





Oysters
Oysters are clams, representatives of backboneless inhabitants of the seas. Externally a sink at them an asymmetric form. One shutter has the convex large form, and with its help the mollusk fastens to the rock or a stone. Second shutter several smaller sizes, more flat and thin. From an internal surface the sink is covered with a nacre, and in it there is an edible mollusk. Taste at oysters various – from sweetish to salty, also depends on the region of dwelling and the environment of a mollusk.
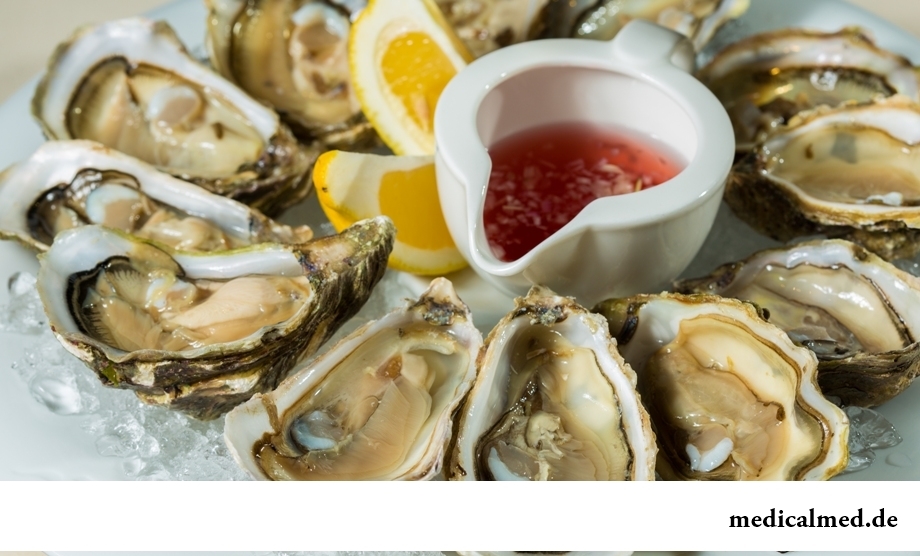

The main trade type is the oyster living in the Mediterranean and Black seas. Distinguish about fifty kinds of oysters which have classification, depending on weight and dimensional characteristics. For example, there are oysters No. 00 to whom the largest mollusks by the size concern. And here oysters from No. 0 to No. 5 have the smallest sizes. The oysters No. 3, most widespread in Europe, whose weight averages 80-100 g. Oysters Adriatic, rocky, Portuguese, Black Sea, lamellar, Japanese distinguish, huge, etc. Besides, there are oysters improved (or affined, grown up in special conditions), and are grown up in the conditions of the full sea.
There live oysters as colonies, and one by one, at a depth of 1-70 m. They fasten to stones, sand-stony soil or rocks. There are even so-called "oyster banks" (the settlement of mollusks which are at a distance from the coast), and "coastal settlements" of mollusks.
History
Archeological excavations indicate that oysters were eaten since ancient times. It is authentically known that in China they were parted in the 4th millennium B.C. In Europe oysters for the first time mention in 500 B.C. in Ancient Greece and Rome.
They received especially wide popularity at the time of government of the French king Louis XVI that led to the fact that in the middle of the 19th century their population began to disappear. But there's no evil without good: oysters learned to part in the artificial way. For this purpose oyster babies were caught and placed in specially prepared creeks where their growth was artificially controlled.
In pre-revolutionary Russia the oyster was widely adopted as a restaurant dish, and generally propertied segments of the population ate it. In Soviet period demand for them was sharply reduced and, begun was, their import from Cuba in the seventies had to be stopped. The dish did not enjoy popularity even at restaurants. Here, it should be noted, the big role was played by lack of culinary practice and some fastidiousness as an oyster it is necessary to eat live.
Oysters in cookery
In France and Belgium oysters are a delicacy, and they need to be eaten in a live look. If the oyster dead, so she is spoiled and is her it is impossible. The most important criterion of freshness is densely closed sink. And here if in a sink the small crack is observed at least, so the oyster already stale, and is it it is impossible. Open an oyster a special oyster knife or a medical scalpel. It is entered into the place where shutters are connected by a lock, and seen on the center of an oyster and from the flat party of a sink, to the muscle locking shutters. When the sink opens, it is necessary to concern from edge where it is possible to distinguish the darkish line of cilia. If the oyster is live – she will shudder if it remains motionless, so it is dead and in food is not suitable.
Eat oysters very simply – slightly sprinkle lemon juice and just "drink" from the deepened, curved party of a shutter. Jam an oyster, as a rule, black bread (into France it is imported only for the sake of oysters), and wash down with either light beer, or dry white wine.
In a number of the countries the tinned oysters representing already fried or boiled semi-finished product who, like mussels and crabs, apply in salads and soups in a melkonarezanny look release. They have no useful properties of oysters fresh and taste at them absolutely other.
Structure and caloric content of oysters
100 g of oysters contain 82,06 g of water, 9,45 g of proteins, 4,95 g of carbohydrates, 2,3 fats, 1,23 g of ashes; vitamins: Retinolum (A), thiamin (B1), Riboflavinum (B2), Niacinum (RR), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), folic acid (B9), cyanocobalamine (B12), vitamin C; macrocells: phosphorus, sodium, magnesium, calcium, potassium; microelements: selenium, zinc, copper, manganese, iron.
Caloric content at oysters is low and makes about 78 kcal on 100 g.
Advantage of oysters
The main advantage of oysters consists in their rich mineral and vitamin composition (group B vitamins, niacin, Niacinum, iodine, iron, phosphorus, selenium, copper, zinc, etc.) Besides, a large amount of digestible protein and low caloric content of oysters gives the chance to rank them as dietary food stuffs.

Useful properties of oysters consist in normalization of work of a nervous system, strengthening of a bone tissue, advantage for sight, improvement of function of a liver and kidneys.
The American scientists found in the list of oysters ceramides – fatty acids which allowed to open one more positive property of oysters – suppression of growth of cancer cells.
Besides, in collaborations of the Italian and American scientists the advantage of oysters is that at their structure there are unique amino acids which stimulate production of sexual hormones.
Contraindications
Oysters are contraindicated to the people having intestines diseases with frequent disturbances of a chair, a spleen and stomach. Also crude oysters pregnant women and the feeding women are not recommended to use.
Work which to the person not to liking, is much more harmful to his mentality, than lack of work in general.

Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Nye...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, pathologies of a thyroid gland in the world more than 500 million people have. Failures in work of this body lead to heavy disbolism, development of heart diseases, vessels, a reproductive and nervous system. In hard cases excessive...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and the strengthened reproduction of this microorganism lead to weakening of protection of mucous membranes and their erosive damage. Displays of an illness seriously reduce quality of life: patients regularly test attacks of severe pain, heartburn, nausea. On this background also psychoemotional malfunctions develop: a kidney-vetch, as a rule, shows an acrimony, ча...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. Statistics we get sick...
Section: Articles about health
According to World Health Organization, every third inhabitant of Earth has excess weight, and every tenth has obesity. The reason of this phenomenon, according to specialists, roots in one not very comforting fact: most of people consume much...
Section: Articles about health
No, probably, the person who would not have cold. Cold, cough, a headache – these symptoms are known to everyone. The peak of catarrhal diseases is the share of fall. SARS already came to schools and kindergartens, flu slowly makes the way to the cities, in a word, winter close!...
Section: Articles about health
The nature does not stand stagnation and monotony. It is known that tissues of a human body atrophy if do not receive necessary loadings...
Section: Articles about health
It is difficult to revaluate importance of kidneys for an organism. These bodies not only perform work on purification of blood of decomposition products and removal of excess liquid. They are responsible also for production of some hormones necessary for normality maintenance...
Section: Articles about health
Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on lips is called) – one of the most widespread illnesses. Statistically, only 5% of inhabitants of our planet are unreceptive to its activator, and the reasons of this feature are still not found out. Other people are virus carriers....
Section: Articles about health
The stroke is one of the most widespread diseases of the person, annually in the world about 6 million cases эт are registered...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too h...
Section: Articles about health
One of the useful properties presented to the person by the nature is ability to feel fear. This ability is designed to signal about approach of a dangerous situation and to help to avoid in advance it to keep life. However if the fear is persuasive and is not reasonable, it can seriously limit possibilities of the person in respect of socialization and self-realization. Such pathological fear is called a phobia....
Section: Articles about health
The sudden heat on all body which is followed by perspiration and a cardiopalmus – the phenomenon familiar to many people. Most often t...
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor with age forgetfulness and problems with concentration of attention. This disease has the autoimmune nature. Pathological process of a vyrazh...
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to get access to various apparatuses and an opportunity to train under the leadership of the experienced consultant. Many consider fitness the best way of maintenance of physical shape and receiving dynamic loads which the people occupied preferential with brainwork so need. Nevertheless, representations of most of consumers of similar services about специф...
Section: Articles about health
Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. Fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding...
Section: Articles about health
It is known that the person for 80% consists of water which participates in all processes of an organism. The person loses liquid daily – as a result of sweating, breath, an urination, and its insufficient completion due to various reasons can bring to обезвожив...
Section: Articles about health
Condition of lips (their morbidity, outward) – one of indicators of health of the person. The peeling, dryness, pallor, and also cracks in corners of a mouth can be not only the cosmetic shortcoming which arose owing to physical damages and weather conditions but also the satellite of some diseases and disturbances in an organism needing treatment. Let's consider 10 possible reasons of emergence of angular cracks (perleches) in corners of a mouth and ways of their elimination....
Section: Articles about health
For many women the word "fat" sounds as a sentence. In aspiration to an ideal figure they try to exclude, first of all, from with...
Section: Articles about health
The climax, or menopause is the normal process of the termination of genital function of the woman which is followed by serious hormonal changes in an organism. Usually the menopause begins at the age of 50-55 years, but characteristics of this process are very individual. T...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly ways of storage and transportation of food ingredients changed, and people of the whole world had an opportunity to regularly use those products about which their grandfathers and grandmothers did not even know....
Section: Articles about health
Epilepsy is one of widespread neurologic diseases. To parents, whose children suffer from this illness, it is necessary...
Section: Articles about health
Residents of big cities quite often have a disease which is known as the syndrome of chronic fatigue (SCF) today. This illness affects the people belonging to various social and demographic groups and living on all continents. Most of all SHU to a podverzha...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on chemical composition of biological liquids of an organism. Specialists consider that PH value of these solutions has to be in range of 7,35-7, 45. The deviation in the smaller party (so-called "acidulation") is fraught with development of many heavy illnesses, failures in work of immune system, decrease in working capacity and deterioration of life. To avoid serious fluctuations of acidity of internal liquids it is necessary to adhere разумног...
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" also "assimilation"...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital within walking distance. And, nevertheless, Internet drugstores become more popular – what it is possible to explain such phenomenon with? Actually m reasons...
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far he already helped a significant amount of married couples to become happy parents. Usually to the EKO procedure difficult and very expensive, resort in those situations when all other ways to help couple to bring the child are inefficient. "Conception in a test tube" yields quite good results in cases of infertility of one of partners, existence at the woman of impassability of uterine tubes...
Section: Articles about health
