





Heart
Heart represents the hollow muscular body having the cone-shaped form. Its main function is pumping of the blood coming to it on venous trunks in an artery. Relaxation of a muscle of heart is called a diastole, and reduction – a systole.
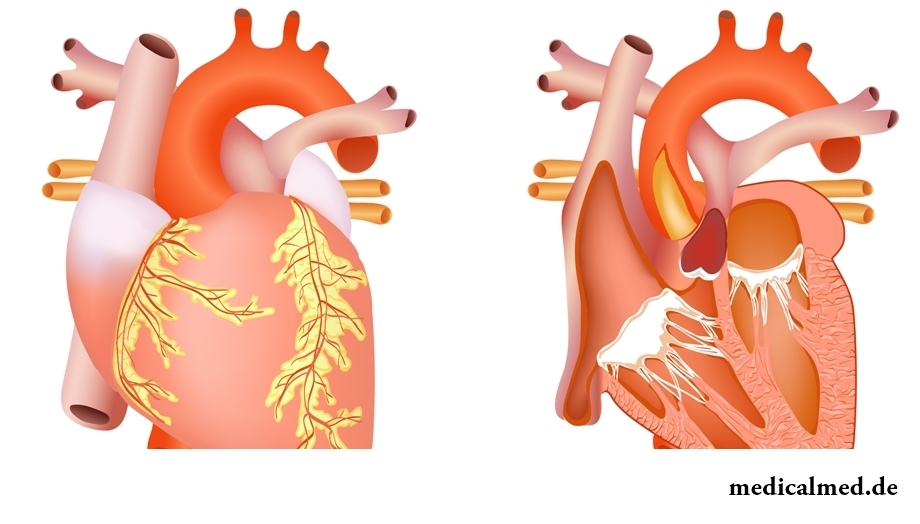
Heart structure
Heart is located in the left part of a thorax. Outside of it covers the pericardium forming a cordial bag in which a small amount of serous liquid contains. The middle muscular part of heart is called a myocardium. Inside the cardial cavity by means of partitions is divided into four cameras: two auricles and two ventricles. Blood comes to the left auricle on pulmonary veins, and in right on venas cava. The left ventricle leaves the ascending aortic arch, and from right – the pulmonary arteries forming pulmonary a trunk. In the camera of heart are covered with extremely smooth cover – an epicardium.
The right auricle and left ventricle close a big circle of blood circulation, and the left auricle and a right ventricle – a small circle.
Heart structure in the right and left department variously. So, for example walls of a right ventricle are almost three times thinner, than a left ventricle. It is connected with the fact that at reduction of the last blood is pushed out in a big circle of blood circulation and goes to all bodies and body tissues. In addition resistance and pressure in a big circle are much higher, than in small.
Valve device of heart
The structure of heart is unique since blood in it flows only in one direction. It is provided with its valve device. Valves in the fullness of time open, passing a blood flow, or are on the contrary closed, interfering with the return current (regurgitation).
Between the left ventricle and an auricle the double-wing (mitral) valve is located. It has two shutters. At the time of its opening blood from the left auricle through an atrioventricular opening comes to a left ventricle. At reduction (systole) of a left ventricle of a shutter of the valve are closed, and blood directs in an aorta.
The three-leaved or tricuspid valve is located between the right ventricle and auricles. At the time of its opening blood freely passes from the right auricle in a right ventricle. Shutters of this valve are closed at the time of a systole of a right ventricle. As a result of it blood cannot back come to an auricle and the trunk is pushed out in pulmonary.
At the very beginning of a pulmonary trunk one more valve which function is prevention of the return blood flow in a right ventricle during its diastole is located.
The entrance to an aorta closes the aortal valve having three semi-lunar shutters. It opens at the time of a systole of a left ventricle and is closed at its diastole.
Many heart troubles are caused by pathology of its valve device.
Blood supply of heart
Directly two coronary (coronal) arteries depart from an aorta. They disperse on a set of branches which like a wreath braid all heart, providing intake of oxygen and nutrients to each its cell. Through coronary arteries there passes the fifth part of everything of the blood volume which is thrown out in an aorta.
Regulation of cardiac performance
Reductions and relaxations of heart are regulated by the potassium ions which are contained in blood and calcium, and also an endocrine and nervous system. The nervous system is directly involved in regulation of force and heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous system weakens effort of reductions, and sympathetic on the contrary strengthens them.
The endocrine system influences cardiac performance by means of hormones which can lead to change of heart rate, their strengthening or easing. For regulation of action of the heart adrenal hormones – acetylcholine and adrenaline which action is similar to impact on a myocardium of a parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system have the greatest value.
Heart troubles
In recent years around the world cardiovascular diseases mortality grows. All heart troubles, depending on the reason and the nature of their emergence, can be divided into several groups conditionally:
- Functional;
- Inborn;
- Atherosclerotic and hypertensive;
- Syphilitic;
- Rheumatic.
In addition there is a number of heart troubles which do not get to the listed above categories and it is necessary to tell about them separately. Treat them:
- Acute dilatation (expansion) of heart. This pathology results from the expressed weakness of a myocardium and an overload of departments of heart in the large volume of blood;
- The atrial flutter – consists in the accelerated regular reduction of auricles behind which ventricles do not manage to be reduced;
- Fibrillation of auricles – at this state is observed the chaotic accelerated reduction of separate muscle fibers of auricles therefore the full-fledged systole is not observed. Fibrillation of auricles is observed against the background of heart failure;
- Bouveret's disease – periodically arising attacks of sharply speeded up reductions of heart;
- The thrombosis of coronal vessels arising against the background of atherosclerosis;
- Myocardial infarction;
- The heart failure which is a final outcome of any heart trouble.
Diagnosis of heart troubles
The modern medicine has great opportunities for carrying out exact and timely diagnosis of heart troubles. Among tool methods in cardiology X-ray, electrophysiologic and electrocardiographic inspections, catheterization of vessels of heart, an echocardiography, a positron and issue and magnetic resonance tomography are most often used. Diagnosis of heart troubles is accompanied by insignificant risk which increases at increase in severity of a disease and technical complexity of the procedure.
Cardiology: treatment of heart
Cardiologists are engaged in therapy of heart diseases. Treatment of heart can be conservative or surgical. An operative measure is shown at numerous defects of the valve device. In this case perform reconstructive operations or replace worn-out valves with artificial. Surgeries carry out also at a row inborn heart diseases.
Conservative treatment of heart is carried out in case of arrhythmias, coronary heart disease, heart failure. At inefficiency of conservative therapy there are indications to an operative measure.
According to WHO researches the daily half-hour conversation by the mobile phone increases probability of development of a tumor of a brain by 40%.

It is pleasant to state a possibility of improvement of quality of life of people with problems of functioning of secretory system. By efforts that...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant, but not exhausting a physical activity. In the presence of various illnesses specialists often advise patients to do swimming which by right borrows ведущ...
Section: Articles about health
For the time being the perspective of heart diseases seems to most of people remote and foggy. But sooner or later practically each adult faces extremely unpleasant feelings: sudden stethalgia. To be consoled at this time in a thought of what for a heart attack still early, will hardly turn out: if the person is impressionable, he, as a rule, has feeling of panic and fear of fast death. And meanwhile, it is very often possible to confuse pains with cardiac pains невралгическог...
Section: Articles about health
Water with a lemon - idle time in preparation drink which supporters of a healthy lifestyle already managed to appreciate. Upo...
Section: Articles about health
For residents of the countries of Southeast Asia various algas are an obligatory component of a daily diet. Their popularity is connected not only with high tastes, but also with numerous curative properties. Russians are a little familiar with...
Section: Articles about health
Epilepsy is one of widespread neurologic diseases. Parents, whose children suffer from this illness, should face rumors and delusions, many of which remained since the Middle Ages....
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, at the address to doctors seven of each ten patients complain of a headache. Actually people, periodically...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is the prices...
Section: Articles about health
Diapers for adults – individual one-time means of hygiene which in some situations is irreplaceable and from such situations any person is not insured. Though nobody perceives need of their use with enthusiasm, however without such means already problematic situation could be heavier....
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. Statistics we get sick...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include...
Section: Articles about health
The summer of this year in Russia was very ambiguous. Regions suffered from a merciless heat, from pouring rains, the hail from time to time dropped out, then there was again a heat which alternated with rainfall again. Many people suffer from such sharp changes of weather. Even flu epidemics and a SARS were recorded....
Section: Articles about health
The medicine promptly develops, and the fact that else quite recently it seemed by miracle can now. We are not surprised any more to the fact that sport...
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn – whether you have or your relatives problems....
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be studied already up and down, and each person, at least once to them had (and the number of such people in our country aims at 100%), has to know the basic rules of its treatment. However as shows experience of doctors, there is no it, and often people, self-confidently thinking what is known as it is necessary to be treated, make mistakes....
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In большинс...
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, not too modest, and excessively curvy shapes become the reason of sincere discomfort sometimes. Except psychological problems, a big bust sometimes with...
Section: Articles about health
In consciousness of our many compatriots idea that folk remedies if are no more effective, than medicinal "chemistry" strongly took roots, then are precisely less harmful. Unfortunately, it is not always fair: some methods of treatment consecrated with "century national experience" can work so on the patient that it will need urgent intervention of physicians....
Section: Articles about health
Healthy lifestyle today in fashion, and many parents think of that the child from the early childhood played sports. To a Torah...
Section: Articles about health
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. However visit of salon where work with biological material of clients, not always harmlessly is conducted. Today it is known Bol...
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make that process of weight loss did not give you an inconvenience, and, on the contrary, brought joy?...
Section: Slideshow
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor about age...
Section: Articles about health
The mankind knows that some toxins at intake in the minimum quantities have therapeutic effect from an extreme antiquity. Many substances recognized poisonous are applied in the medical purposes also today, being the main deystvuyushch...
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutrients and receiving pleasure from process of its satisfaction demonstrates that the organism functions without special deviations. On the other hand, appetite of the person is not a constant. It depends on the culture of food, flavoring addictions imparted since the childhood which can change during life, weather, mood and many д more than once...
Section: Articles about health
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches....
Section: Articles about health
The sudden heat on all body which is followed by perspiration and a cardiopalmus – the phenomenon familiar to many people. Most often such states called by "inflows" result from nervous or physical overworks and disappear right after rest. Odn...
Section: Articles about health
Food with the increased content of sugar is attractive to most of people - it is scientifically confirmed fact. Business here not in intemperance or dissoluteness: the sweet food is associated since childhood with feeling of rest and safety which tests the kid when it absorbs maternal milk. Besides, getting into a human body, sugar strengthens production of "happiness hormones" which all of us so need. And still life of sweet teeth seldom happens cloudless: their too big loss...
Section: Articles about health
