





Overhydratation
Overhydratation – the excess volume of water which is contained in an organism or in its separate parts, a special form of disturbance of water-salt balance of an organism. Clinical displays of an overhydratation are hypostases of body tissues, lungs, a brain, excess accumulation of liquid in an abdominal cavity – ascites. Some states at an overhydratation are critical for the patient's life.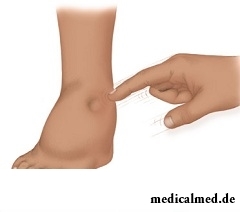
The human body consists to some extent of water which volume changes with age. So, water volume in an organism of the newborn reaches 75% while the organism of the elderly person only for 55% consists of water. Water in a human body is distributed by liquid sectors: the intracellular space contains about 60% of all water which is in an organism, other volume of water is distributed in extracellular space – intercellular space, a blood plasma, transcellular liquid (digestive tract, the spinal channel, chambers of the eye, uric channels, epinephral tubules).
The water balance of an organism is supported by the correlated volume of the arriving and removed liquid at the same time. The standard daily rate of liquid of an organism (2,5 l) arrives with food stuffs (about 1 l), drink (about 1,5 l), and also in the form of oksidatsionny liquid which is formed in the course of oxidation of fats (about 0,3 - 0,4 l). Liquid is removed from an organism by evaporation (with about 0,6 l of liquid are removed then), through kidneys (about 1,5 l of liquid), with expired air (excretion of 0,4 l of liquid a day), with a fecal masses (to 0,2 l a day are removed).
At disturbance of a water balance (overhydratation) not only the volume of the liquid which is contained in an organism changes but also the level of content of minerals in an organism changes. Excessive change of concentration of sodium, potassium and other minerals (electrolytes) at an overhydratation can lead to a hyponatremia, a hypopotassemia, the general electrolytic imbalance of an organism.
The overhydratation can arise in an organism owing to excess consumption of liquid or insufficient excretion of liquid an organism. In some cases with the diagnosed overhydratation both factors are present at the patient's organism. The overhydratation can develop both at influence of external factors, and owing to disturbance of functioning of bodies, organism diseases.
Organism overhydratation: reasons, types of a disgidriya
Are the main reasons for an overhydratation of an organism:
- Excess administration of liquid in an organism (water intoxication) which is characterized by the lowered content of salts or their total absence. Most often such state develops at repeated enteral administration of liquid in an organism (overconsumption of liquid at some types mental disturbances, excess administration of water in a GIT at a gastric lavage);
- Decrease in excretory function of kidneys at a renal failure;
- Circulatory unefficiency with formation of hypostases;
- The increased level of maintenance of ADG (antidiuretic hormone);
- Congestive heart failure;
- Cirrhosis.
Treat main types of an overhydratation of an organism:
- Izoosmolyarny overhydratation of an organism – increase in level of extracellular liquid with normal osmolarity. As a rule, this disturbance has short-term character and quickly is eliminated with an organism on condition of normal functioning of the systems supporting its water balance;
- The Gipoosmolyarny overhydratation – this type of an overhydratation develops at the same time in cellular and intercellular spaces, is characterized by radical disturbance of acid-base and ionic balance, and also membrane potential of cellular structures;
- Giperosmolyarny overhydratation – the overhydratation form developing at the forced use of sea water as drinking at which rapid growth of concentration of electrolytes is observed.
Overhydratation: disturbance symptoms
At an overhydratation symptoms are shown as follows:
- Change of volume of the circulating blood;
- Increase in the ABP;
- Disturbance of cordial rhythms;
- Development of hypostases;
- Disturbance of release of urine (diuresis) – a polyuria, an anury;
- Organism intoxication, vomiting, diarrhea;
- Disorders of psychoneurological character – spasms, apathy, consciousness disturbance, slackness.
In rare instances at an overhydratation erubescence, fervescence, sleep disorders, disgust for food are observed.
At an overhydratation symptoms are subject to the careful analysis for definition of a form of a disgidriya and purpose of the corresponding treatment.
Main effects of an overhydratation
Carry to number of the main effects of an overhydratation:
- Development of hypostases of fabrics – the pathological processes which are characterized by increase in content of liquid in extravasated space of an organism;
- Fluid lungs – a state at which in a pulmonary interstitium the increased liquid level is diagnosed;
- Wet brain – the pathological process which is characterized by excess accumulation of liquid in cells of a head and spinal cord;
- Hyponatremia – one of overhydratation symptoms which is characterized by decrease in concentration of ions of sodium in a blood plasma (level is lower than 135 mmol/l);
- Hypopotassemia – the lowered level of content of potassium in blood provoked by the lowered number of intake of potassium in an organism, its migration in cells of fabrics, its strengthened removal;
- Bystry addition in weight.
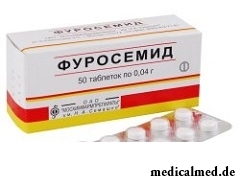
Treatment of an overhydratation
The main risk group of development of an overhydratation of an organism are patients with a renal failure, heart failure, other diseases of kidneys and a liver, and also the people subject to the raised exercise stresses, and also keeping to a rigid diet. In treatment of an overhydratation a key role is played by causes of infringement of a water balance of an organism.
The insignificant overhydratation does not demand additional medicamentous correction. At normal functioning of all systems, the organism independently copes a lot of liquid.
At detection of an overhydratation which symptoms include a headache irritability, confusion of consciousness, dizziness, to patients is recommended to limit liquid consumption.
At hard cases of an overhydratation the drug treatment (are appointed diuretics) directed to recovery of water and electrolytic balance of an organism is applied. In rare instances of an overhydratation the symptomatic treatment is appointed. At irregular shapes of an overhydratation to patients the hemodialysis is appointed.
At observance of a diet the organism lacks for minerals. Patients are recommended to reduce water consumption which surplus can lead to decrease in level of electrolytes in an organism. In order to avoid an overhydratation at the raised exercise stresses, diets the complete elimination of salt is not recommended. For completion of water and electrolytic balance the use of mineral water is recommended.
Having fallen from a donkey, you more likely will kill yourself, than having fallen from a horse. Only do not try to disprove this statement.

Statistically, in Russia about 34% of citizens smoke. Most of consumers of tobacco has problems about health sooner or later...
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" and "assimilation" of information is strongly slowed down. Especially this problem urgent for persons of age becomes more senior than fifty years. "It is already bad with...
Section: Articles about health
Climax - process of fading of reproductive function of an organism in process of its aging. At women the main sign of its approach is the termination of a menstrual cycle. Officially the menopause is diagnosed when periods are not observed within 12 months. Age changes quite often are followed by emotional failures, disturbance of thermal control and sweating, dizzinesses and headaches, tachycardia and other unpleasant phenomena. This complex of symptoms...
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. A contribution of drugs to rescue of people from...
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. However for nonspecialists this disease remains to not less mysterious, than in the ancient time. Many delusions are connected with epilepsy, and it sometimes very unpleasantly affects quality of life of patients and their relatives. In this article we will try to dispel the most known of similar myths....
Section: Articles about health
Very often as a source of the infection which caused a disease serves our house - the place which a priori has to be safe. However...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too h...
Section: Articles about health
The sclera and mucous membrane of an eye are intensively supplied with blood vessels which problem - to saturate nervous tissues of body with nutrients and oxygen. In a normality vessels are almost not noticeable, however at their expansion (owing to thinning of walls) become visible, painting a sclera in red color. Quite often red eyes - the signal of any trouble in an organism caused as external irritants, allergens, and diseases which need in about...
Section: Articles about health
Health and attractiveness - eternal values, pursuing which people often use the most unusual ingredients and technicians...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow
Color of plants is caused by presence at them of certain chemical compounds. Let's talk about what is meant by various colors of vegetables and fruit and what properties they give them....
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead body to decrease in protective forces...
Section: Articles about health
Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. There is even a so-called gastronomic tourism which, according to gourmets, not only allows to receive new feelings, but also is capable to show life the friend...
Section: Articles about health
The business lady, the become mother, it is necessary to solve an array of problems. But of them is main: how to combine the beloved child and work? What traps trap the working mother and how she needs to behave?...
Section: Slideshow
(Xerostomia) many people consider feeling of a xerostomia small and easily removable inconvenience. This delusion...
Section: Articles about health
The person, as well as all other beings living on our planet feels weather changing. It is the normal meteosensitivity which is not causing to healthy people of special troubles. Meteodependence, on the contrary, is morbid condition, характеризующимс...
Section: Articles about health
For many women the word "fat" sounds as a sentence. In aspiration to an ideal figure they try to exclude, first of all, from the menu all dishes containing fats without having at the same time a clear idea of a role of these substances in exchange processes, and of effects for health with which food restrictions of this sort are fraught. For what the human body needs fats and as their deficit in a diet is shown, we also will try to find out....
Section: Articles about health
Coffee - the tonic loved by many for the invigorating aroma and deep taste. Having the stimulating effect, coffee raises ра...
Section: Articles about health
Heart disease and blood vessels lead to disturbance of blood supply of bodies and fabrics that involves failures in their work, deterioration in health of the person, decrease in its working capacity and standard of living. Annually such perishes from pathologies more...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, can only one of ten of our compatriots brag of a decent condition of an oral cavity. Six teeth affected with caries are the share of the average Russian. For comparison, this indicator for Europeans is almost six times less....
Section: Articles about health
Bathing in broths of medical flowers and plants (phytobathtub) was eurysynusic since Cleopatra who is a good judge of everything...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs when walking on heels, frequent painful sprains, pain on average and anonymous toes even after small nagruzo...
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching of oral cavities over health periodically has problems: enamel of teeth darkens under the influence of some products, on it the deposits giving to teeth a grayish or yellowish shade collect....
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal from ку...
Section: Articles about health
It seems, quite recently you brought the baby from maternity hospital, but time flew by, and here it is already going to join the first in life children's collective. How to prepare the child for visit of a garden? What needs to teach him to facilitate process адап...
Section: Articles about health
An eye of the person daily experiences considerable strain. The problem of preservation of sight is for many years directly connected with a question of supply of tissues of eye enough oxygen and nutrients. This task is carried out by small vessels – capillaries. For normal functioning of the visual device extremely important that they kept the integrity, but it works well not always. Microtraumas of eye vessels during which there are small hemorrhages it is extraordinary расп...
Section: Articles about health
