





Gall bladder
Gall bladder – the unpaired subsidiary body of the person accumulating bile and controlling its receipt in a digestive tract. It represents a muscular bag of the extended pear-shaped form and the hypochondrium under a liver is located in right. As a rule, the size of a gall bladder varies from 2 to 3 cm in width and from 7 to 10 cm in length, and its capacity makes 50 ml.
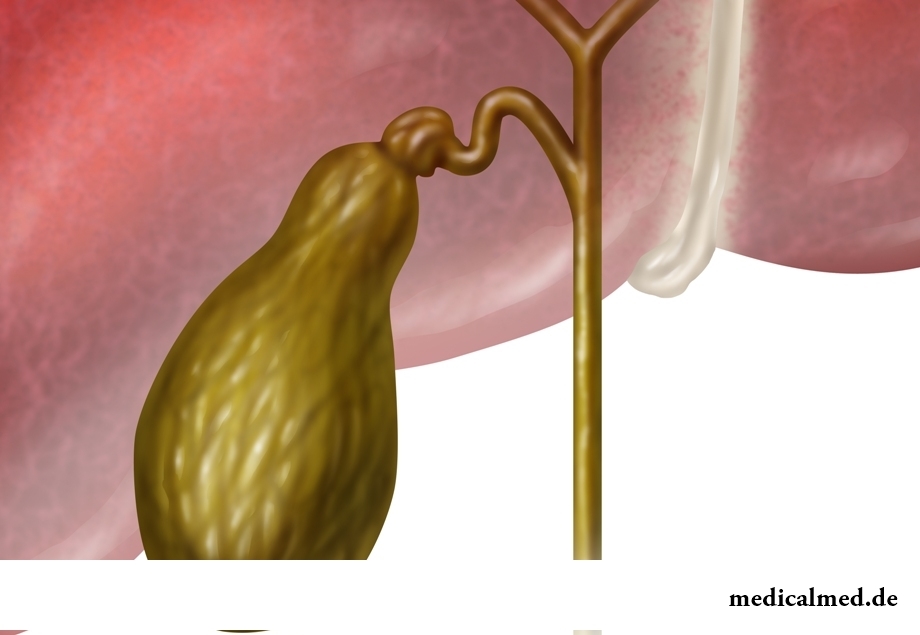
The gall bladder is not irreplaceable body and in case of its removal function of accumulation of bile passes to a duodenum.
Structure of a gall bladder
In a gall bladder distinguish three parts:
- The bottom which is the part seen in front;
- Body – the main venter which is located between a vesical channel and a bottom;
- Neck – the narrow part passing into the vesical canal 3-4 cm long through which there is the general bilious channel.
Bile from a bubble comes to a duodenum gleam that is, as a rule, connected with digestion process. The strengthened bile production arises at the use of greasy food.
Control of work of a gall bladder is exercised by the autonomic nervous system.
Being located near a liver, the gall bladder is tied with it by means of fine connecting fabric. Bystry distribution of any inflammatory processes happening in a bubble on a liver parenchyma is explained by it.
The wall of a gall bladder multilayer also includes:
- Muscular framework;
- Inside layer (epithelium);
- Enveloping layer (serous cover);
- Mucous membrane.
Blood supply of a gall bladder is provided:
- Arterial – the portal artery departing from the right hepatic artery;
- Venous drainage – a bilious vein.
Functions of a gall bladder
Treat the main functions of a gall bladder:
- Accumulation and storage of bile. The bubble stores the bile arriving from a liver, and also is capable to increase its concentration for storage of large volume in small space;
- Biliation which occurs as the response to receipt of food (nervous and hormonal factors) by means of muscular contractions of its wall.
Diseases and pathologies of a gall bladder
(For example, cholecystitis and a cholangitis) can lead the long stagnation of bile caused to development of many inflammatory diseases:
- Stones in a gall bladder;
- Helminths;
- Excess of a gall bladder.
The excess of a gall bladder which is formed, as a rule, on border of a body and a bottom of a bubble belongs to one of widespread pathologies, and often occurs at children of various age. In cases of an insignificant excess this pathology can not exert any impact on the movement of bile and overall health.
Obviously expressed or double excesses of a gall bladder can cause the stupid, aching, long pains against the background of heavy feeling in right hypochondrium which quite often are followed by nausea and feeling of bitterness in a mouth.
Cholelithiasis is one of the most widespread diseases of a gall bladder. The disease, as a rule, does not develop suddenly. Its development can proceed several years, at the same time are subject to it not only inclined to completeness and elderly people, but also rather young. The disease is usually diagnosed at ultrasonic and X-ray inspection.
Stones in a gall bladder are formed of salts of cholesterol, bile acids and bilirubin. Origins of stones are various. Treat the most frequent:
- Improper feeding;
- Slow-moving way of life;
- Obesity;
- Bystry weight loss;
- Starvation.
Such symptoms as bitterness in a mouth and weight in right hypochondrium after food at cholelithiasis are especially expressed after the use of marinated, salty and smoked products and greasy food.
Drug treatment usually long, and the drugs dissolving stones it is necessary to accept for several years. At the same time it is necessary to create conditions for prevention of development of new stones.
For prevention of formation of gallstones follows:
- To avoid the use of plentiful food with the high content of fats;
- To apply a low-calorie diet and to increase exercise stresses in the presence of excess body weight;
- To reduce intake of cholesterol in an organism;
- To avoid treatment by estrogen at detection of stones in a gall bladder.
Not all types of stones will respond to drug treatment and most efficiently treatments of cholelithiasis removal of a gall bladder is. At a laparoscopic cholecystectomia there is considerably smaller load of cardiovascular and respiratory system in comparison with other types of operations.
Removal of a gall bladder by method of a laparoscopic cholecystectomia usually takes place without complications at all forms of cholelithiasis. Contraindications to carrying out operation is big duration of gestation and a coagulopathy.
As a rule, after removal of a gall bladder it is possible to be returned to usual exercise stresses in five-seven days.
After the performed operation it is necessary to keep to the special diet allowing to reduce risk of formation of stagnation of bile. At a diet after removal of a gall bladder greasy food, alcohol, heavy, hot, tinned and fried dishes are categorically excluded. Ensuring sufficient level of salt and vitamin structure also is important.
Many drugs initially moved ahead in the market as drugs. Heroin, for example, was initially brought to the market as children's cough medicine. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as anesthesia and as the means increasing endurance.

Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. Fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding...
Section: Articles about health
The main role in development of a peptic ulcer of a stomach and duodenum the bacterium Helikobakter plays pilor. Activity and the strengthened reproduction of this microorganism lead to weakening of protection of mucous membranes and their erosive damage. Manifestations not...
Section: Articles about health
Summer in the heat. Many are going to spend vacation abroad. Travelers the tender seas, rest on beaches wait, for sightseeing, campaigns on natural and cultural reserves. But, unfortunately, on vacation also problems with health can wait for us. On a foreign trip it is possible to face also diseases which not only will spoil long-awaited issue, but also will force to be treated within long months after its termination. To be insured completely from troubles of it a sort...
Section: Articles about health
Ayurveda - the most ancient tselitelsky practice which came to us from India. It represents the doctrine about maintenance physical, ps...
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In certain cases inflammatory process is not limited to discomfort, being followed by emergence of hypostasis, consolidations, increase температ...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist of iodine more than for 65%. The lack of iodine leads to decrease in production of hormones and, as a result, development of a hypothyroidism. The long condition of deficit can become a source of problems of the cardiovascular, bone, digestive SI...
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutritious...
Section: Articles about health
All like to sing. Small children with pleasure are engaged in a vocal, not especially thinking of hit in a melody. Adults most often hesitate, being afraid to show lack of talents in this area, and it is vain: singing is very useful for health....
Section: Articles about health
Tick-borne encephalitis – one of the most dangerous viral diseases which causative agents transfer and is given to people by ixodic mites. These are the small blood-sicking insects living in the considerable territory of our country. The person bitten by a tick can catch also erlikhiozy, bartonnelezy, babeziozy, mycoplasmosis and Lyme's disease. As well as encephalitis, these illnesses affect the central nervous system, and as specific antiviral therapy does not exist, the forecast very to a neuta...
Section: Articles about health
Neurosis is called pathology of a nervous system at which deviations in functioning of the highest nervous processes are observed. Nye...
Section: Articles about health
Traveling all over the world, many try to try the most exotic dishes of national cuisines. There is even a so-called gastronomic tourism which, according to gourmets, not only allows to receive new feelings, but also is capable to show life the friend...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. The contribution of drugs to rescue of people from epidemics of dangerous infections is huge, however at careless use antibiotics are capable to cause to an organism serious damage. Negative action can be shown in the form of easing of immunity, disturbance of balance of microflora in кишеч...
Section: Articles about health
It seems, quite recently you brought the baby from maternity hospital, but time flew by, and here it is already going to join the first...
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In most cases pathological reactions cause the substances which are contained in food stuffs, hair of animals, medicines...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of use of table salt in the therapeutic purposes contains not one century. Applications which do by means of the fabric impregnated with saline solution are considered especially effective. They have antibacterial and antiinflammatory effect, help to heal wounds, exempt fabrics from excess liquid. Hypertonic salt solution of potassium chloride is applied outwardly at many morbid conditions. Let's tell about the most known of them....
Section: Articles about health
About 20% of the population of our planet have a hypertension (permanent increase in arterial pressure). This disease negatively narrations...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing an optimum set of nutrients, and which is best adapted in order that the baby normally developed and it was protected from harmful factors of external environment, unusual for it. Unfortunately, breastfeeding process not always does without complications. Sometimes, that the kid begins to bite a breast, giving to mother an essential inconvenience. Some women...
Section: Articles about health
The endocrine system carries out in a human body extremely important role, practically all processes of life activity регулируютс...
Section: Articles about health
On health of the person physicians know about salutary action of animals long ago. About 7 thousand years ago great Hippocrates recommended to the patients riding walks for strengthening of a nervous system and increase in vitality....
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need of a visit to the gynecologist. Certainly, it is possible to establish the exact diagnosis only after inspection, but on the basis of some signs it is possible to assume existence of this or that pathology. Let's consider symptoms of the female diseases which are found most often....
Section: Articles about health
Shops of household appliances offer us the huge choice of various devices for the house. Whether there are among this abundance devices which...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital within walking distance. And, nevertheless, Internet drugstores become more popular – what it is possible to explain such phenomenon with? Actually m reasons...
Section: Articles about health
With age in a human body harmful substances collect. We receive them with food and water, at inhalation of the contaminated air, reception of medicines, use of household chemicals and cosmetics. A considerable part of toxins accumulates in a liver which main function is continuous purification of blood. This body begins to knock as any got littered filter, and efficiency of its work decreases....
Section: Articles about health
Some people consider what for medicine of the 21st century of secrets in the field of health of the person almost does not exist. It absolutely not so. Than Bol...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow
All parents are ready to what the baby often and pisat much. Since then, as the absorbing diapers strongly became current, keeping of the kid in dryness does not represent any problems. But if the grown-up kid continues to urinate in panties, parents begin to feel concern – whether it is normal, or the kid has an urine incontience? Let's try to understand what is enuresis why it arises at children and at what age it is necessary to begin it to treat....
Section: Articles about health
