Subclavial artery
Structure of a subclavial artery
The subclavial artery represents the pair body consisting of the right and left subclavial arteries supplying with blood a hand and a neck.
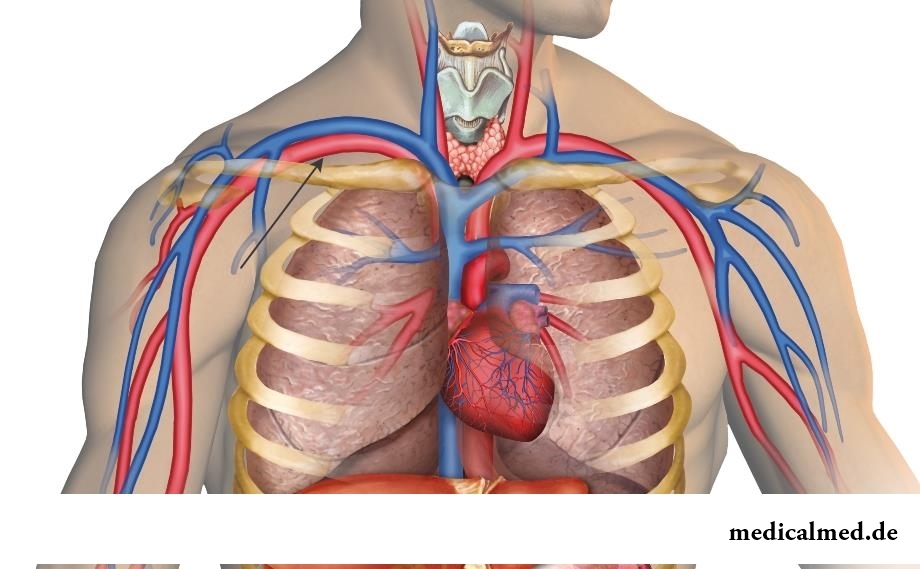
It is a part of a big circle of blood circulation and originates in a front mediastinum: the right subclavial artery proceeds from a brachiocephalic trunk, being its final branch, left departs from an aortic arch. The left subclavial artery is longer than right: its intrathoracic part lies behind a brachiocephalic vein.
The direction of a subclavial artery in relation to an upper aperture of a thorax lies lateralno and up, forming a little convex arch which is bending around a top of a lung and a dome of a pleura.
Having reached the I edge, the subclavial artery comes into an interladder interval which is formed by adjacent surfaces of average and front scalenes. In the specified interval on it there is a brachial plexus.
Having rounded the I edge, the subclavial artery leaves under a clavicle and gets into an axillary cavity where is already called an axillary artery.
Distinguish three main departments of the left and right subclavial arteries:
- The first. Originates from the place of its education to an entrance to an interladder interval;
- The second. Begins in an interladder interval;
- The third. Begins at the exit from an interladder interval up to an entrance to an axillary cavity.
From the first department the following branches of a subclavial artery depart:
- Vertebral artery (a.vertebralis). Its way lies through a transverse foramen of the sixth cervical vertebra, rising up and entering a head cavity through foramenmagnum — a big occipital opening. Further she unites to an artery on the other hand, forming together with it a basilar artery. Function of a vertebral artery — to supply with blood a spinal cord, muscles and a firm cover of a brain (its occipital shares);
- The internal chest artery (a. thoracicainterna) originates from the lower surface of a subclavial artery. It supplies with blood with the nutrients dissolved in it a thyroid gland, primary bronchi, a diaphragm, a breast, a breast, fabric of a front and upper mediastinum, and also a breast and a direct muscle of a stomach;
- Shchitosheyny trunk (truncusthyrocervicalis). Departs from an inner edge of a scalene, reaching length about 1,5 cm, and it is subdivided into several branches which krovosnabzhat a mucous membrane of a throat, a muscle of a neck and a shovel.
The second department of a subclavial artery has only one branch: costal and cervical trunk (truncuscostocervicalis). It originates on the back surface of a subclavial artery and also is subdivided into several branches: a deep cervical artery and the highest intercostal artery from which also spinal branches depart back (the spins conducting to muscles).
Branch of the third department of a subclavial artery is the cross artery of a neck penetrating a brachial plexus and which is subdivided into the superficial artery supplying with blood of a muscle of a back, a deep branch of a subclavial artery and a dorsal artery of a shovel which falls up to a wide muscle of a back, feeding it and the accompanying small muscles.
Damages of a subclavial artery
Stenosis (narrowing of a gleam) – the basic disease affecting a subclavial artery and its branches.
Stenoses, most often, are a consequence of atherosclerotic changes in vessels or fibrinferment. Disturbances of exchange processes in an organism, inflammatory diseases and new growths are the reasons of the acquired (not inborn) stenosis of a subclavial artery.
The deposits on walls of vessels corking an artery have a lipidic basis, being, in fact, cholesterol derivatives.
Narrowing or the stenosis of a subclavial artery reducing about 80% of a gleam of a vessel leads to reduction of a volume blood-groove that results in very negative effect – short-reception by fabrics which krovosnabzhatsya from a subclavial artery, nutrients and oxygen.
The stenosis of arteries often is followed by emergence of the atherosclerotic plaques capable to completely block a blood flow in an artery and to increase probability of emergence of an ischemic stroke.
The main complaint of patients at a stenosis of a subclavial artery: the pain amplifying at exercise stresses, preferential on side of the affected extremity.
Treatment
The main methods of treatment of stenoses of subclavial arteries are:
- X-ray endovascular stenting;
- Sleepy and subclavial shunting.
Sleepy and subclavial shunting is carried out at patients of a hypersthenic constitution (at whom allocation of 1 department of a subclavial artery is accompanied by certain difficulties), and also at detection of a stenosis on the second department of a subclavial artery.
X-ray endovascular stenting has big advantages over open surgical intervention: operation is carried out under a local anesthesia through small (2-3 mm) a section on skin through a puncture opening.
In Great Britain there is a law according to which the surgeon can refuse to do to the patient operation if he smokes or has excess weight. The person has to refuse addictions, and then, perhaps, he will not need an operative measure.

According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but sees a doctor from them меньшинс...
Section: Articles about health
The saying "the rich do not know how the other half lives" is known to all. In a broad sense it is that we can not always understand the person whose features of a state are unknown to us. If with physiological characters of diseases the situation is more or less clearly (having noticed and...
Section: Articles about health
What will only not be thought up by persons interested to have a beautiful figure. Here the last innovation – for weight loss needs to be eaten greasy food. Let's understand whether there is at a fatty diet common sense....
Section: Slideshow
Musicotherapy – a treatment method which caused and causes a set of a controversy concerning its efficiency. However the facts are relentless:...
Section: Articles about health
Any person who faced a disease knows that treatment costs expensive. It belongs also to consultations of qualified specialists, and to the diagnostic procedures which are not included in the list of obligatory medical services. Question of cost of medicinal Wednesday...
Section: Articles about health
History of cultivation of a buckwheat contains more than five thousand years. Grain which is received from this plant is used for preparation of porridges, soups, baked puddings and puddings, do flour which is one of the main ingredients of the noodles popular in many countries of it. Buckwheat dishes are useful and tasty, they are perfectly combined with meat, milk, eggs, mushrooms, fruit and vegetables....
Section: Articles about health
Among a set of the perfumery and cosmetic goods which are released today the special group is made by the means containing anti-bacterial...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too h...
Section: Articles about health
The brain of the person is studied not one hundred years, but the quantity of the riddles connected with this body increases rather, than decreases. Perhaps, numerous delusions concerning a structure and functioning of a brain are explained by it, many of which arose long ago, but continue to exist and today. Such we are ready to acquaint readers with the most widespread myths....
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters in any...
Section: Articles about health
An eye of the person daily experiences considerable strain. The problem of preservation of sight is for many years directly connected with a question of supply of tissues of eye enough oxygen and nutrients. This task is carried out by small vessels – capillaries. For holes...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance of physical, psychological and moral health of the person by means of the complex of procedures including a diet, cleaning of an organism, breathing exercises, massage, and in case of a disease - and medicinal therapy. The healers practicing Ayurveda assign very important part to spices, and at the heart of Ayurvedic drugs, as a rule, there are they. It is considered that spices not of t...
Section: Articles about health
Striya (extension) are the defects of skin having an appearance of direct or wavy strips from 1 to 10 cm long and 1-5 mm wide. In the majority with...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which is felt by the kid, to...
Section: Articles about health
Tea is loved and use almost everything. This drink has tonic properties, contains the tannins capable to suppress activity of causative organisms. Recently great popularity was gained by teas with vegetable additives. The medicative herbs, spices and fruit which are a part of such mixes enrich drink with vitamins and microelements, increasing its nutritional value and creating additional curative effect....
Section: Articles about health
The way of life of people promptly changes from year to year: if about ten years ago the personal computer was not in each family...
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear are similar, however if the fear is natural protective function of mentality, then the phobia is its deviation. So the person can an ispytyva...
Section: Articles about health
The sudden heat on all body which is followed by perspiration and a cardiopalmus – the phenomenon familiar to many people. Most often such states called by "inflows" result from nervous or physical overworks and disappear right after rest. However in certain cases similar reaction of an organism can speak about diseases which need treatment. What? About it below....
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it are...
Section: Articles about health
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions is connected with various factors among which the important place belongs to excessive "clutter" of an intestinal path. In an organism скаплив...
Section: Articles about health
The pancreas performs two functions in a human body: release of enzymes without which digestion of carbohydrates, fats and proteins, and a producing hormones is impossible. The most important of them - insulin, is the main participant of carbohydrate metabolism normalizing processes of education and utilization of glucose, the main energy source for an organism....
Section: Articles about health
About 10-15 years ago existence of the computer in the apartment of the Russian was considered as a rarity and office rooms were only on перв...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital within walking distance. And, nevertheless, Internet drugstores become more popular – what it is possible to explain such phenomenon with? Actually m reasons...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning they laugh and joke, and in the evening cry or are irritated....
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot on...
Section: Articles about health
Stroke (acute disorder of cerebral circulation) – one of the most widespread neurologic diseases. Annually in the world more than 6 million people die of this illness. From the survived patients about 80% become disabled people, and nearly a thirds from them впо...
Section: Articles about health
The advantage of swimming for the person is so high that this sport is not only the most popular, but also is widely applied in medicine and rehabilitation processes. If you look for for yourself the occupation allowing pleasantly and to spend time, then swimming with advantage – the fact that it is necessary for you. And give learns several facts about swimming....
Section: Slideshow