. Therefore the person who is in a condition of cardiogenic shock faints and most often dies.
Painful shock, as well as cardiogenic, acute anaphylaxis – the widespread depressed case arising at acute reaction on traumatized (traumatic shock) or a burn. And it is important to understand that burn and traumatic shock is kinds of shock hypovolemic, loss of a large amount of plasma or blood (hemorrhagic shock) is their reason. It can be internal and outside bleedings, and also exudation of plasma liquid through the burned sites of skin at burns.
The help at shock
 Giving help at shock it is important to understand that often wrong transportation of the victim and first-aid treatment is the reason of overdue depressed cases at shock therefore holding elementary rescue procedures before arrival of an ambulance crew is very important.
Giving help at shock it is important to understand that often wrong transportation of the victim and first-aid treatment is the reason of overdue depressed cases at shock therefore holding elementary rescue procedures before arrival of an ambulance crew is very important.
The help at shock, consists in the following events:
1. To remove the shock cause, for example, to stop bleeding, to release the jammed extremities, to extinguish the clothes burning on the victim;
2. To check existence of foreign objects in a mouth and the victim's nose, if necessary to remove them;
3. To check existence of breath, pulse, and if necessary to carry out a cardiac massage, an artificial respiration;
4. To track that the victim lay the head sideways, so he will not choke with own emetic masses, at him language will not sink down;
5. To establish whether there is a victim in consciousness and to give it anesthetic. It is desirable to give to the patient hot tea, but to exclude before it stomach wound;
6. To weaken clothes on a belt, a breast, the victim's neck;
7. The patient needs to be warmed or cooled depending on a season;
8. The victim it is impossible to leave one, he cannot smoke. Also it is impossible to put a hot-water bottle to the injured places – it can provoke outflow of blood from vital bodies.
During life the average person develops neither more nor less two big pools of saliva.

Life of the modern child is extremely active and difficult. Information strain which is experienced by the school student and did not dream the pupil...
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. Trainings will help it to become strong and hardy, will improve coordination of movements, and also will exert positive impact on mentality: it...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. The contribution of drugs to rescue of people from epidemics of dangerous infections is huge, however at careless use antibiotics are capable to cause to an organism serious damage. Negative action can be shown in the form of easing of immunity, disturbance of balance of microflora in кишеч...
Section: Articles about health
About 10-15 years ago existence of the computer in the apartment of the Russian was considered as a rarity and office rooms were only on перв...
Section: Articles about health
Sooner or later hair turn gray at all. Many people try to hide these changes, returning natural color of the hair by means of coloring, or considerably changing it for the purpose of creation of absolutely new image. All know that the gray hair is a sign приближающ...
Section: Articles about health
It is difficult to revaluate importance of kidneys for an organism. These bodies not only perform work on purification of blood of decomposition products and removal of excess liquid. They are responsible also for production of some hormones necessary for maintenance of a normality of a bone tissue, and also for a producing red blood cells – erythrocytes....
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far it already helped znach...
Section: Articles about health
Ability of an organism to resist to adverse environmental factors (to impact of temperature drops, humidity and pressure, to the attacks of causative organisms, etc.) directly depends on what the person eats. Business here not only in, that C...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste because of which it is included almost in all dry mixes of spicy herbs, and also give to meat and fresh fish dishes....
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also contain...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which not only facilitate house work, but also help to keep health of the person? Of course, and we will tell about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Obesity is called a disease of 21 centuries, for the last 100 years the number of the people suffering from excess body weight considerably increased. Statistically, on Earth already about 1,5 billion corpulent people, and 500 million from them have the extreme degree of completeness negatively affecting quality and duration of their life. What served as the reason of growth of stout persons on the planet? How not to get to their ranks? Let's consider five main premises for increase in body weight in conditions современнос...
Section: Articles about health
(Xerostomia) many people consider feeling of a xerostomia small and easily removable inconvenience. This delusion...
Section: Articles about health
Scientists always aimed to offer fundamental explanations for medical problems. Their theories formed the basis of modern methods of treatment of the hardest pathologies and helped to save a set of lives. However stories are known also such theoretical constructions, following to...
Section: Articles about health
Milk and products of its processing by right occupy one of the main places in a diet of the modern person. They contain proteins, necessary for normal life activity, fats, vitamins and microelements, and are an important part of various medical diets....
Section: Articles about health
The cosmetics intended for improvement of a condition of skin, nails and hair are used by each woman. Expenses on регуля...
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to get access to various apparatuses and an opportunity to train under the leadership of the experienced consultant. Many consider fitness on...
Section: Articles about health
Frosty air, fresh wind and easy snowball at most of Russians are associated with cheerfulness, health and cheerful entertainments on which our winter is so generous. But, unfortunately, cold season sometimes brings also troubles with health. It is not about seasonal colds and frostbites, and about those chronic illnesses which symptoms are shown preferential in the winter....
Section: Articles about health
What will only not be thought up by persons interested to have a beautiful figure. Here the last innovation – for weight loss needs to be eaten greasy food. Give ра...
Section: Slideshow
Residents of big cities quite often have a disease which is known as the syndrome of chronic fatigue (SCF) today. This illness affects the people belonging to various social and demographic groups and living on all continents. Most of all SHU to a podverzha...
Section: Articles about health
To look healthy and means well-groomed not only to be pleasant to people around, but also to feel strong, sure and taken place. Specialists in the field of cosmetology quite often note that not all women are able to look after face skin. Many women incorrectly apply cosmetics, ineptly use various procedures, without having exact information on their real influence and dividing numerous delusions about it. All this not the best...
Section: Articles about health
You heard that laughter prolongs life? To establish longevity direct link with sincere fun to researchers yet not удалос...
Section: Articles about health
The name of this disease precisely reflects the problem reason: it consists in the bra fastener pressure upon a certain zone of a back. At the same time one of vertebrae of chest department of a backbone is as if blocked and loses mobility, and falling on it is nude...
Section: Articles about health
For the last decades the diabetes mellitus of the second type became really world problem. The number of cases annually increases, and average age of patients for whom the illness is diagnosed, steadily decreases. Specialists consider that one of the main reasons for this trouble is disturbance of a diet. In other words, the huge number of people regularly overeats or excessively is fond of the products causing glucose exchange process failures....
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot", since ancient times испол...
Section: Articles about health
The nature does not stand stagnation and monotony. It is known that tissues of a human body atrophy if do not receive necessary loadings. It fully belongs also to a cerebral cortex: when it is not given full-time job, it begins to function worse. In резуль...
Section: Articles about health
We live during an advertizing era. Daily each person receives a solid portion of persuasive councils about what to eat to be healthy and successful. Products about which we will talk today are combined by the following circumstance: all of them are positioned as the most useful and the most suitable for inclusion in a morning meal. Unfortunately, it is not true: these 10 products do not suit for breakfasts at all....
Section: Articles about health
