





Ivadal
Application instruction:
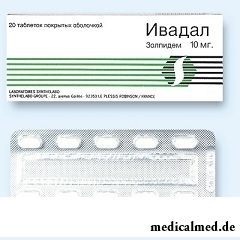 Ivadal – drug with somnolent action.
Ivadal – drug with somnolent action.
Form of release and structure
Ivadal release in the form of tablets, film coated: almost white or white color, oblong, with the line of a break and a text of "SN 10" on one of the parties (on 7 or 20 pieces in blisters, on 1 blister in a cardboard pack; on 10 pieces in the blister, on 2 blisters in a cardboard pack).
Is a part of 1 tablet:
- Active agent: tartrate of a zolpidem – 10 mg;
- Auxiliary components: monohydrate of lactose, sodium carboxymethylstarch (type A), microcrystallic cellulose, gipromelloza, magnesium stearate.
Structure of a cover: titanium dioxide (E171), gipromelloz, macrogoal 400.
Indications to use
Ivadal appoint for treatment of sleeplessness at adults (passing and situational), including difficulties with backfilling, early and night awakenings.
Contraindications
- Respiratory insufficiency (heavy and/or acute);
- Apnoea syndrome in a dream;
- Chronic or heavy acute liver failure (because of risk of development of encephalopathy);
- Inborn galactosemia, deficit of lactase, sprue of a galactose or glucose;
- Age up to 18 years (due to the lack of the clinical data necessary for assessment of efficiency and safety of reception of Ivadal);
- First trimester of pregnancy;
- Hypersensitivity to drug components.
Ivadal patients should take with caution with a heavy pseudoparalytic myasthenia (asthenic bulbar paralysis), functional disturbances of a liver, an alcoholism, drug addiction and other types of dependence (because of the increased risk of emergence of dependence on a zolpidem).
In the II-III trimesters of pregnancy and during a lactation Ivadal's use is not recommended. In need of drug use by pregnant women it is necessary to estimate carefully expected advantage of therapy for health of mother with potential risk for a fruit at this period.
The women of childbearing age receiving Ivadal at the planned or occurred pregnancy have to warn about it the doctor who appointed treatment.
Route of administration and dosage
Ivadal accept inside, just before withdrawal to a dream (inclusion already in beds is possible).
Therapy is always begun with the smallest effective dose, at the same time it is impossible to exceed the maximum daily dose (10 mg).
The recommended adult daily dose makes 10 mg. The weakened or elderly patients and patients with functional disturbances of a liver should accept the initial dose reduced twice (5 mg). Its increase is possible at good tolerance of Ivadal and insufficiency of clinical effect.
Duration of therapy has to be minimum – 2-28 days (including the period of decrease in a dose). Extension of the period of reception of Ivadal from above the most admissible is possible only with extra care after repeated clinical assessment of a condition of the patient.
At passing sleeplessness (for example, during the travel) the recommended duration of use of drug makes 2-5 days, at situational sleeplessness (for example, at the psychoinjuring situation) – 14-21 days.
In case of very short period of therapy gradual drug withdrawal is not required. After long treatment for decrease in possibility of ricochet sleeplessness Ivadal's cancellation should be carried out gradually.
Side effects
During therapy development of disturbances from some systems of an organism which are shown with various frequency is possible (≥10% – are very frequent; ≥1% and <10% – is frequent; ≥0,1% and <1% – sometimes; ≥0,01% and <0,1% – are rare; <0,01% – are very rare, including separate cases; at impossibility of definition from development frequency on the basis of the available data – with an unknown frequency):
- Alimentary system: often – abdominal pains, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting; with an unknown frequency – increase in activity of liver enzymes;
- Central nervous system: often – strengthening of sleeplessness, dreadful dreams, feeling of intoxication, drowsiness, dizziness, a headache, an ecmnesia (can arise at Ivadal's use in therapeutic doses, at the same time the risk of its development increases in proportion to a dose) sometimes along with behavioural disturbances, excitement, hallucinations; sometimes – irritability, confusion of consciousness; with an unknown frequency – excitability, consciousness disturbances, aggression, a dysphoria, visual and auditory hallucinations, behavioural aberrations, circulation in a dream (noctambulation), dependence which can develop even at use of therapeutic doses of drug (after the termination of therapy ricochet sleeplessness or a withdrawal can develop), decrease in sexual desire, an ataxy, disturbance of gait, falling (as a rule, at elderly patients and at non-compliance with the ordered recommendations about reception), accustoming to Ivadal (decrease in somnolent and sedative action at administration of drug within several weeks);
- Musculoskeletal system: with an unknown frequency – muscular weakness;
- Organ of sight: sometimes – a diplopia;
- Allergic reactions: with an unknown frequency – a Quincke's disease, a small tortoiseshell;
- Dermatological reactions: with an unknown frequency – an itch, rash, a hyperhidrosis (plentiful sweating);
- Others: often – feeling of fatigue.
The side effects arising during therapy, especially from the central nervous system, depend on a dose and individual reaction of the patient. Most often they arise at patients of advanced age. Theoretically their expressiveness has to be less at Ivadal's reception just before withdrawal to a dream or already in a bed.
Special instructions
In all cases before Ivadal's appointment it is necessary to establish the reason which caused sleep disorders and to carry out its correction (including medicamentous). At preservation of sleeplessness within 1-2 weeks of therapy it is necessary to pay attention to existence of disturbances from a nervous system and/or primary mental disorders.
At mental diseases Ivadal is not recommended to apply as the main treatment.
Use of drug for patients with symptoms of a depression demands extra care. Because the depression can be one of the reasons of sleeplessness, in cases of preservation of persistent sleeplessness it is necessary to carry out repeated assessment of a mental condition of the patient for detection of a possible depression.
Drug can cause an ecmnesia. Most often this state is observed in several hours after Ivadal's reception therefore for reduction of risk of its development patients have to have conditions for an uninterrupted dream for 7-8 hours.
At Ivadal's use there can be a nervousness, strengthening of sleeplessness, nonsense, nightmares, agitation, psychotic symptoms, hallucinations, euphoria, confusion of consciousness and an onirizm, disinhibition with impulsiveness, the increased suggestibility, excitability, an ecmnesia and aggression. These disturbances can be followed such potentially dangerous to the patient or surrounding with behavioural frustration as: behavior, unusual to the patient, self-aggression or aggression in relation to people who try to prevent dangerous actions of the patient; automatic behavior with his subsequent amnesia. At development of such effects Ivadal's reception should be interrupted. The probability of development of similar disturbances is higher at elderly patients.
At some patients during therapy circulation in a dream and other related difficult behavior was observed: calls by phone, commission of sexual intercourse, preparation and meal at incomplete awakening with amnesia of these actions, driving in a dozing state. Combined use of Ivadal with alcohol and other medicines with the oppressing action on the central nervous system, and also administration of drug in exceeding recommended doses, most likely increases risk of emergence of such behavior. In cases if such changes of behavior are observed, therapy needs to be cancelled.
After course reception of Ivadal for several weeks perhaps some decrease in somnolent and sedative effects.
Long administration of drug can lead to formation of mental and/or physical dependence. The risk of development of dependence increases at increase in a dose of Ivadal and duration of therapy. Also it is higher at patients with instructions in the anamnesis on an alcohol abuse, not medicinal substances or other medicines. Such patients need especially careful observation. However in extremely exceptional cases dependence can develop also at Ivadal's use in therapeutic doses and/or at patients without individual risk factors.
In case of dependence at the termination of administration of drug development of the withdrawal which is characterized by such symptoms as is possible: dysphoria, sleeplessness, irritability, mialgiya, headache, tension of muscles and uneasiness. In more hard cases of a withdrawal can arise (less often): spasms, hallucinations, numbness and paresthesia of extremities, depersonalization, agitation or even episodes of confusion of consciousness, a derealization, excessive sensitivity to physical contact, noise or light.
The withdrawal after the termination of treatment can be observed within several days. At Ivadal's reception development of symptoms of cancellation in a break between two administrations of drug, especially in high doses is possible.
Irrespective of indications to Ivadal's use, the risk of development of dependence increases at its simultaneous use with benzodiazepines.
There are abuses of drug given about cases.
At cancellation of therapy development of ricochet sleeplessness – a passing syndrome in the form of return of sleeplessness in the strengthened form is possible. This disturbance can be combined with other reactions, including concern, changes of mood and a dysphoria.
At Ivadal's appointment patients of advanced age should be careful because of danger of development of myorelaxation and/or sedative effects which can lead to falling with serious effects.
During therapy development of dizziness and drowsiness (especially at simultaneous use with alcohol and/or other drugs with sedative action) is possible that patients whose activity is connected with control of motor transport and performance of other potentially dangerous types of the works demanding bystry psychomotor reactions need to consider.
Medicinal interaction
At simultaneous use of Ivadal with some medicines there can be undesirable effects:
- Ethanol and medicines with the content of alcohol: potentiation of sedative action of Ivadal (simultaneous use is not recommended);
- The drugs oppressing the central nervous system: barbiturates, neuroleptics, other hypnagogues, antidepressants with sedative action, the anxiolytics/sedatives derivative of morphine (antibechics, opioid analgetics), anesthetics, antihypertensives of the central action, antiepileptic drugs, antihistaminic drugs with sedation, a thalidomide, Baclofenum, пизотифен: weakening of psychomotor reactions, strengthening of the oppressing action on the central nervous system and, respectively, risk of respiratory depression that at overdose can lead to a lethal outcome (especially at a combination to barbiturates, morphine derivatives) decline in the ability to management of transport (simultaneous use demands care);
- Buprenorphine: strengthening of risk of respiratory depression up to a lethal outcome (the combination demands care; in need of simultaneous use it is necessary to estimate carefully a ratio advantage/risk);
- Ketokonazol (powerful CYP3A4 inhibitor): insignificant increase in sedative action of a zolpidem;
- Itrakonazol (CYP3A4 inhibitor): insignificant, clinically insignificant change of a pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of a zolpidem;
- Rifampicin (inductor CYP3A4): reduction of efficiency of a zolpidem.
Terms and storage conditions
To store in the place, unavailable to children, at a temperature up to 25 °C.
Period of validity – 4 years.
Each person has not only unique fingerprints, but also language.

One of the major chemical processes happening in a human body are oxidation reactions. They go with participation of fats...
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead to decrease in protective forces of an organism, and it becomes vulnerable for a set of diseases. It is wrong to think that the stress is a problem of the present. Life of people and hundred...
Section: Articles about health
It is difficult to revaluate importance of kidneys for an organism. These bodies not only perform work on purification of blood of decomposition products and removal of excess liquid. They are responsible also for production of some hormones necessary for maintenance of a normality of a bone tissue, and also for a producing red blood cells – erythrocytes....
Section: Articles about health
The popular expression "run from a heart attack" became the motto of the people supporting active lifestyle. Moreover, run became peculiar...
Section: Articles about health
Nightmares belong to the most unpleasant frustration. Statistically, they happen at 4% of adults, and almost at 70% of children and teenagers. During a nightmare of people dreams himself in extremely difficult, life-threatening situation. It wakens suddenly, in...
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. The use of sugar in food is based rather on the psychological dependence caused by desire to indulge itself with something tasty, and further and the biological, caused need of an organism for glucose as a result of big emissions of insulin in blood. Such circulation of insulin and glucose with continuous increase in portions of sugar is rather offensive and can become the reason for a narusha...
Section: Articles about health
Energy saving lamps are one of the most popular products of innovative technologies, and there is no wonder: they much эк...
Section: Articles about health
Tuberculosis – a serious infectious disease which development is caused by mycobacteria (Koch's bacilli). The illness is known from an extreme antiquity. Long time fight against it was considered as ineffective. Quite often the disease affected the whole families, and mortality from it was very much...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, a sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease in physical and intellectual activity and a number of other symptoms reducing quality of life. Abstinence can be strong: an essential part of attempts comes to an end leaving off smoking failure, and people are returned to the use of cigars...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – in...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital within walking distance. And, nevertheless, Internet drugstores become more popular – what it is possible to explain such phenomenon with? Actually m reasons...
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be studied already up and down, and each person, at least once to them had (and the number of such people in our country aims at 100%), has to know the basic rules of its treatment. However as shows experience of doctors, there is no it, and often people, self-confidently thinking what is known as it is necessary to be treated, make mistakes....
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In большинс...
Section: Articles about health
Let's begin with the fact that a separate illness which is called "adjournment of salts", just does not exist. In practice this household name of disbolism leading to development of a number of diseases. Pathological process consists that in an organism проис...
Section: Articles about health
Modern footwear is extremely various. It stopped being only protection for legs long ago. Today shoes, boots, barefoot persons choose not so much proceeding from their convenience and functionality how many being guided by outward, brand and an opportunity to add with them a stylish dress. At the same time, buying footwear, think of its safety a little. Meanwhile, many popular models can do essential harm to health....
Section: Articles about health
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that a plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which is felt by the kid, to...
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some methods of treatment consecrated with "century national experience" can work so on the patient that it will need urgent intervention of physicians....
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also contain...
Section: Articles about health
Tick-borne encephalitis – one of the most dangerous viral diseases which causative agents transfer and is given to people by ixodic mites. These are the small blood-sicking insects living in the considerable territory of our country. The person bitten by a tick can catch...
Section: Articles about health
The healthy nutrition is the invariable principle of health and good health for long years of the woman. Nevertheless, in a diet at each stage of life there are the features allowing to support an organism by those substances which are most necessary for it at present. Eating according to them, the woman will be able to feel vigorous and strong, and also to adapt to changes in an organism so that they allowed it to lead active lifestyle at any age....
Section: Articles about health
The metabolism at each person proceeds in own way. However dependence between the speed of this process and disposal from superfluous in...
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to get access to various apparatuses and an opportunity to train under the leadership of the experienced consultant. Many consider fitness on...
Section: Articles about health
Olive oil – the product capable to make a powerful contribution to health of the person if it includes it in the diet. The rich vitamin composition of oil does it by a product number one from many diseases including from deadly. Only two tablespoons of oil from olives in day prevent emergence of diseases of vessels and heart, cancer, problems with digestion, presenilation, a depression and many other illnesses which treatment would demand a lot of time and forces. Let's consider on...
Section: Articles about health
Work of a brain is extremely complex and in many respects is not studied yet. It is confirmed also by the features of thought processes which are shown in...
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make that process of weight loss did not give you an inconvenience, and, on the contrary, brought joy?...
Section: Slideshow
The modern person not always manages to find housing in the environmentally friendly region and such work which would not do harm to health. With food stuffs at first sight the situation is much better: shops are overflowed with goods which are positioned by producers as very useful and absolutely safe. Many Russians are absolutely sure that the choice of products with marking "bio", "эко" or "organik" guarantees them and members of their families an optimal variant of food. To a sozhala...
Section: Articles about health
