Disease of Girshprunga
Disease of Girshprunga – one of the most widespread anomalies of development of a large intestine which is shown by lack 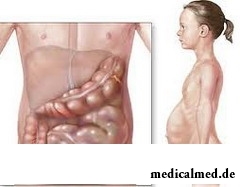 of an innervation of a certain department or all gut. The disease of Girshprunga has a genetic etiology. The disease is characterized by lack of ganglionic cells in distal department of intestines. The disease has hereditary character and is caused by a mutation in the 10th chromosome. At untimely diagnosis can provoke development of acute inflammatory processes in intestines, and also lead to a lethal outcome.
of an innervation of a certain department or all gut. The disease of Girshprunga has a genetic etiology. The disease is characterized by lack of ganglionic cells in distal department of intestines. The disease has hereditary character and is caused by a mutation in the 10th chromosome. At untimely diagnosis can provoke development of acute inflammatory processes in intestines, and also lead to a lethal outcome.
Pathogeny of a disease of Girshprunga
Ganglionic (or ganglionic) cells – the general name of some types of large neurons which in intestines are responsible for communication between nervous structures. During ontogenesis ganglionic cells migrate from upper parts of intestines to its distal department. Disturbance of migration leads to formation of the aganglionarny site of a gut (a zone of functional narrowing) with the lowered or completely absent innervation (ability to make forward сокращательные the movements). In certain cases the aganglionarny site can abnormally extend, creating megacolon that is one of serious complications of a disease of Girshprunga.
The place of localization of the aganglionarny site, as a rule, is the distal department of a large intestine. In rare instances forms of a disease of Girshprunga at which the aganglionarny segment forms on the site from a splenic column, or develops аганглиоз all large intestine meet. At such form of a disease at patients total paralysis of a vermicular movement is observed.
Disease of Girshprunga at children
Owing to the etiology the disease of Girshprunga is diagnosed for newborns or in the first year of their life. However there are special forms of a disease which fully develop only in an adult organism. Both the hereditary factor, and disturbance of pre-natal development is the reasons of a course of a disease of Girshprunga at children in ontogenesis. Frequency of diagnosing of a disease of Girshprunga at children makes about 1:5000. The disease is more often diagnosed for boys, than for girls (5:1). At timely diagnosis and treatment the forecast favorable. At most of patients the peristaltics of intestines completely renews and the natural excrement is normalized. At 1% of patients need of a kolostoma (brought to a front abdominal wall and the opened end of a colon fixed there) for removal of fecal masses and gases remains.
Disease of Girshprunga: symptoms, diagnostic methods
The main symptoms of a disease of Girshprunga are:
- Locks;
- Nausea, vomiting; Abdominal
- cavity pains;
- Abdominal distention, meteorism.
The aganglionic segment of a large intestine plays a role of a functional stenosis above which abnormal expansion of a gut where there is accumulation of fecal masses forms. Expressiveness of symptoms of a disease of Girshprunga will be directly proportional to the extent of a segment of the struck gut.
In many cases at a palpation accumulation of fecal masses is found. The main symptom of a disease of Girshprunga at children is the meconium otkhozhdeniye delay in the first 24-48 hours. At some children development of symptoms can begin only during the period an otnyatiya from a breast and upon transition to firm food.
In rare instances at a disease of Girshprunga which symptoms are very similar to symptoms at intestinal impassability at patients the coloenteritis (an inflammation of a large and small bowel) provoking diarrhea develops.
The main 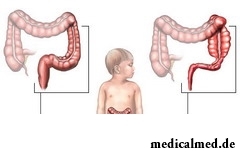 diagnostic methods of a disease of Girshprunga are a radiographic research of intestines using contrast agents, and also a biopsy of a large intestine. The data obtained by these methods are quite enough for diagnosis and definition of localization and a stage of development of a disease. Also ultrasonography and an anorectal manometriya are in rare instances applied.
diagnostic methods of a disease of Girshprunga are a radiographic research of intestines using contrast agents, and also a biopsy of a large intestine. The data obtained by these methods are quite enough for diagnosis and definition of localization and a stage of development of a disease. Also ultrasonography and an anorectal manometriya are in rare instances applied.
Treatment of a disease of Girshprunga: main methods
Treat the main methods of treatment of a disease of Girshprunga:
- Dietotherapy;
- Conservative treatment;
- Radical treatment.
Dietotherapy and conservative treatment of a disease of Girshprunga – temporary measures when training the patient for radical (operational) treatment. The dietotherapy is directed to reduction of manifestation of symptoms at the patient while conservative treatment is applied to elimination of symptoms or their simplification.
Radical treatment of a disease of Girshprunga assumes an operative measure at which the aganglionic site of intestines with imposing of an anastomosis is excised. Until recently, operations at a disease of Girshprunga were performed with opening of an abdominal cavity and imposing of a kolostoma before resuming of a normal vermicular movement of intestines. A repeated operative measure was carried out later certain time for closing of the removed kolostoma and sewing together of healthy sites of intestines.
Modern low-invasive laparoscopic techniques allow to carry out at a disease of Girshprunga operation in one step assuming excision of the site deprived innervations and formation of an anastomosis through rectal access. Now at a disease of Girshprunga operations with open access are performed only in the presence of serious complications, such as a coloenteritis or megacolon which are resistive to conservative methods of treatment.
The person accepting antidepressants in most cases will have a depression again. If the person coped with depression by own efforts, he has every chance forever to forget about this state.
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible on...
Section: Articles about health
For the time being the perspective of heart diseases seems to most of people remote and foggy. But sooner or later practically each adult faces extremely unpleasant feelings: sudden stethalgia. To be consoled at this time in a thought of t...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly ways of storage and transportation of food ingredients changed, and people of the whole world had an opportunity to regularly use those products about which their grandfathers and grandmothers did not even know....
Section: Articles about health
Energy saving lamps are one of the most popular products of innovative technologies, and there is no wonder: they much эк...
Section: Articles about health
The cosmetics intended for improvement of a condition of skin, nails and hair are used by each woman. Expenses on regular acquisition of the fashionable widely advertized products of well-known companies for many become very notable and significantly to an obrema...
Section: Articles about health
Musicotherapy – a treatment method which caused and causes a set of a controversy concerning its efficiency. However the facts are relentless: during the numerous researches curative impact of music on an organism was scientifically confirmed. Since then in a number of the countries the technique is included complex therapy of diseases of cardiovascular and respiratory system, dorsodynias and a backbone, psychosomatic disturbances and many other illnesses. The musicotherapy in a pedi is especially widely applied...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying...
Section: Slideshow
Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes the bed patient, and remains in such state for a long time. It extremely suppresses both the most injured, and all it to...
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make that process of weight loss did not give you an inconvenience, and, on the contrary, brought joy?...
Section: Slideshow
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant but which is not exhausting, motive...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is the prices...
Section: Articles about health
During foot walks blood moves on vessels more actively and one and all bodies are supplied with a large amount of oxygen. It affects the state of health of the person very positively....
Section: Slideshow
Not without reason doctors say that 90% of diseases begin or develop because of misoperation of intestines. Disturbance of its functions связ...
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? While physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the industry of hairdresser's art a few years ago there was a sensation – methods of hair extension appeared. It would seem, dreams came true...
Section: Articles about health
The concept "gluten" (differently, a gluten) combines group of the proteins which are a part of rye, barley and wheat. For most of people the use of the food stuffs containing a gluten not only is safe, but also it is very useful. Nevertheless, there is a number of myths about negative effect which allegedly gluten has on health of the person....
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be study...
Section: Articles about health
For most of the working people the problem of having a snack is particularly acute enough. Sooner or later there is a question: what can be eaten quickly between a breakfast and a lunch or a lunch and leaving from service so that to receive necessary power feed, but not an overload...
Section: Articles about health
The word "onikhokriptoz" is unfamiliar to most of people, meanwhile quite so physicians call very widespread problem: the growing of edge of a nail into surrounding fabrics causing inflammatory process. Usually the illness affects thumbs of legs, and is followed by reddening, hypostasis, and in the started cases – release of pus. Patients complain of the pain amplifying when walking, problems with the choice of footwear....
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence ег...
Section: Articles about health
Each of us faces from time to time that other people need the immediate help. We react to it differently: one at once call doctors and police, others rush to victims and try to save them independently. Some at all...
Section: Articles about health
Stability of a hormonal background is one of the most important conditions of preservation of health of the woman. At the same time endocrine system – the thin device extremely sensitive to any external influences. Changes of a way of life (for example, a diet), emotional stresses, infectious diseases, reception of some drugs can become the reason of hormonal failure. Besides, work of hemadens has the natural specifics in certain moments of life: on various St...
Section: Articles about health
Long time antibiotics were considered as a panacea from all diseases and were appointed even at insignificant symptoms of an infection. Even now...
Section: Articles about health
At this plant there are a lot of names: tuberiferous sunflower, Jerusalem artichoke, solar root, earth pear. Contrary to popular belief, it is not an exotic plant at all. The wild girasol grows in a midland of Russia practically everywhere: at the edges of roads...
Section: Articles about health
There is a lot of fans of beer in our country. Statistically, on each average Russian (including women and children) in a year about 60 liters of this drink are consumed. It is not a lot of, as in the Czech Republic or Germany, but figure all the same impressive. There is nothing to rejoice here: despite assurances of producers that beer is absolutely harmless, effects of its active consumption cannot be considered positive in any way. Here only part of that negative impact, which popular нап...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects on...
Section: Articles about health
Frosty air, fresh wind and easy snowball at most of Russians are associated with cheerfulness, health and cheerful entertainments on which our winter is so generous. But, unfortunately, cold season sometimes brings also troubles with health. It is not about a season...
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn – whether you have or your relatives problems....
Section: Articles about health