





Jaw osteomyelitis
Short characteristic of a disease
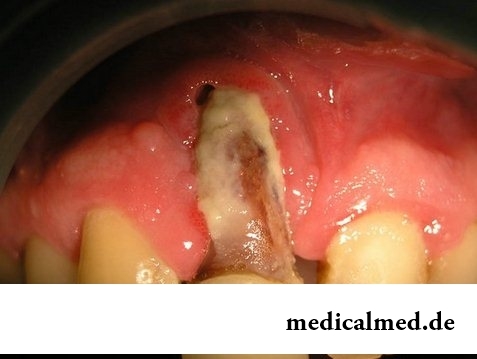
Osteomyelitis of a jaw is one of the most dangerous diseases of a bone tissue. It strikes all elements of a bone, is followed by development of inflammatory and infectious processes, has a set of serious complications. It is enough to tell that jaw osteomyelitis quite often leads to generalization – the phenomenon at which not only a certain area of marrow, but also all bone system of the person in general suffers.
Damages of a bone tissue are known to doctors for a long time. The first references of osteomyelitis of a jaw meet in Avicenna, Galen, Hippocrates and Paracelsus's works, however the reasons and techniques of treatment of inflammations were found only at the end of the 19th century. Then researchers came to a conclusion that osteomyelitis of a mandible is caused by golden staphylococcus. Today gram-negative bacteria, a pyocyanic stick, a klebsiyella and colibacillus are added to number of contagiums. Besides, at the diagnosis jaw osteomyelitis, treatment means antiviral therapy as the inflammation develops in more than 50% of the registered cases against the background of viral infections.
As for ways of penetration of bacteria and viruses to an organism, as a rule, they filter through a painful tooth, or through blood as a result of traumatizing the maxillary device.
Jaw osteomyelitis types
The dontogenous form of a disease is a consequence of the started caries. That is why timely sealing of channels of teeth is so important. From a carious cavity the infection gets into a pulp, and then and into a bone tissue directly through a fang. Besides, microorganisms can extend also on absorbent vessels. Dontogenous osteomyelitis of a mandible develops in 70% of cases at the patient. The rest of defeats is the share of an upper jaw.
Hematogenous osteomyelitis of a jaw is observed at transmission of infection from primary center of an inflammation on healthy sites of fabric. Sources of infection are: tonsillitis and other chronic diseases, acute infections, inflammatory processes.
Acute osteomyelitis of a jaw is a consequence of reaction of an organism to penetration of an infection. The patient feels a headache, an indisposition, weakness, lack of appetite, a problem with a dream. Also at people body temperature up to 38 degrees increases. At the diagnosis acute osteomyelitis of a jaw, treatment has to begin as soon as possible as the patient cannot normally eat because of constant pains and discomfort at a food chewing. In addition, in process of development of infectious process, at the person reddening of a mucous membrane of a mouth, a hyperadenosis and strong mobility of the teeth adjoining to the inflammation center is noted. In certain cases acute osteomyelitis of a mandible leads to damage of a spleen and liver.
Subacute osteomyelitis of a jaw develops if there was no adequate treatment of an acute form. The patient has fistulas and sequesters – devitalized sites of skin. At the same time typical symptoms of an inflammation can become dull because of outflow of liquid and pus, but nothing means as inflammatory process in a bone tissue continues, and every day it becomes more and more dangerous.
Chronic osteomyelitis of a jaw – proceeds is long, and for some time the patient has all external signs of an absolute recovery. Certainly, it is only visibility as inflammatory process continues to develop and, sooner or later, leads to new exacerbations, formation of fistulas, rejection of dead fabrics and formation of sequesters.
Jaw osteomyelitis symptoms
Having summed up all aforesaid, we can allocate several main symptoms of a disease:
- existence of symptoms of poisoning (headache, bad dream, weakness, temperature increase);
- pain around the infected tooth which has property to amplify at a palpation or percussion;
- mobility of teeth in the field of infection;
- swelling of a mucous membrane;
- hyperadenosis.
Jaw osteomyelitis – treatment of a disease
First of all, process of treatment means removal of the infected tooth. Let's note that osteomyelitis of a mandible belongs just to those cases when extraction of tooth is absolutely necessary, otherwise process of an inflammation will extend to healthy fabrics and it will be far more difficult to stop it. Also to patients the early periostotomy – the procedure at which periosteum cuts for free removal of exudate become (liquid which is formed at development of an infection and dying off of fabrics) is appointed. Reception of antibiotics, washing of a bone cavity by antiseptic agents and symptomatic therapy is shown to patients. In especially hard cases doctors make the decision on surgical removal of sequesters.
The most high temperature of a body was recorded at Uilli Jones (USA) who came to hospital with a temperature of 46,5 °C.

At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to spread...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is the prices...
Section: Articles about health
Small appetite at the child – the complaint which pediatricians should hear practically from each mother. Most often it is carried to the category of children's whims, however the refusal of food in certain cases can be to alarming symptoms therefore it cannot be ignored....
Section: Articles about health
Quite large number of people adheres to the principles of vegetarian food. But how to be if in a family of vegetarians is д...
Section: Articles about health
During foot walks blood moves on vessels more actively and one and all bodies are supplied with a large amount of oxygen. It affects the state of health of the person very positively....
Section: Slideshow
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible to find the person who at least once did not try them. At the same time, most of our compatriots have a vague idea of what dietary supplements as they affect a human body consist of and what differ from the real medicines in. Let's try to understand these questions, and at the same time and to understand, such additives are how necessary for us....
Section: Articles about health
Reactive pancreatitis - the disease which is characterized by inflammatory process in a pancreas which arises more often everything...
Section: Articles about health
Work of a brain is extremely complex and in many respects is not studied yet. It is confirmed also by the features of thought processes which are shown when the person sleeps. Let's tell about some of them....
Section: Articles about health
The brain of the person is studied not one hundred years, but the quantity of the riddles connected with this body increases rather, than decreases. Perhaps, numerous delusions concerning a structure and functioning of a brain are explained by it, many of which arose long ago, but continue to exist and today. Such we are ready to acquaint readers with the most widespread myths....
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create since early years...
Section: Articles about health
Modern footwear is extremely various. It stopped being only protection for legs long ago. Today shoes, boots, barefoot persons choose not so much proceeding from their convenience and functionality how many being guided by outward, brand and an opportunity to add with it...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one of the most ancient methods of disposal of the most different diseases. Bathtubs, souls, wrappings and inhalations, in combination with water reception inside help to improve a condition of the patients suffering from disturbances of work of a musculoskeletal system, bodies of digestive tract, cardiovascular, nervous, respiratory and secretory system, skin and endocrine п...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which...
Section: Articles about health
The cosmetics intended for improvement of a condition of skin, nails and hair are used by each woman. Expenses on regular acquisition of the fashionable widely advertized products of well-known companies for many become very notable and significantly to an obrema...
Section: Articles about health
Each woman has preferences in the field of use of those goods which help us to look good, feel young and effective. Besides: selection process of favourite perfume, shampoo or decorative cosmetics already lightens the mood and serves as a peculiar stress medicine. Happens very offensively when the acquired perfumery and cosmetic products not only do not meet our expectations, but also becomes the reason of problems with health. Sources неприятн...
Section: Articles about health
Each person knows that fervescence is an illness sign. However about existence of diseases can to suite...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some methods of treatment consecrated with "century national experience" can work so on the patient that it will need urgent intervention of physicians....
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance physical, ps...
Section: Articles about health
The thought that the mass of their body is too big at least once in life visits from 80 to 95% of women. Many women are so obsessed with this idea that constantly try all new and new ways of weight reduction. Considerable part of these method...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include it in the diet, having given preference "to safer" to vegetable fats. Meanwhile, the last researches showed that harm of butter for health is strongly exaggerated. But the product has a number of unique properties, to...
Section: Articles about health
Such trouble as the milkwoman's attack, at least once in life happened almost to each woman. Prevalence забол...
Section: Articles about health
About 10-15 years ago existence of the computer in the apartment of the Russian was considered as a rarity and office rooms were only at the first stage of equipment by these useful devices. Today practically in each house there is a computer (and often not one), and to constants...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow
Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Nye...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. A contribution of drugs to rescue of people from...
Section: Articles about health
Musicotherapy – a treatment method which caused and causes a set of a controversy concerning its efficiency. However the facts are relentless: during the numerous researches curative impact of music on an organism was scientifically confirmed. Since then in a number of the countries the technique is included complex therapy of diseases of cardiovascular and respiratory system, dorsodynias and a backbone, psychosomatic disturbances and many other illnesses. The musicotherapy in a pedi is especially widely applied...
Section: Articles about health
