Sweat glands
Sweat glands represent small unbranched structures of a tubular form whose task in 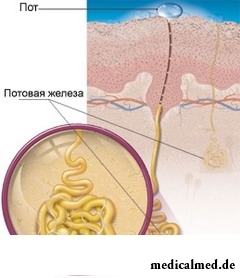 a human body and other mammals consists in development and release of sweat on a skin surface.
a human body and other mammals consists in development and release of sweat on a skin surface.
The human body contains about 2-2,5 million sweat glands located on all body unevenly: their density on square centimeter of skin can vary from 45-400 elements. The greatest density of sweat glands is observed on soles of legs, dorsums of brushes and feet, skin of palms. In particular, stalemate structures do not occur on a balanus and a prepuce at men, and also on the interior of big and small vulvar lips, a clitoris at women.
Structure of sweat glands rather simple: they consist of the secretory balls lying at various depth in a hypodermic fatty tissue and deeper layers of a derma and output channels.
Functions of sweat glands
Allocate two types of sweat glands essentially excellent from each other:
- Ekkrinny (exocrine) sweat glands;
- Apocrenic sweat glands.
Ekkrinny or small sweat glands for 99% consist of water, 1% of structures contains the organic and inorganic matters giving to the surface of skin acid reaction. The total amount of sweat made by ekkrinny glands is regulated by a hormonal and nervous system and depends on density of sweat glands and intensity of their work. On average, exocrine sweat glands of the person excrete about 250-800 ml of sweat a day.
Ekkrinny sweat glands promote maintenance of stable body temperature, and also a conclusion of toxins and harmful substances from an organism. They are responsible for creation on the surfaces of skin hydro - an acid and lipidic film – the natural moistening factor preventing drying of skin.
Apocrenic sweat glands are located, preferential, in axillary hollows, on nose wings, centuries, in the field of generative organs. They do not participate in thermal control processes, however, are capable to react to a stress by means of the viscous secret possessing a specific smell which is formed due to merge of fat and cholesterol. Function of sweat glands of this type – to regulate saprophytic microflora of epidermis, preventing emergence of inflammations of skin.
It is considered that the secret of apocrenic sweat glands excitingly affects representatives of an opposite sex – therefore they are called still glands of a sexual smell.
The peak of activity of work of apocrenic sweat glands is observed at teenage age, and in process of a growing of the person – weakens.
Distinguish several functions of sweat glands of the person. Treat them:
- Sweating or implementation of protective function of a sweat gland;
- Thermoregulatory sweating. It is reached due to evaporation of sweat from the surface of skin;
- Psychogenic sweating. Has fundamental differences from thermoregulatory as it arises only in case of mental tension and after elimination of an irritant instantly stops. As a rule, has local character, being formed on palms, soles of legs, axillary hollows, some sites of the person;
- Besides, sweat glands support secretory function of an organism, exempting it from a number of toxic products of metabolism.
Diseases of sweat glands
The majority of pathologies, work-related sweat glands are caused by existence in a human body of associated diseases. Allocate such disturbances of this body as:
- Anhidrosis;
- Hyperhidrosis;
- Oligogidroz;
- Osmidrosis;
- Hydradenitis.
Anhidrosis – lack of sweating. This disease is caused by either insufficient activity of sweat glands, or defective development of nervous elements. The anhidrosis is one of syndromes of an acute form of cancer of lung.
Oligogidroz – the disease having the general roots with an anhidrosis: it is characterized by insufficient release of sweat and shown, most often, at advanced age due to aging of skin.
Hyperhidrosis – a disease of the increased sweating. She reckons the general and localized. The general hyperhidrosis is shown by uncontrolled release of sweat on all body surface, localized is characterized by the increased perspiration of separate parts of a body – axillary hollows, palms, soles of legs. The hyperhidrosis is observed at the people having a bazedovy disease, tuberculosis, a neurasthenia, psoriasis and neurodermatitis.
Osmidrosis – a disease which is characterized by the unpleasant smell caused by decomposition of sweat under the influence of some bacteria. The osmidrosis can be caused by endocrine disturbances, the increased perspiration, an intertrigo, non-compliance with personal hygiene.
Hydradenitis (inflammation of sweat glands) – a disease which in the people is called "we roll out an udder". It is characterized by a purulent inflammation of sweat glands in axillary hollows, area of vulvar lips and an anus. The hydradenitis symptomatology is as follows: in a hypodermic and fatty layer appears small and painful consolidation which increases further. Skin in the struck place reddens, bulks up, there is a tumor which, when opening, allocates a significant amount of pus.
Hormonal disturbances of an organism (especially, in the period of a climax), and also the obstruction of a sweat gland caused by an intertrigo, grazes, a bacterial infection (streptococci, stafilokokka), frequent use of antiperspirants, insufficient hygiene of skin can be the reasons of a hydradenitis.
Obstruction of a sweat gland, undesirable to organism, can be prevented due to strengthening of immunity, the normal drinking mode, respect for personal hygiene, refusal of the antiperspirants containing aluminum and zinc in favor of usual deodorants.
Removal of sweat glands
Removal of sweat glands 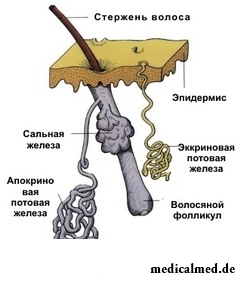 is understood as the surgery designed to stabilize process of sweating at the people suffering from a hyperhidrosis.
is understood as the surgery designed to stabilize process of sweating at the people suffering from a hyperhidrosis.
Distinguish several ways of treatment of a hyperhidrosis in the surgical way:
- Endoscopic sympathectomy. This procedure consists in introduction through a small puncture on a back or a breast of the person of a tube with the video camera by which the surgeon determines the site, "guilty" in the strengthened sweating and cuts the corresponding sympathetic trunk;
- Liposuction of sweat glands. Removal of sweat glands is carried out by introduction to a cannula hypodermic fatty tissue – a hollow needle which as if sucks away sweat glands;
- Curettage. On the site of the increased sweating the small section then under the influence of local anesthesia, there is a scraping of sweat glands by means of special tools becomes.
Removal of stalemate glands is a radical method of a solution of the problem of the increased sweating which result remains for the rest of life.
During life the average person develops neither more nor less two big pools of saliva.

Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary miny...
Section: Articles about health
Tuberculosis – a serious infectious disease which development is caused by mycobacteria (Koch's bacilli). The illness is known from an extreme antiquity. Long time fight against it was considered as ineffective. Quite often the disease affected the whole families, and mortality from it was very much...
Section: Articles about health
Almost each of us during life faced dissatisfaction with own body. At such moments, as a rule, we begin to shame ourselves, urgently we go on the most rigid diet promising minus of 10 kg in a week, or we exhaust ourselves in the gym to almost death. As a rule, similar attempts come to an end with a campaign to the refrigerator for jamming of the next stress. Further history repeats itself with individual frequency....
Section: Articles about health
We live during an advertizing era. Daily each person receives a solid portion of persuasive councils about what to eat to be здо...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need of a visit to the gynecologist. Certainly, it is possible to establish the exact diagnosis only after inspection, but on the basis of some signs it is possible пр...
Section: Articles about health
Energy saving lamps are one of the most popular products of innovative technologies, and there is no wonder: they much more economic also are more long-lasting than usual filament lamps. At the same time there are fears that energy saving bulbs can become the reason of emergence of problems with health. Unfortunately, some of similar opinions have the real reasons....
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters in any...
Section: Articles about health
Long time antibiotics were considered as a panacea from all diseases and were appointed even at insignificant symptoms of an infection. Even now not everyone knows in what force of antibiotics how and when they should be accepted. Let's discredit 7 popular myths about such drugs...
Section: Articles about health
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that the plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those who incorrectly eat smokes and badly brushes teeth. But the paradox is available: at everything the variety of toothpastes, brushes existing today for toothbrushing and conditioners for a mouth the number of the people hesitating of a plaque on teeth does not decrease. Moreover, the plaque is formed even at small children who definitely do not smoke and have no coffee. So in what business, and опас...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit and...
Section: Articles about health
Milk and products of its processing by right occupy one of the main places in a diet of the modern person. They contain proteins, necessary for normal life activity, fats, vitamins and microelements, and are an important part of various medical diets....
Section: Articles about health
Stroke (acute disorder of cerebral circulation) – one of the most widespread neurologic diseases. Annually in the world more than 6 million people die of this illness. From the survived patients about 80% become disabled people, and nearly a third from them needs afterwards permanent care. In fact, the stroke creates a situation at which a part of cells of a brain loses blood access, loses an opportunity to receive oxygen and nutrients, and perishes. As a result of a razviv...
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is the prices...
Section: Articles about health
Osteoporosis this general disease which main sign is decrease in density of a bone tissue. On distribution width it takes the fourth place among noninfectious diseases. The illness develops at mature age more often: in our country about a third of women and a quarter of men suffers from it 50 years are more senior....
Section: Articles about health
The advantage of swimming for the person is so high that this sport is not only the most popular, but also is widely applied in copper...
Section: Slideshow
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice from 40th years of the last century. Originally antibiotics were called only substances natural (animal, vegetable or микробног...
Section: Articles about health
From sexual contacts each person can test insufficiently strongly expressed sexual desire or lack of satisfaction from time to time. However when it happens regularly, it is an occasion to think about health. Most of people does not hurry to ask similar questions physicians: one consider that they will be able to cope with malfunctions independently, others hesitate to report to strangers about so delicate problems and hope that troubles will stop by itself....
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot", since ancient times испол...
Section: Articles about health
Each person supports all life a SARS about 200 times. The peak of incidence falls on cold season, but it is possible to get sick with a temperature and a pharyngalgia, and sometimes and very possibly, even during a heat. The reasons for development of catarrhal diseases exists множество:...
Section: Articles about health
There is a lot of fans of beer in our country. Statistically, on each average Russian (including women and children) in a year about 60 liters of this drink are consumed. It is not a lot of, as in the Czech Republic or Germany, but figure all the same impressive. There is nothing to rejoice here: despite assurances of producers that beer is absolutely harmless, effects of its active consumption cannot be considered positive in any way. Here only part of that negative impact, which popular нап...
Section: Articles about health
For residents of the countries of Southeast Asia various algas are an obligatory component of a daily diet. Their priest...
Section: Articles about health
We present to yours the TOP of the medicamentous means exerting the stimulating impact on a potentiality, i.e. on ability of the man to commission of sexual intercourse. At once it is necessary to tell that not always disturbances of erectile function can be eliminated with reception of t...
Section: Articles about health
The thought that the mass of their body is too big at least once in life visits from 80 to 95% of women. Many women are so obsessed with this idea that constantly try all new and new ways of weight reduction. A considerable part of these techniques is ineffective, and some in general are unsafe for health....
Section: Articles about health
The next flu epidemic leads to the next panic, from year to year we give in on these manipulations: professionally alarming goal...
Section: Articles about health
Each person has easy indispositions which he transfers "standing", trying not to ask for medical care. Arguments at the same time are adduced same: "it is a trifle, itself will pass", "I have too many important issues", "there are no wish to spend time on...
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In certain cases inflammatory process is not limited to discomfort, being followed by emergence of hypostasis, consolidations, temperature increase. At the wrong treatment the acute miositis can lead to a chronic disease or aggravation of other pathologies of a back (vertebral hernia, osteochondrosis) therefore it is important to pay attention to symptoms of an illness in time and to start to...
Section: Articles about health