





Large intestine
The large intestine belongs to final department of a digestive tract.
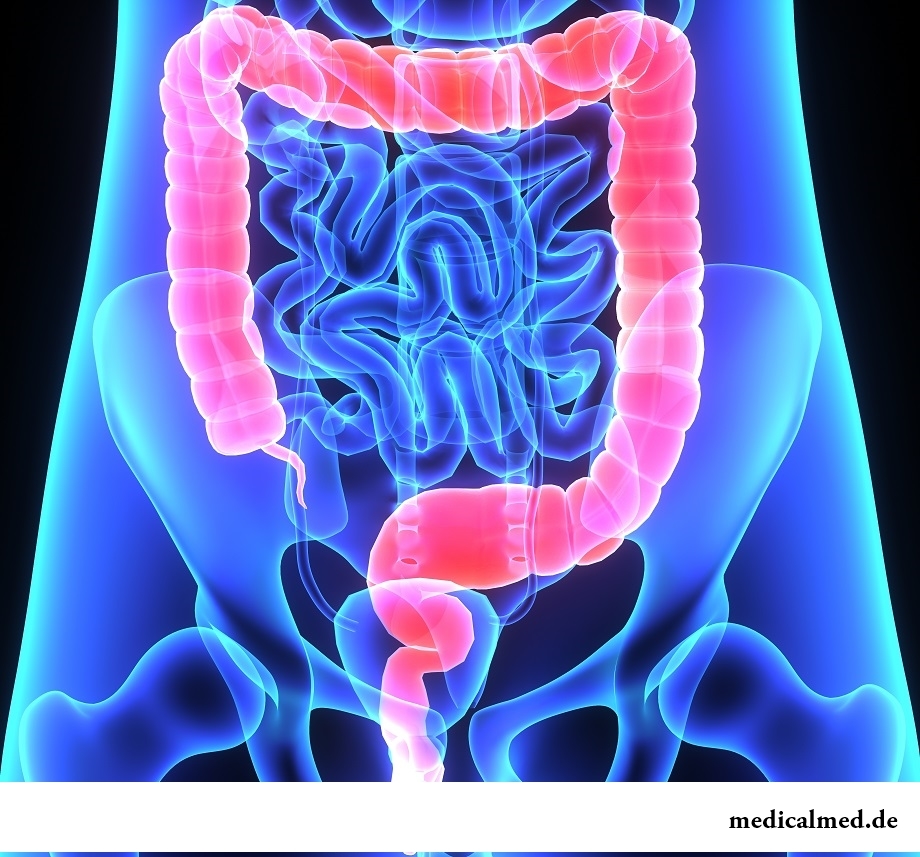
This body is placed in an abdominal cavity and in a small pelvis.
Anatomists divide a large intestine into several departments: a caecum with an appendix, colonic (ascending, cross, descending, sigmoid) and a rectum.
Average diameter of a large intestine fluctuates from four to ten centimeters. Length of a large intestine makes one-two meters.
The caecum is located in the field of transition of an ileal gut to a large intestine. Length of body – 6-8 cm, average diameter – 7 cm.
The caecum passes into the ascending colon with two bends – right (hepatic) and left (splenic). Between bends in an abdominal cavity it passes into a cross colon which length averages 40-50 cm. Its situation depends on age, and also on constitution type. In the left part of an abdominal cavity the cross gut passes into the descending gut.
The descending gut, reaching the left ileal pole, passes into a sigmoid colon which length varies from 16 to 67 cm. This gut has an appearance of two loops which size and a form are subject to essential individual variations. The sigmoid gut is placed intraperitoneally and from all directions is covered with a peritoneum. The gut is attached by a mesentery to a back abdominal wall that provides its mobility.
Rectum – final department of a large intestine. Its narrowest part passing through area of a crotch is called the proctal (anal) channel. The proctal channel comes to an end with an opening - an anus (anus).
In an anatomic structure of a wall of a gut allocate four layers - a mucous membrane, a submucosal layer, a muscular layer and a serous cover.
Inside layer of a large intestine is the mucous membrane. Throughout a gut it is covered with a cylindrical epithelium, and near the proctal canal – a cylindrical and squamous (flat) epithelium. In some sites (around anorectal transition) the proctal channel is covered by anodermy – the epithelial vystilka of special type which is not containing sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
The mucous membrane forms numerous folds. In ampullar department they cross, in proctal department – longitudinal. Distinguish three constant folds of cross type - upper, lower and average. The submucosal layer is presented by the connecting fabric containing lymphatic and blood vessels. The muscular layer consists of outside longitudinal and internal circular muscles.
Functions of a large intestine
Let's list the main functions of a large intestine:
- Digestive function of a large intestine consists in final processing of the remains of food enzymes (release of water and residual nutrients). In a caecum process of consolidation of liquid contents of intestines begins;
- Soaking up – water and nutrients spread from the blind person ascending and the descending departments of a large intestine of all bodies via circulatory and lymphatic channels;
- Muscular (motor) – a large intestine strengthens or reduces the frequency of reductions of muscles, thereby providing continuous advance of a chyme on the digestive channel.
Besides, the large intestine through an anus removes substances, toxic and useless for an organism.
Inflammation of a large intestine
Inflammation of a large intestine (colitis) – the most widespread disease of digestive tract.
Rough errors in food, various infections, hit in an organism of household and industrial poisons can be the reasons of an inflammation of a large intestine. In certain cases the inflammation arises repeatedly as the independent disease having the immune nature or as a result of the disturbances which happened in a small bowel or a stomach.
Now allocate a chronic, acute, ulcer and spastic inflammation. Symptoms of display of a disease is emergence of slime and impurity of blood in fecal masses, breakdown, slackness, temperature increase, the increased gas generation, diarrhea, appetite loss.
Ulcer colitis - an inflammation mucous a large intestine, followed by formation of ulcers. At this form of an inflammation most often the periods of an aggravation are replaced by the remission periods. The first symptom of ulcer colitis - a colicy pain in the lower area of a stomach.
At a spastic colitis the fecal mass of the patient in a form reminds dense lumps.
Polyps of a large intestine call outgrowths of a mucous intestinal wall. Similar growth of mucous can have the form of a sphere, a mushroom, a semicircle (without leg or on a leg).
Polyps of a large intestine represent high-quality new growths most of which often regenerate in cancer (through five – ten years after their education). Growth of polyps considerably slows down motility of intestines that can result in its impassability.
Most often formation of polyps happens asymptomatically, but sometimes growth of mucous is followed by pain, emergence of slime and blood in fecal masses. Kolonoskopiya - the main diagnostic method of polyps.
Large intestine – treatment
Treatment of a large intestine consists in purpose of a special diet and medicines (antiseptic agents, analgetics, spasmolysants, laxatives, calmatives, vitamins, bacterial drugs), medical enemas. A medical enema – one of the most effective methods of treatment of a large intestine.
All types of polyps of a large intestine are removed in the surgical way. For cauterization of polyps in medicine use an electrothermic coagulation method.
In Great Britain there is a law according to which the surgeon can refuse to do to the patient operation if he smokes or has excess weight. The person has to refuse addictions, and then, perhaps, he will not need an operative measure.

Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on is called...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning...
Section: Articles about health
New year, wedding, birthday, office party – an occasion to drink at the Russian person will always be. How to reduce a negative impact of alcohol by an organism and to avoid a condition of strong intoxication? The most correct council – to refuse the use of alcoholic drinks. Council is true, but not always feasible. We offer several advice which will help you in cases when it is impossible to avoid alcohol intake....
Section: Articles about health
Scientists have no unambiguous opinion on a proximate cause of emergence of a carcinoma cutaneum today. Are precisely established only фа...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that our country is one of the most "drinking" in the world. At clear understanding that the use of hard alcoholic drinks – occupation extremely harmful, most of Russians belong to alcoholism with unjustified loyalty. These...
Section: Articles about health
For many spouses the question of planning of a family is one of the main. The problem of the choice of effective and safe contraceptives at the same time comes out on top. Russians still not often resort to operation of a vasectomy extremely popular in the USA, and also in some European and Asian countries. The reason is simple: most of men simply do not possess the complete information about specifics and effects of this procedure. Let's try to meet this lack and to acquaint readers about those...
Section: Articles about health
It is impossible to imagine human life in which there would be no plants. Practically in each apartment and any of productions...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads...
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. However for nonspecialists this disease remains to not less mysterious, than in the ancient time. Many delusions are connected with epilepsy, and it sometimes very unpleasantly affects quality of life of patients and their relatives. In this article we will try to dispel the most known of similar myths....
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make, h...
Section: Slideshow
(Xerostomia) many people consider feeling of a xerostomia small and easily removable inconvenience. This delusion: the symptom can demonstrate existence of serious diseases. It is worth to remember also that saliva performs important functions...
Section: Articles about health
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. However visit of salon where work with biological material of clients, not always harmlessly is conducted. Today more than 100 pathogenic microorganisms who can catch in beauty shop including deadly to health are known....
Section: Articles about health
For most of the working people the problem of having a snack is particularly acute enough. Sooner or later there is a question: what is possible quickly for a sja...
Section: Articles about health
Doctors claim that the people not so familiar with a dorsodynia occur among adult Russians very seldom. At the same time the vast majority of the patients who are periodically testing this indisposition do not hurry to ask for medical care at all. With one St...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – one of the most vulnerable areas on a face therefore age changes concern them first of all. Whether it is possible to keep look youth for many years and what procedures are offered for achievement of this purpose by cosmetologists? And maybe, the only option of rejuvenation is surgery – a blepharoplasty? Let's try to understand this question....
Section: Articles about health
For residents of the countries of Southeast Asia various algas are an obligatory component of a daily diet. Their priest...
Section: Articles about health
The list of stereotypes of which, apparently, all know strongly includes following: British surely eat porridge for breakfast. Perhaps, not all modern residents of Britain arrive quite so, but for those from them which continue to follow this t...
Section: Articles about health
The depression not without reason is considered one their main troubles of our century: for scientific and technical progress, acceleration of rate of life and a surplus of information of people it is forced to pay with stresses, negative emotions and weakening of protective forces of an organism. As a result widely the states which are characterized by the increased uneasiness, falling of interest in life, spiritual and physical discomfort extend....
Section: Articles about health
There is a lot of fans of beer in our country. Statistically, on each average Russian (including women and children) in...
Section: Articles about health
When overcomes feeling of hunger, and an opportunity to have dinner fully is absent, having a snack − the meals, small on volume, stabilizing sugar level in blood comes to the rescue. The relation of nutritionists to having a snack is more often negative, but only because in кач...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
All like to sing. Small children with pleasure are engaged in a vocal, not especially thinking of hit in a melody. Adults most often...
Section: Articles about health
The naturopathy sometimes moves as the new direction of medicine, something like fashionable hobby, and there is nothing farther from the truth. This most ancient direction, the word "naturopathy" is translated as "treatment by the nature", and, no doubt, treatment приро...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant, but not exhausting a physical activity. In the presence of various illnesses specialists often advise patients to do swimming which by right takes the leading place by efficiency of improvement, having at the same time a few contraindications. Today we will talk about the main directions of therapeutic impact of swimming on a human body....
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance physical, ps...
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, not too modest, and excessively curvy shapes become the reason of sincere discomfort sometimes. Except psychological problems, a big bust sometimes with...
Section: Articles about health
Health and attractiveness - eternal values, pursuing which people often use the most unusual ingredients and technicians. Let's consider 11 most exotic and sometimes not most pleasant Spa procedures to which the person in a pursuit of beauty and youth agrees....
Section: Articles about health
