Gastrointestinal bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding is not an independent disease, but a complication of many diseases of digestive tract. Help at gastrointestinal bleeding has to be given as soon as possible and in full as this terrible complication, in hard cases it can lead to a lethal outcome.
Reasons of gastrointestinal bleeding
Damage of a wall of digestive tract with involvement of a blood vessel or small capillaries on any of its sites is the reason of gastrointestinal bleeding. Causal gastrointestinal bleeding the following diseases are the most frequent:
- Stomach ulcer and duodenum;
- Hemorrhoids;
- Tumors, both high-quality (polyposes), and malignant in any of departments of digestive tract;
- Gullet varicosity;
- Cracks of a mucous membrane of a gullet;
- Cracks of an anal orifice;
Gastrointestinal bleeding is most often caused in children by an injury of a gullet or stomach, including a corrosive burn, and also a hemorrhagic disease of newborns.
Types of gastrointestinal bleeding
Distinguish gastrointestinal bleeding from an upper part of digestive tract to which the gullet and a stomach, and the lower part consisting of intestines belong.
Gastrointestinal bleeding on duration can be:
- Single (incidental);
- Recurrent (periodically renewing);
- To chronic (constants).
In a form:
- Acute;
- Chronic.
On the nature of manifestation:
- Hidden;
- Explicit.
Symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding
The general symptoms of gastrointestinal bleeding are similar to blood loss symptoms in general. Pallor of integuments, weakness, a sonitus, cold sweat, tachycardia, an asthma, dizziness, front sights before eyes, a lowering of arterial pressure concern to them. Pain, or strengthening of already available pain are not inherent to gastrointestinal bleeding.
Character of the most emitted blood depends on in what site of digestive tract there was a disturbance of integrity of a blood vessel, and from that, the concealed this hemorrhage or explicit.
In the beginning we will stop on explicit gastrointestinal bleedings.
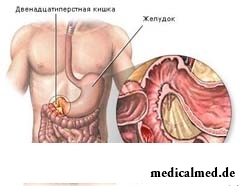
Gastrointestinal bleedings from an upper part of a GIT prove a hematemesis (hematemesis). Vomiting may contain not changed blood that is peculiar to bleedings from a gullet, or to have an appearance of a coffee thick if bleeding occurred in a stomach, the characteristic look to it is given by the blood which turned under the influence of hydrochloric acid. However gastric arterial bleeding of significant force can also have a vomiting appearance with not changed blood as blood at the same time does not manage to be turned.
Gastrointestinal bleeding from a small intestine and a colon can be shown as in the form of vomiting by "a coffee thick", and in the form of a melena – the bloody diarrhea having a tar-like consistence and black color. The melena can proceed some more days after the termination of bleeding in an upper part of digestive tract, tar-like the kcal will be allocated in process of advance of contents on intestines.
If bleeding occurred in a lower part of digestive tract (a large intestine, a rectum, an anus), then it is shown as a bloody chair (gematokheziya). In this case the kcal contains impurity of invariable scarlet blood, sometimes in significant amounts. However the bloody chair can sometimes be also at bleeding of significant force in a small intestine when because of a large amount of blood contents of a small intestine move very quickly.
The concealed gastrointestinal hemorrhages are found at laboratory researches a calla and a gastric juice. The concealed hemorrhage from upper parts of a GIT can look as impurity of black flakes in vomiting, in all other cases to a naked eye it is imperceptible, and proves only the general symptoms of the accruing anemia.
There is no special difference in display of gastrointestinal bleedings at children and at adults, only anemia at children develops much quicker, and because of smaller compensatory opportunities of an organism of an effect can be more dangerous.
First aid at gastrointestinal bleeding
If there was acute bleeding, pre-medical first aid at gastrointestinal bleeding is as follows:
- As soon as possible to call the ambulance;
- To immediately put the patient to bed;
- To exclude receipt in digestive tract of any substances, including water, drugs and food;
- To put on a stomach a bubble with ice;
- To provide access of fresh air to the room where the patient lies;
- To provide constant observation of it before arrival of ambulance, without leaving one.
First aid at gastrointestinal bleeding at children does not differ from that at adults. It is important to provide to the child rest that it is slightly more difficult, than at the adult, especially, if the small child. If presumably gastrointestinal bleeding is caused in children by an injury, it is necessary to try as it is possible to define more precisely the injuring factor (a sharp object, chemical).
The emergency medical assistance at gastrointestinal bleeding depends first of all at most bleeding and its character, and also on a condition of the patient. If bleeding of significant force, with scarlet (arterial) blood, and he does not manage to be stopped during certain time usual means, the patient is brought to department of the emergency surgery.
Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding
Treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding, depending on its character, is carried out by surgical or conservative means.
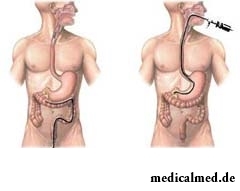
At bleedings of significant force if it is not possible to stop blood loss, resort to resuscitation techniques and an immediate surgery. Before operation it is desirable to fill at least partly the volume of the lost blood for what carry out infusional therapy, by intravenous injection of blood preparations or its substitutes. In case of threat of life urgent operation without similar preparation is possible. Operation can be performed as a classical, open method, and endoscopic (FGS, a laparoscopy a rektoromanoskopiya, a kolonoskopiya), depending on indications. Operational treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding consists in bandaging of veins of a gullet and stomach, imposing of a sigmostoma, resection of the site of a stomach or a gut, coagulation of the damaged vessel, etc.
Conservative treatment of gastrointestinal bleeding consists of the following events:
- Introduction of styptic means;
- Evacuation of blood from a GIT by introduction of the nazogastralny probe and cleansing enemas (if bleeding not from a lower part of a GIT);
- Completion of blood loss;
- Support of the vital systems of an organism;
- Treatment of the basic disease which led to bleeding.
Many drugs initially moved ahead in the market as drugs. Heroin, for example, was initially brought to the market as children's cough medicine. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as anesthesia and as the means increasing endurance.
History of mankind contains several tens of epidemics whose emergence was compared by eyewitnesses and historians to doomsday. With...
Section: Articles about health
The trophic ulcer is not an independent disease. This heavy complication arising owing to a thermal injury (a burn or a frostbite), chronic pathologies of arteries or veins of the lower extremities, a diabetes mellitus, and also some defeats of a soyeda...
Section: Articles about health
Smoking not only exerts a negative impact on the state of health of the consumer of tobacco products, but is an air polluter the substances potentially dangerous to people around. In recent years significantly the number of the people aiming to get rid of an addiction increased. Business this difficult: having left off smoking, the person immediately begins to suffer from abstinence. Besides, many yesterday's smokers feel at first great disappointment as улучш...
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" also "assimilation"...
Section: Articles about health
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) – one of those drugs which are known literally to all. It is available in each home first-aid kit, and many accept it at the first signs of an indisposition, often without having a fair idea of properties and a therapeutic eff...
Section: Articles about health
Bathing in broths of medical flowers and plants (phytobathtub) was eurysynusic since Cleopatra who is a good judge in all that concerns beauty and health. And today phytobathtubs is the simple and available means allowing not only to remove nervous tension, but also to recover from many diseases. Grass bathtubs at treatment of cold, osteochondrosis, radiculitis, skin diseases, and also diseases of urinary tract and vessels are especially effective....
Section: Articles about health
Transfusion of donor blood has almost century history. In spite of the fact that this procedure is quite usual for many people, itself п...
Section: Articles about health
Such trouble as the milkwoman's attack, at least once in life happened almost to each woman. Prevalence of a disease is explained by the fact that the causative agent of an illness belongs to the so-called opportunistic microflora living on mucous an obol...
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? While physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the industry of hairdresser's art a few years ago there was a sensation – methods of hair extension appeared. It would seem, dreams came true: though the procedure of building also does not belong to the category cheap, practically any woman can increase several times the volume of hair, change their length and color – generally, to become the real beauty queen....
Section: Articles about health
Coffee – favourite drink of many. For the last decades it more than once already declared very harmful, extremely useful and even...
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number the myth...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include it in the diet, having given preference "to safer" to vegetable fats. Meanwhile, the last researches showed that harm of butter for health is strongly exaggerated. But the product has a number of unique properties, to...
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor about age...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one of the most ancient methods of disposal of the most different diseases. Bathtubs, souls, wrappings and inhalations, in combination with reception of water vnut...
Section: Articles about health
Heart disease and blood vessels lead to disturbance of blood supply of bodies and fabrics that involves failures in their work, deterioration in health of the person, decrease in its working capacity and standard of living. Annually more than 17 million inhabitants of our planet perish from pathologies such....
Section: Articles about health
What will only not be thought up by persons interested to have a beautiful figure. Here the last innovation – for weight loss needs to be eaten greasy food. Give ра...
Section: Slideshow
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers...
Section: Articles about health
All parents are ready to what the baby often and pisat much. Since then, as the absorbing diapers strongly became current, keeping of the kid in dryness does not represent any problems. But if the grown-up kid continues to urinate in panties, parents begin to feel concern – whether it is normal, or the kid has an urine incontience? Let's try to understand what is enuresis why it arises at children and at what age it is necessary to begin it to treat....
Section: Articles about health
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that a plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those...
Section: Articles about health
All got used long ago that, having addressed the plastic surgeon, it is possible to modify natural parameters of a figure or to minimize the damages put to appearance with ruthless time. Many people (preferential women) worldwide е...
Section: Articles about health
Subfebrile temperature call fervescence to 38 degrees, and subfebrile condition - existence of such temperature over 3 days, and quite often it happens without the visible reasons. Existence of subfebrile condition - a strong indication of disturbances in an organism which can be caused by various reasons: disease, stresses, hormonal failures. Despite the seeming inoffensiveness it is a state at which people often continue to lead a usual life, often is a sign of many of a zabolev...
Section: Articles about health
Zone hypostases under eyes - very widespread problem giving to people is a lot of inconvenience. Hypodermic fabric in these parts having...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it receive only useful substances, necessary vitamins and microelements. In this case there will be no problems with digestion, with лишн...
Section: Articles about health
For the time being the perspective of heart diseases seems to most of people remote and foggy. But sooner or later practically each adult faces extremely unpleasant feelings: sudden stethalgia. To be consoled at this time in a thought of what for a heart attack still early, will hardly turn out: if the person is impressionable, he, as a rule, has feeling of panic and fear of fast death. And meanwhile, it is very often possible to confuse pains with cardiac pains невралгическог...
Section: Articles about health
The next flu epidemic leads to the next panic, from year to year we give in on these manipulations: professionally alarming goal...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – as a result of sweating, breath, an urination, and its insufficient completion due to various reasons can bring to обезвожив...
Section: Articles about health
Some people consider what for medicine of the 21st century of secrets in the field of health of the person almost does not exist. It absolutely not so. The more answers scientists receive, the more the most difficult questions are raised for them by life. Besides, there are diseases which are not explained with science in any way of which existence people know for 100-150 years. These diseases meet not so often, but from some of them nobody is insured....
Section: Articles about health