





Acoustic organ
Acoustic organ. General information
The acoustic organ at the person is the pair body intended for perception of sound signals that, in turn, influences quality of orientation in the environment.
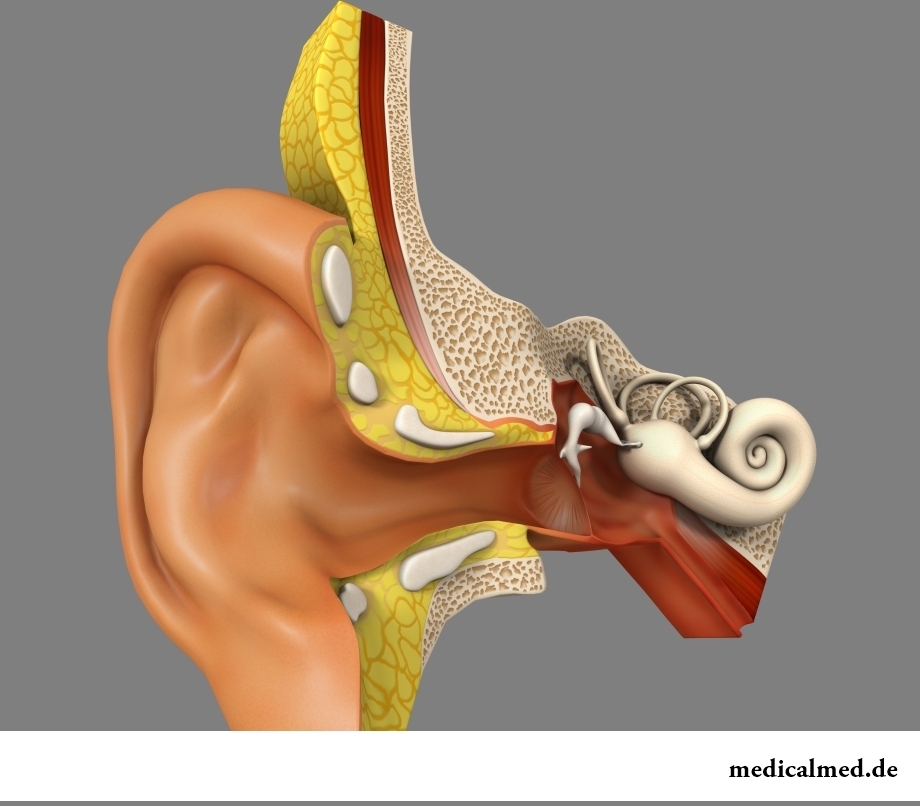
Sound signals are perceived by means of the sound analyzer which main unit of a structure are phonoreceptors. Carries out information in the form of signals the acoustical nerve which is a part of an eighth cranial nerve. A terminal point of reception of signals and the place of their processing – the cortical department of the acoustic analyzer located in bark of big hemispheres in its temporal share. More detailed information on a structure of an acoustic organ is given below.
Acoustic organ structure
Acoustic organ at the person – an ear in which allocate three departments:
- The outside ear presented by an auricle, outside acoustical pass and a tympanic membrane. The auricle consists of the elastic cartilage covered with skin and has irregular shape. In most cases it is not mobile, its functions are minimum (in comparison with animals). Length of outside acoustical pass makes from 27 to 35 mm, diameter – about 6-8 mm. Its main objective – to carry out sound vibrations to a tympanic membrane. At last, the tympanic membrane formed by connecting fabric is an outside wall of a drum cavity and separates a middle ear from outside;
- The middle ear is placed in a drum cavity – deepening in a temporal bone. In a drum cavity three acoustical stones known as a hammer, an anvil, a stirrup are located. Besides, on average to fish soup there is an Eustachian tube connecting a tympanic cavity to a nasopharynx. Interacting with each other, acoustical stones direct sound vibrations to an inner ear;
- Internally the ear represents the webby labyrinth located in a temporal bone. Internally the ear is divided into a threshold, three semicircular channels, a snail. Directly only the snail while two other elements of an inner ear – a part of an organ of equilibrium treats an acoustic organ. The snail has an appearance of the thin cone twirled in the form of a spiral. On all length it by means of two membranes is divided into three channels – a threshold ladder (upper), cochlear channel (average) and a drum ladder (lower). At the same time the lower and upper channels are filled with special liquid – a perilympha, and the cochlear channel is filled with an endolymph. The main membrane of a snail supports кортиев body – the device which perceives sounds;
- Kortiyev body is presented by several rows of the voloskovy cells performing functions of receptors. Except receptor cells кортиев the body contains the cover membrane hanging over voloskovy cells. In kortiyevy body there is a transformation of fluctuations of the liquids filling an ear to nervous impulse. Schematically this process looks as follows: sound vibrations are transferred from liquid, the filling snail, to a stirrup thanks to what the membrane with the voloskovy cells located on it begins to fluctuate. During fluctuations they concern a cover membrane that brings them to an excitement state, and it, in turn, involves formation of nervous impulse. Each voloskovy cell is connected to sensitive neuron which set forms an acoustical nerve.
Diseases of acoustic organs
Protection of acoustic organs and prevention of diseases has to have regular character as some diseases are capable to cause not only disorder of hearing and, as a result, orientation in space, but also to affect sense of equilibrium. Besides, rather complex structure of an acoustic organ, some isolation of a number of its departments quite often complicate diagnosis of diseases and their treatment.
The most widespread diseases of an acoustic organ can be divided into four conditional categories: the inflammatory, noninflammatory, resulted injuries and caused by a fungal invasion:
- Inflammatory diseases of an acoustic organ among which are often meeting otitis, labyrinthitis, otosclerosis arise after the postponed viral or infectious diseases. Carry suppurations, pain and an itch around acoustical pass to displays of otitis of an outside ear. Sometimes a symptom is deterioration in hearing. In the absence of timely treatment otitis quite often passes into a form chronic, or gives complications. The inflammation of a middle ear is followed by the temperature increase expressed by deterioration in hearing, the sharp shooting ear pain. Emergence of purulent discharges is a sign of purulent otitis. At overdue treatment of this disease of an acoustic organ the probability of emergence of injuries of a tympanic membrane is high. At last, otitis of an inner ear causes dizziness, rapid falling of quality of hearing, inability to focus a look. The labyrinthitis, meningitis, brain abscess, blood poisoning can be complications of this disease;
- Noninflammatory diseases of an acoustic organ. Carry to those, in particular, an otosclerosis – the hereditary damage of a bone of the ear capsule causing decrease in hearing. At other disease of an ear – Menyer's disease – the amount of liquid in a cavity of an inner ear which puts pressure upon a vestibular mechanism increases. Symptoms of a disease are vomiting, nausea, a sonitus, the progressing decrease in hearing. One more kind of noninflammatory diseases is eighth cranial nerve neuritis. It can provoke relative deafness emergence. Most often surgical methods are applied to treatment of noninflammatory diseases of an ear, because timely and careful protection of acoustic organs is important that it will allow to prevent deterioration in a course of diseases;
- Fungus diseases of an acoustic organ, as a rule, are caused by opportunistic mushrooms. The course of such diseases complicated quite often leads to sepsis. In certain cases otomycoses develop in the postoperative period, at traumatic injuries of skin, etc. At fungus diseases complaints to allocations from an ear, a constant itch and a sonitus become frequent complaints of patients. Treatment of diseases long, but existence of a fungus in an ear not always provokes development of a disease. Due prevention and care of acoustic organs will not allow a disease to develop.
According to researches, the women drinking several glasses of beer or wine in a week have the increased risk to develop breast cancer.
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that a plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those...
Section: Articles about health
Work of a brain is extremely complex and in many respects is not studied yet. It is confirmed also by the features of thought processes which are shown when the person sleeps. Let's tell about some of them....
Section: Articles about health
Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. The fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding in a family and various illnesses immediately affect a condition of hair and skin. And there is a wish to look safe and attractive so! Substantially competently picked up diet can improve situation....
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
The saying "the rich do not know how the other half lives" is known to all. In a broad sense it is that we can not always understand the person whose features of a state are unknown to us. If with physiological characters of diseases the situation is more or less clearly (having noticed them, we realize that to the person nezdorovitsya), then with symptoms of the illnesses affecting the mental sphere everything is much more difficult. Not absolutely usual behavior is quite often perceived surrounding as a ridiculous eccentricity, or that much ху...
Section: Articles about health
The hysteromyoma is diagnosed more than at a third of women 35 years are more senior. This high-quality new growth, which on early a stage...
Section: Articles about health
The word "onikhokriptoz" is unfamiliar to most of people, meanwhile quite so physicians call very widespread problem: the growing of edge of a nail into surrounding fabrics causing inflammatory process. Usually the illness affects thumbs of legs, and is followed покр...
Section: Articles about health
Not everyone can brag of the shining Hollywood smile. Even the person who is regularly visiting the stomatologist and watching of oral cavities over health periodically has problems: enamel of teeth darkens under the influence of some products, on it the deposits giving to teeth a grayish or yellowish shade collect....
Section: Articles about health
All are familiar with cold, and practically everyone believes that he has sufficient knowledge and experience that correctly to treat it. N...
Section: Articles about health
We present to yours the TOP of the medicamentous means exerting the stimulating impact on a potentiality, i.e. on ability of the man to commission of sexual intercourse. At once it is necessary to tell that not always disturbances of erectile function can be eliminated with reception of t...
Section: Articles about health
An eye of the person daily experiences considerable strain. The problem of preservation of sight is for many years directly connected with a question of supply of tissues of eye enough oxygen and nutrients. This task is carried out by small vessels – capillaries. For normal functioning of the visual device extremely important that they kept the integrity, but it works well not always. Microtraumas of eye vessels during which there are small hemorrhages it is extraordinary расп...
Section: Articles about health
Almost each of us during life faced dissatisfaction with own body. At such moments, as a rule, we beginning...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease физич...
Section: Articles about health
Mushrooms - the surprising inhabitants of our planet having a set of wonderful qualities. Thanks to one of them, a mold mushroom of Penicillium notatum, the first natural antibiotic - penicillin was received nearly 80 years ago. The mankind is obliged to this opening by millions of saved lives....
Section: Articles about health
The number of long-livers is very small. One person from 5 thousand lives up to age of 90 years, and the centenary boundary steps only about...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads...
Section: Articles about health
Since the moment when the child becomes a school student, his sight begins to be exposed to the strengthened loadings which are supplemented with viewing of animated films and long computer games. During this period of life of the child development of not completely created organs of sight, it is very easy to break the excessive loading which is aggravated with lack of a work-rest schedule. As a rule, and occurs: according to WHO statistics, every fourth child of school age has these or those diseases of eyes, Wednesday...
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. To a Torah...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
Osteoporosis this general disease which main sign is decrease in density of a bone tissue. On distribution width it takes the fourth place among noninfectious diseases. The illness develops at mature age more often: in our country about a third of women and a quarter of men suffers from it 50 years are more senior....
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. Use...
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some receptions treating...
Section: Articles about health
The problem of diagnosis was and remains to one of the most important in medicine. From that, the reason of an indisposition of the patient will be how precisely defined, eventually success of treatment depends. In spite of the fact that the majority of the diagnostic methods applied in official clinical practice has very high informational content and reliability, mistakes directed by diagnoses nevertheless are not excluded....
Section: Articles about health
Epilepsy is one of widespread neurologic diseases. To parents, whose children suffer from this illness, it is necessary...
Section: Articles about health
The winter swimming in open reservoirs called in our country by "winter swimming" – officially recognized sport and one of the most extreme ways of a hardening of an organism. This occupation has an old story and adherents in many countries. Are annually carried out...
Section: Articles about health
Reactive pancreatitis - the disease which is characterized by inflammatory process in a pancreas which arises most often because of excess activity of digestive enzymes. It − the emergency state which treatment has to take place in surgical department under control of doctors. The acute inflammation of gland can become the reason of its transition to a chronic form, and also development is purulent - necrotic pancreatitis which the extensive necrosis of fabrics can follow. Zabolev...
Section: Articles about health
