





Upper vena cava
Upper vena cava – the short thin-walled vein with a diameter from 20 to 25 mm located in a front mediastinum. Its length on average varies from five to eight centimeters. The upper vena cava belongs to veins of a big circle of blood circulation and is formed by merge of two (left and right) brachiocephalic veins. It collects a venous blood from the head, upper parts of a thorax, a neck and hands and falls into the right auricle. The only inflow of an upper vena cava is the unpaired vein. Unlike many other veins, this vessel has no valves.
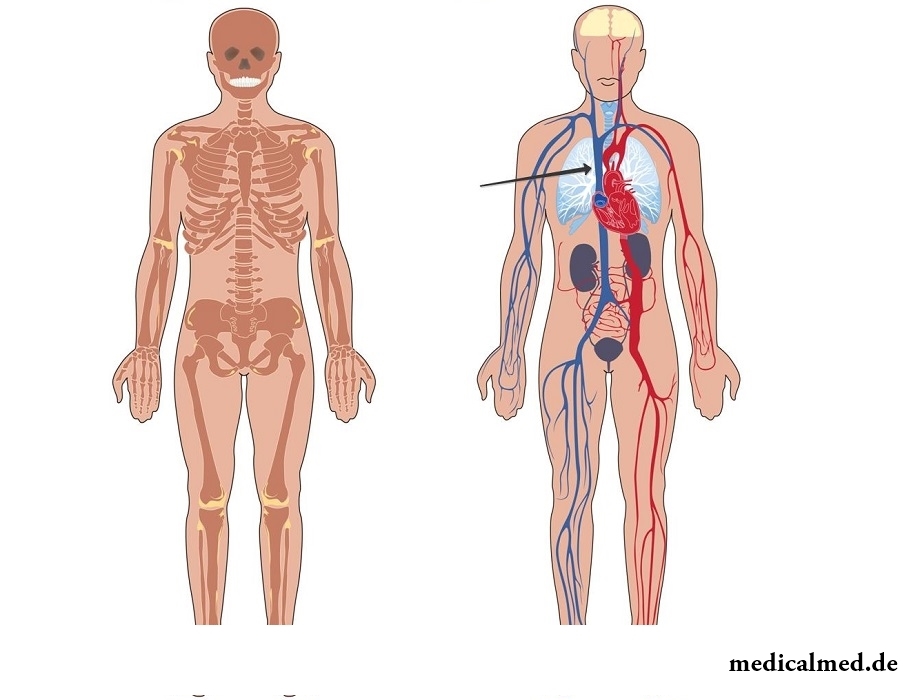
The upper vena cava is directed down and enters a pericardium cavity at the level of the second edge, and falls into the right auricle slightly below.
The upper vena cava is surrounded:
- At the left – an aorta (the ascending part);
- On the right – a mediastinal pleura;
- Ahead – a thymus gland (thymus) and the right lung (the mediastinal part covered with a pleura);
- Behind – a root of the right lung (a front surface).
System of an upper vena cava
All vessels which are logging in an upper vena cava are located rather close to heart, and during relaxation appear as a result of prisasyvayushchy operation of its cameras. Also affects them during respiratory movements a thorax. At the expense of these factors in system of an upper vena cava rather strong negative pressure is created.
The main inflows of an upper vena cava are valveless brachiocephalic veins. In them also always very low pressure therefore there is a risk of hit of air at their wound.
The system of an upper vena cava is made by veins:
- Areas of a neck and head;
- Chest wall, and also some veins of walls of a stomach;
- Upper shoulder girdle and upper extremities.
Venous blood from a chest wall comes to inflow of an upper vena cava – an unpaired vein which incorporates blood from intercostal veins. At an unpaired vein two valves located in its mouths.
The outside jugular vein is located at the level of a mandible corner under an auricle. In this vein blood from the fabrics and bodies located in the head and a neck gathers. Veins fall into an outside jugular vein back ear, occipital, nadlopatochny and front jugular.
The internal jugular vein originates about a jugular foramen of a skull. This vein together with a vagus nerve and the general carotid artery forms a bunch of vessels and nerves of a neck, and also includes brain veins, meningeal, eye and diploichesky veins.
The vertebral veniplexes which are logging in a hollow upper vein are subdivided on internal (passing in the spinal channel) and outside (located on the surface of bodies of vertebrae).
Syndrome of a prelum of an upper vena cava
The syndrome of a prelum of an upper vena cava which is shown as disturbance of its passability can develop for several reasons:
- When progressing development of oncological diseases. At a disease of lung cancer and lymphoma lymph nodes in close proximity to which there passes the hollow upper vein often are surprised. Also metastasises of a breast cancer, myagkotkany sarcomas, a melanoma can lead to disturbance of passability;
- Against the background of cardiovascular insufficiency;
- At development of a retrosternal craw against the background of pathology of a thyroid gland;
- When progressing some infectious diseases, such as syphilis, tuberculosis and гистиоплазмоз;
- In the presence of iatrogenic factors;
- At an idiopathic fibrous mediastinitis.
The syndrome of a prelum of an upper vena cava depending on the reasons which caused it can gradually progress or develop quickly enough. It is possible to carry to the main symptoms of development of this syndrome:
- Puffiness of the person;
- Cough;
- Convulsive syndrome;
- Headache;
- Nausea;
- Dizziness;
- Dysphagy;
- Change of features;
- Drowsiness;
- Asthma;
- Faints;
- Thorax pains;
- Swelling of veins of a thorax, and in certain cases – a neck and upper extremities;
- Cyanosis and plethora of upper parts of a thorax and person.
For diagnosis of a syndrome of a prelum of an upper vena cava the X-ray analysis allowing to reveal the pathological center, and also to define borders and extent of its distribution is, as a rule, carried out. Besides, in certain cases carry out:
- Computer tomography – for obtaining more exact data on an arrangement of bodies of a mediastinum;
- Flebografiya – for assessment of extent of the center of disturbance and carrying out differential diagnosis between vascular and extravasated defeats.
After the conducted researches taking into account the speed of progressing of pathological process the issue of performing drug treatment, himio-or radiation therapy or operation is resolved.
In cases when thrombosis is the reason of changes of a vein, carry out thrombolytic therapy with the subsequent purpose of anticoagulative drugs (for example, heparin sodium or therapeutic doses of warfarin).
In Great Britain there is a law according to which the surgeon can refuse to do to the patient operation if he smokes or has excess weight. The person has to refuse addictions, and then, perhaps, he will not need an operative measure.

Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes lying бо...
Section: Articles about health
What is in our understanding weeds? It plants which are considered to be suitable only for compost pits and feeding of animals. Meanwhile, among the weeds growing literally under legs it is possible to find the mass of the officinal herbs possessing invaluable Paul...
Section: Articles about health
Cold is such painful that each sigh becomes a victory, heat "knocks" down, and the ache in joints forces to think only of pain. Some people with approach of the first symptoms of cold make the self-sacrificing decision to have a disease standing, and at best to rest in bed with a cup of hot tea. There is an opinion that if not to treat cold, then the organism itself, sooner or later, will overcome an illness. Whether so it? It is known that if in time it is simple not to begin treatment, apparently, harmless...
Section: Articles about health
Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Nye...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – unique body on the structure thanks to which the person obtains about 80% of information on the world around: about a form, color, size, the movement, and also many other parameters of objects or phenomena. But whether much we know about the most valuable body...
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters there is not only a seasonal domestic production, but the vegetables and fruit which are grown up in the countries with more comfortable conditions of cultivation at all seasons of the year. However what we see in shops and in the vegetable markets, is only a small part of those edible plants with which the nature is so rich. Today we want to acquaint the reader with rare and very useful vegetables which on...
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In большинс...
Section: Articles about health
For the help to doctors in the choice of optimal solutions for treatment of various diseases the Cochrane scientific organization (Cochrane) conducts joint researches with representatives of scientific community around the world. The analysis of a series became carried out by one of the last methanolyses...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need of a visit to the gynecologist. Certainly, it is possible to establish the exact diagnosis only after inspection, but on the basis of some signs it is possible to assume existence of this or that pathology. Let's consider symptoms of the female diseases which are found most often....
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In некото...
Section: Articles about health
Almost each of us during life faced dissatisfaction with own body. At such moments, as a rule, we begin to shame ourselves, urgently we go on the most rigid diet promising minus of 10 kg in a week, or we exhaust ourselves in the gym to полусм...
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers and cavities), and then small consolidations, the so-called effect of an orange-peel is shown. Changes in a condition of hypodermic cellulose are a consequence of a hormonal imbalance in an organism....
Section: Articles about health
It seems, quite recently you brought the baby from maternity hospital, but time flew by, and here it is already going to join the first in life children's collective. How to prepare the child for visit of a garden? What needs to teach him to facilitate adaptation process? What to tell and how to behave that the kid transferred changes in the life without serious consequences? Let's try to find answers to these questions....
Section: Articles about health
The sudden heat on all body which is followed by perspiration and a cardiopalmus – the phenomenon familiar to many people. Most often t...
Section: Articles about health
Such trouble as the milkwoman's attack, at least once in life happened almost to each woman. Prevalence of a disease is explained by the fact that the causative agent of an illness belongs to the so-called opportunistic microflora living on mucous an obol...
Section: Articles about health
Subfebrile temperature call fervescence to 38 degrees, and subfebrile condition - existence of such temperature over 3 days, and quite often it happens without the visible reasons. Existence of subfebrile condition - a strong indication of disturbances in an organism which can be caused by various reasons: disease, stresses, hormonal failures. Despite the seeming inoffensiveness it is a state at which people often continue to lead a usual life, often is a sign of many of a zabolev...
Section: Articles about health
The word "onikhokriptoz" is unfamiliar to most of people, meanwhile quite so physicians call very widespread problem: growing...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person weakness leans: he suffers from drowsiness, complains of bad mood, loss of interest in life and failures in affairs....
Section: Articles about health
Quite large number of people adheres to the principles of vegetarian food. But how to be if in a family of vegetarians there are children? Whether it is possible to eat also it the same as to parents, or after all the children's organism is not adapted for the use of exclusively vegetable food? Let's try to understand....
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis thyroid гормо...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep look youth for many years and what procedures are offered for achievement of this purpose by cosmetologists? And maybe, only thing of a vari...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs when walking on heels, frequent painful sprains, pain on average and anonymous toes even after small loadings. Usually people with such pathology take off unpleasant effects by means of the anesthetizing pulverizing and ointments, but it does not lead to radical elimination of a problem. Meanwhile, at the known persistence it is possible to strengthen an ankle to the house...
Section: Articles about health
The saying "the rich do not know how the other half lives" is known to all. In a broad sense it is that we can not always understand the person, about...
Section: Articles about health
Musicotherapy – a treatment method which caused and causes a set of a controversy concerning its efficiency. However the facts are relentless: during the numerous researches curative impact of music on an organism was scientifically confirmed. Since then in a number of the countries a method...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often give trouble, serving as the reason of a headache, an acrimony, sleep disorders, and in certain cases and the states close to a depression. How to get rid of undesirable satellites of a disease if near at hand there are no antiallergic...
Section: Articles about health


