





Edges
Edges – the arc-shaped pair flat bones which, connecting a backbone and a chest bone, form a thorax. On the thickness the edge seldom exceeds 5 millimeters.
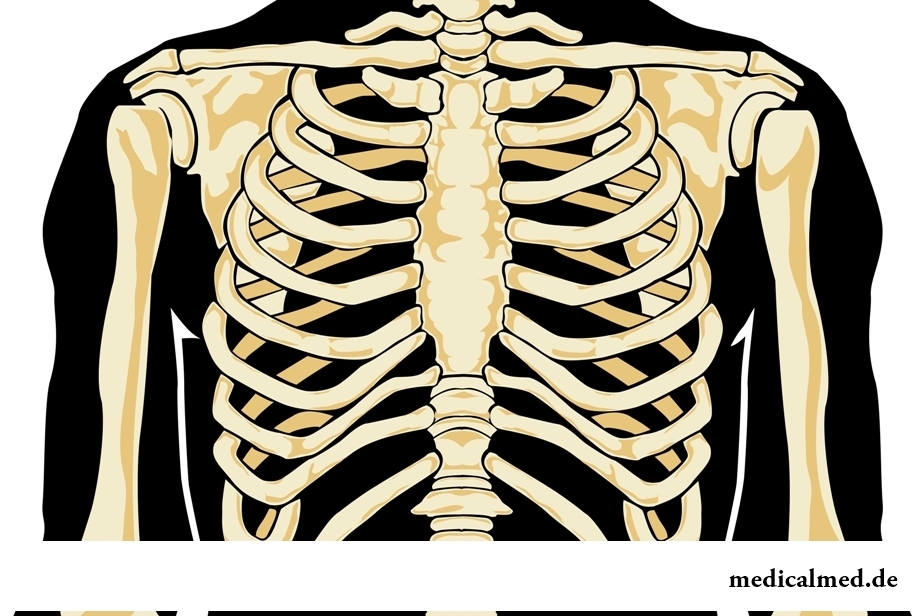
Structure of edges
Edges represent the curved narrow plates consisting from:
- Bones (long spongy bones with a head, a neck and a hillock) – in the longest (back) part;
- Cartilage – in shorter (front) part.
The body of an edge has internal (concave) and outside (convex) the surfaces limited rounded off and acute to edges. Vessels and nerves are located in the furrow passing on an internal surface of bottom edge.
At the person up to twelve edges on each party which are connected to bodies of chest vertebrae the back ends. Edges on a way of fastening divide into three groups:
- Seven upper edges (true edges) the front ends connect directly to a breast;
- Three following, false edges, are connected by the cartilages to a cartilage of the previous edge;
- Two lower edges (the fluctuating edges) the front ends lie freely.
Connect to a breast and vertebras of an edge by means of all types of connections:
- Synarthroses (syndesmoses and synchondroses);
- Symphyses;
- Diarthrosis.
The thorax is covered by a connective tissue cover from within, at once under which the pleura consisting of two smooth leaves is located. Freely allows to slide between leaves at breath a thin layer of lubricant.
Function of edges
Treat the main functions of edges:
- Protective function. Edges, forming a thorax, close heart, easy and large vessels from injuries and external influences;
- Frame function. The thorax promoting deduction of bodies in a chest cavity in the necessary situation does not allow heart to be displaced in the parties and to be fallen down by a lung.
Fracture of edges
It is possible to allocate three main groups of the reasons because of which edges hurt:
- Damage of the internals located directly in a thorax;
- Defeat of vessels and nerves;
- Disturbance of a framework of a chest wall.
The fracture of edges belongs to one of the most widespread injuries of a thorax and, as a rule, meets at elderly people more often that is connected with age change of elasticity of bone structures of a thorax.
Most often injuries as a result are the reasons of a fracture of edges:
- Falling;
- Direct stroke to the area of edges;
- Thorax prelums.
Edges break more often on the side surfaces of a thorax (in places of the greatest bend) that causes pain in this area. In many cases of an edge hurt not right after an injury, and a bit later when bone fragments begin to rub at breath (especially at a breath) and the movement.
The partial disturbance of integrity of an edge without the shift of bone fragments arising because of an injury or pathological process in an organism is called an incomplete change.
The incomplete change can arise both because of an injury, and because of defeat of an inert part of an edge the pathological process leading to reduction of durability of a bone tissue, for example:
- At osteoporosis (states at which salts of calcium are washed away from a bone tissue);
- At development of tumors in a thorax;
- At tuberculosis of edges;
- At a chronic inflammation of a bone tissue of an edge;
- At diseases of blood (multiple myeloma).
Uncomplicated fractures of one or several edges usually do not represent threat for health and human life. The main danger at this injury is:
- Internal injury;
- Breath disturbance;
- Development of the accompanying complications.
More serious danger is constituted by multiple fractures of edges that is connected with increase of risk of development of plevropulmonalny shock and life-threatening complications (for example, pheumothorax and a hemothorax). Besides, at a multiple fracture it is often observed by the shift of fragments which pose a threat for a pleura, easy and intercostal vessels because of the acute ends.
Also the change can bring:
- To development of the hypodermic emphysema caused by penetration of air into hypodermic cellulose at injury of a lung;
- To plentiful bleeding in soft tissues or a pleural cavity at damage of intercostal vessels.
At multiple fractures edges strongly hurt, at the same time pain amplifies at the movements, breath, cough, a conversation and decreases at rest and in a sitting position. Also at multiple fractures of edges shallow breathing and lag of a thorax on the party of defeat is observed.
The broken rib comes to light at a palpation as the most healthy place, and also on a peculiar crunch of bone fragments (bone crepitation). The diagnosis can usually be confirmed by means of a thorax X-ray analysis, and in suspicion cases on pneumo - and a hemothorax it is necessary to carry out in addition ultrasonography of a pleural cavity, a roentgenoscopic research and a pleurocentesis.
To thicket front and side fractures of edges which are, as a rule, transferred more hard are followed by disturbance of breath. Damage of back departments of edges causes disturbance of lung ventilation less often.
Treatment of a fracture of edges
At a fracture of edges in most cases fixing is not required, except for the complicated and multiple fractures which treatment has to take place only in hospital conditions.
Fixing of a thorax without indications can lead to a bigger restriction of breath that in turn promotes development of developments of stagnation, including congestive pneumonia.
The average term of treatment of uncomplicated fractures of edges – about one month, and term of treatment of the multiple and complicated changes depends on the general state and weight of the arisen complications.
In operating time our brain spends the amount of energy equal to the 10 Watts bulb. So the image of a bulb over the head at the time of emergence of an interesting thought is not so far from the truth.

The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot", since ancient times испол...
Section: Articles about health
Hemorrhoids – extremely widespread disease. Periodically arising inflammations and bleeding of hemorrhoidal nodes cause serious discomfort to nearly fifteen percent of adults. Meanwhile, having a clear idea of the aggravation reasons...
Section: Articles about health
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As a rule, the varicosis affects preferential superficial vessels, and is shown by characteristic cosmetic defects. The deep vein thrombosis as this illness at the initial stages can imperceptibly proceed is represented much more dangerous, and in the started cases threatens with serious danger – thrombosis. This state, when the blood clot formed...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal from ку...
Section: Articles about health
The fatigue, sleep debt, disturbances of food, bad mood, vagaries of the weather – all these circumstances badly affect our appearance. Especially the person suffers: skin becomes flabby, loses healthy color, becomes covered by wrinkles, zones of hypostases and t appear...
Section: Articles about health
Each person supports all life a SARS about 200 times. The peak of incidence falls on cold season, but it is possible to get sick with a temperature and a pharyngalgia, and sometimes and very possibly, even during a heat. The reasons for development of catarrhal diseases there is a set: from the weakened immunity till an excess portion of ice cream....
Section: Articles about health
About influence of fasting days on an organism it is told much – both about advantages, and about shortcomings. It is considered that fasting day...
Section: Articles about health
Modern footwear is extremely various. It stopped being only protection for legs long ago. Today shoes, boots, barefoot persons choose not so much proceeding from their convenience and functionality how many being guided by outward, brand and an opportunity to add with it...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads, to slopes of ravines, on heathlands. Also several cultural versions different from wild plants are removed by larger and juicy root crops....
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear...
Section: Articles about health
Transfusion of donor blood has almost century history. In spite of the fact that this procedure is quite usual for many people, process of blood donation is still surrounded with numerous myths. Today we aimed to discredit the most widespread of them....
Section: Articles about health
The healthy nutrition is the invariable principle of health and good health for long years of the woman. Nevertheless, in a diet at each stage of life there are the features allowing to support an organism by those substances which are most necessary for it at present. Eating according to them, the woman will be able to feel vigorous and strong, and also to adapt to changes in an organism so that they allowed it to lead active lifestyle at any age....
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn...
Section: Articles about health
The hysteromyoma is diagnosed more than at a third of women 35 years are more senior. This high-quality new growth which at early stages successfully resolves by means of medicines. It is necessary to resort to an operative measure only in those a case...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often give trouble, serving as the reason of a headache, an acrimony, sleep disorders, and in certain cases and the states close to a depression. How to get rid of undesirable satellites of a disease if near at hand there are no antiallergic...
Section: Articles about health
According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but sees a doctor from them меньшинс...
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. According to nutritionists, the separate use of the carbohydrate and proteinaceous products demanding different conditions of assimilation helps to get rid from Bol...
Section: Articles about health
The chia plant, or the Spanish sage, is from South America. The indigenous people of the continent since ancient times used its seeds in food: small, but very nutritious kernels, in a form the reminding fasolina. Indians knew about useful properties of seeds of a chia, and applied them to maintenance of vitality and increase in endurance before serious exercise stresses....
Section: Articles about health
Zone hypostases under eyes - very widespread problem giving to people is a lot of inconvenience. Hypodermic fabric in these parts having...
Section: Articles about health
All know that self-treatment is dangerous. However absolutely it is almost impossible to do without it. Rate of modern life does not allow to handle each small trouble to the doctor and information on ways of independent rendering medical the help...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it receive only useful substances, necessary vitamins and microelements. In this case there will be no problems with digestion, with excess weight, and intellectual and physical activity will remain at the high level....
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In большинс...
Section: Articles about health
Each person knows that fervescence is an illness sign. However too low temperature (hypothermia), especially also can demonstrate existence of diseases when it is observed long enough. Such state is dangerous those...
Section: Articles about health
All like to sing. Small children with pleasure are engaged in a vocal, not especially thinking of hit in a melody. Adults most often hesitate, being afraid to show lack of talents in this area, and it is vain: singing is very useful for health....
Section: Articles about health
Color of plants is caused by presence at them of certain chemical compounds. Let's talk that various colors mean vegetable...
Section: Articles about health
Popular joke that there are no healthy people, and is nedoobsledovanny, most of us considers an honest truth, continually it is necessary to hear that all of us are sick hardly from a school bench. It is hard to say, whether so it actually because...
Section: Articles about health
To look healthy and means well-groomed not only to be pleasant to people around, but also to feel strong, sure and taken place. Specialists in the field of cosmetology quite often note that not all women are able to look after face skin. Many women incorrectly apply cosmetics, ineptly use various procedures, without having exact information on their real influence and dividing numerous delusions about it. All this not the best...
Section: Articles about health
