





Nervous system
The nervous system controls activity of all systems and bodies and provides communication of an organism with external environment.
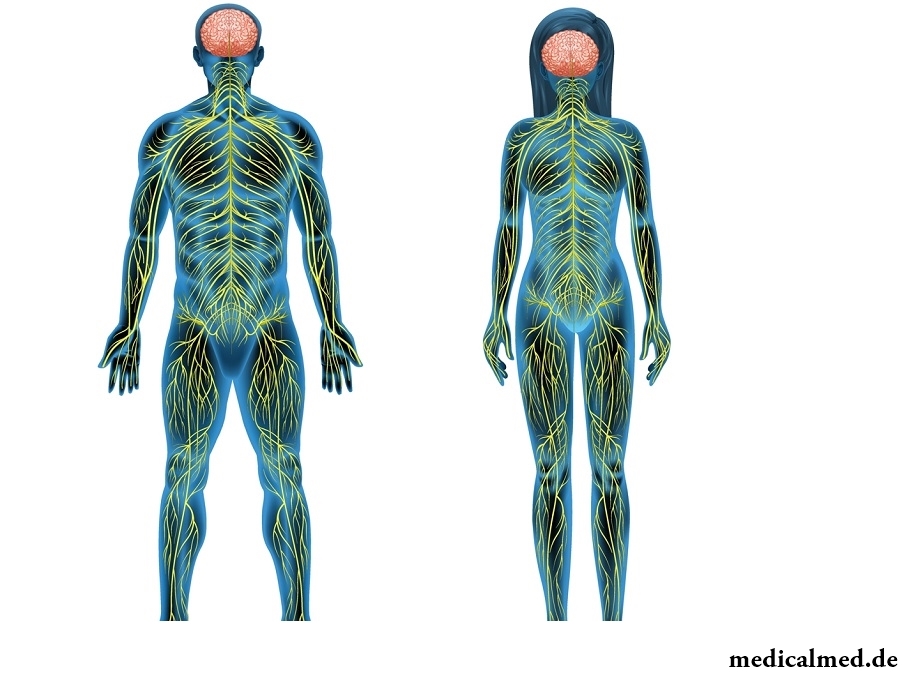
Structure of a nervous system
Structural unit of a nervous system is the neuron – a nervous cell with shoots. In general, the structure of a nervous system represents set of the neurons which are constantly contacting with each other by means of special mechanisms – synapses. On functions and structure the following types of neurons differ:
- Sensitive or receptor;
- Effector – motor neurons which direct an impulse to executive bodies (effectors);
- Switching or inserted (konduktorny).
Conditionally the structure of a nervous system can be divided into two big departments – somatic (or animalny) and vegetative (or autonomous). The somatic system preferential is responsible for communication of an organism with external environment, providing the movement, sensitivity and reduction of skeletal muscles. The vegetative system influences growth processes (breath, a metabolism, allocation, etc.). Both systems have very close interrelation, only the autonomic nervous system is more independent and does not depend on a will of the person. For this reason it still call autonomous. The autonomous system on sympathetic and parasympathetic shares.
All nervous system consists from central and peripheral. Treats the central part back and the brain, and peripheral system represents the departing nerve fibrils from a head and spinal cord. If to look at a brain in a section, it is visible that it consists of white and gray matter.
Gray matter is accumulation of nervous cells (with initial departments of the shoots departing from their bodies). Separate groups of gray matter call still kernels.
White matter consists of the nerve fibrils covered with a myelin cover (shoots of nervous cells of which gray matter is formed). In back and a brain nerve fibrils form conduction paths.
Peripheral nerves share on motive, sensitive and mixed, depending on of what fibers they consist (motive or sensitive). Bodies of neurons whose shoots consist of sensory nerves, are in nerve knots out of a brain. Bodies of motor neurons are in motive kernels of a brain and front horns of a spinal cord.
Functions of a nervous system
The nervous system makes various impact on bodies. Three main functions of a nervous system are:
- Starting, defiant or stopping function of body (gland secretion, reduction of a muscle, etc.);
- Vasomotor, allowing to change width of a gleam of vessels, regulating thereby inflow of blood to body;
- Trophic, lowering or raising a metabolism, and, therefore, consumption of oxygen and nutrients. It allows to coordinate constantly a functional condition of body and its oxygen requirement and nutrients. When on motive fibers to the working skeletal muscle the impulses causing its reduction go, also impulses, the excitometabolic and expanding vessels at the same time arrive that allows to provide a power possibility of performance of muscular work.
Diseases of a nervous system
Together with closed glands the nervous system plays a crucial role in functioning of an organism. It is responsible for harmonious work of all systems and bodies of a human body and combines back, a brain and peripheral system. Physical activity and sensitivity of a body is maintained thanks to nerve terminations. And thanks to vegetative system the cardiovascular system and other bodies is inverted.
Therefore disturbance of functions of a nervous system influences work of all systems and bodies.
All diseases of a nervous system can be divided on infectious, hereditary, vascular, traumatic and chronically progressing.
Hereditary diseases happen genomic and chromosomal. The most known and widespread chromosomal disease is the Down syndrome. This disease the following signs are characteristic: disturbance from a musculoskeletal system, endocrine system, shortage of mental capacities.
Infectious diseases arise owing to influence of bacteria, fungi and parasites. It is possible to rank measles, encephalitis, malaria as diseases of this group, etc. The main symptoms at these diseases are: consciousness disturbance, headache, fervescence, vomiting, nausea.
Traumatic defeats of a nervous system arise owing to bruises and injuries, or when squeezing a head or spinal cord. Such diseases, as a rule, are followed by vomiting, nausea, memory loss, disorders of consciousness, an anesthesia.
Vascular diseases preferential develop against the background of atherosclerosis or a hypertension. It is possible to refer chronic vascular and brain insufficiency, disturbance of cerebral circulation to this category. Are characterized by the following symptoms: attacks of vomiting and nausea, headache, disturbance of a physical activity, sensitivity reduction.
Chronically progressing diseases, as a rule, develop owing to disturbance of exchange processes, influence of an infection, organism intoxication, or because of anomalies of a structure of a nervous system. It is possible to carry a sclerosis, a myasthenia to such diseases, etc. These diseases usually gradually progress, reducing operability of some systems and bodies.
Origins of diseases of a nervous system:
- Viruses (herpes, measles, mumps, chicken pox, HIV);
- Brain bruises;
- Vascular disorders;
- Parasites and fungi (toxoplasmosis, cryptococcosis, malaria);
- Brain tumors.
Also placental way of transfer of diseases of a nervous system during pregnancy (a cytomegalovirus, a rubella), and also on peripheral system (poliomyelitis, rage, herpes, an encephalomeningitis) is possible.
In addition, negatively influences a nervous system endocrine, heart, renal diseases, defective food, chemical and medicines, heavy metals.
Antidepressant Klomipramin causes an orgasm in 5% of patients.

Producers of milk mixes for children assure: mixes are ideally balanced and adapted for needs of babies. In a sluch...
Section: Articles about health
The dietology, as well as other sciences, does not stand still. Food stuffs are exposed to comprehensive study, and scientists obtain new information on their properties and influence on a human body. Unfortunately, this reasonable and natural process from time to time д...
Section: Articles about health
Residents of big cities quite often have a disease which is known as the syndrome of chronic fatigue (SCF) today. This illness affects the people belonging to various social and demographic groups and living on all continents. Most of all SHU are subject women aged from 25 up to 45 years. Statistically, the number of cases fluctuates in the different countries from 10 to 37 people on 100 thousand, but specialists believe that these figures are significantly underestimated as people, страдающ...
Section: Articles about health
According to World Health Organization, every third inhabitant of Earth has excess weight, and every tenth suffers ожирен...
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications of the end of the twentieth century. Researches were conducted since 1984, including placebo - controlled effects. In total клиничес...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. The statistics of incidence is considered not full as at an initial stage the illness, as a rule, does not cause to the person of special inconveniences, and many diseased sees doctors not at once. The cataract is not only one of the most widespread ophthalmologic illnesses, but also the reason of a half of cases of loss of sight....
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot", since ancient times испол...
Section: Articles about health
The healthy nutrition is the invariable principle of health and good health for long years of the woman. Nevertheless, in a diet at each stage of life there are the features allowing to support an organism by those substances which are most necessary...
Section: Articles about health
For the person who daily since morning gathers for work it is very important to wake up vigorous and ready by day of work. Actually, each of us experiences difficulties with this, at first sight, simple business from time to time. After night rest exert impact on a condition of an organism the weather which collected for several days fatigue, household and office problems, quality of a dream and many other factors....
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches....
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include...
Section: Articles about health
Milk and products of its processing by right occupy one of the main places in a diet of the modern person. They contain proteins, necessary for normal life activity, fats, vitamins and microelements, and are an important part of various medical diets....
Section: Articles about health
History of cultivation of a buckwheat contains more than five thousand years. Grain which is received from this plant is used for пригото...
Section: Articles about health
The trophic ulcer is not an independent disease. This heavy complication arising owing to a thermal injury (a burn or a frostbite), chronic pathologies of arteries or veins of the lower extremities, a diabetes mellitus, and also some defeats of a soyeda...
Section: Articles about health
Olive oil – the product capable to make a powerful contribution to health of the person if it includes it in the diet. The rich vitamin composition of oil does it by a product number one from many diseases including from deadly. Only two tablespoons of oil from olives in day prevent emergence of diseases of vessels and heart, cancer, problems with digestion, presenilation, a depression and many other illnesses which treatment would demand a lot of time and forces. Let's consider on...
Section: Articles about health
The pancreas performs two functions in a human body: release of enzymes without which digestion carbohydrate is impossible...
Section: Articles about health
Household skills which to us so diligently imparted in the childhood it appears, not always bring only benefit. According to results of the last researches, some habits which for a long time were considered useful and even necessary can become...
Section: Articles about health
It seems, quite recently you brought the baby from maternity hospital, but time flew by, and here it is already going to join the first in life children's collective. How to prepare the child for visit of a garden? What needs to teach him to facilitate adaptation process? What to tell and how to behave that the kid transferred changes in the life without serious consequences? Let's try to find answers to these questions....
Section: Articles about health
Nightmares belong to the most unpleasant frustration. Statistically, they happen at 4% of adults, and almost at 70% of children and...
Section: Articles about health
Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. The fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding in a family and various illnesses immediately affect a condition of hair and skin. And to look safe and attractive so хоч...
Section: Articles about health
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. However visit of salon where work with biological material of clients, not always harmlessly is conducted. Today more than 100 pathogenic microorganisms who can catch in beauty shop including deadly to health are known....
Section: Articles about health
An eye of the person daily experiences considerable strain. The problem of preservation of sight is for many years directly connected with a question снабж...
Section: Articles about health
Popular joke that there are no healthy people, and is nedoobsledovanny, most of us considers an honest truth, continually it is necessary to hear that all of us are sick hardly from a school bench. It is hard to say, whether so it actually because...
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutrients and receiving pleasure from process of its satisfaction demonstrates that the organism functions without special deviations. On the other hand, appetite of the person is not a constant. It depends on the culture of food, flavoring addictions imparted since the childhood which can change during life, weather, mood and many д more than once...
Section: Articles about health
Sometimes it seems that modern society was divided into two camps: representatives of the first are sure that has to for contraception отвеч...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste, because of to...
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number of myths about negative effect which allegedly gluten has on health of the person....
Section: Articles about health
