Cardiography
 The concept "cardiography" combines different methods of studying of cordial activity. Big distribution was gained by an electrocardiography by means of which write down electric cordial activity. The similar cardiography of vessels, hearts gives the chance to estimate blood supply of a myocardium, conductivity and a cordial rhythm, changes of the sizes of cardial cavities, a thickening of a cardiac muscle, to reveal disturbances of electrolytic balance, prescription of the postponed heart attack, toxic damage of a myocardium.
The concept "cardiography" combines different methods of studying of cordial activity. Big distribution was gained by an electrocardiography by means of which write down electric cordial activity. The similar cardiography of vessels, hearts gives the chance to estimate blood supply of a myocardium, conductivity and a cordial rhythm, changes of the sizes of cardial cavities, a thickening of a cardiac muscle, to reveal disturbances of electrolytic balance, prescription of the postponed heart attack, toxic damage of a myocardium.
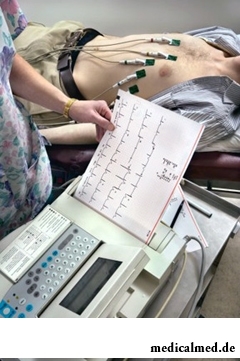
Record of action of the heart from a body surface of the patient (electrodes attach to a thorax, legs and hands) is carried out, results of a cardiography of vessels and heart for 5-10 minutes Register. Result of such diagnosis – the cardiogram of heart according to which the attending physician – the therapist, the cardiologist or other specialist can analyze a condition of the patient.
When appoint a cardiography of vessels and heart
The indication to carrying out a cardiography are pains, unpleasant feelings in heart, a neck, a back, a stomach, a breast (ischemia is so shown in certain cases), short wind, frequent faints, puffiness of legs, supertension, noise in heart, rheumatism, diabetes, a stroke.
To make the cardiogram appoint to patients at a preparation for surgery, during routine annual inspections, pregnancy, at execution of documentation before definition in recreational institutions and sports sections, etc.
Besides to people after 40 years the cardiogram of heart is recommended to do annually, despite the absence of complaints. Only this way it is possible to find the hidden disturbances of a heart rhythm, ischemia, a heart attack in time.
Interpretation of the cardiogram
 To make the cardiogram, the corresponding treatment can decipher the obtained data and appoint if necessary only the specialist. But to understand some terms important for interpretation of the cardiogram also patients can:
To make the cardiogram, the corresponding treatment can decipher the obtained data and appoint if necessary only the specialist. But to understand some terms important for interpretation of the cardiogram also patients can:
- heart rate (HR). The indicator displays the number of reduction of a muscle of heart in a minute. If it is more reductions than is 91 in a minute tachycardia if 59 blows are bradycardia less. Norm ChSS for the adult – 60-90 blows.
- Electrical Axis of Heart (EAH). This indicator received by means of a cardiography helps to understand a heart arrangement, to define functions of its different departments. In the cardiogram of heart the normal, horizontal, vertical and rejected to the left or to the right provision of EOS can be specified.
- Sinoatrial regular rate. So call a normal heart rhythm which sets a sinus node.
- Not sinoatrial rate. Such formulation in the cardiogram of heart indicates that the heart rhythm is set not by a sinus node, but some minor source of electric cardiac potentials that in turn testifies to heart pathology.
- Sinus arrhythmia (sinoatrial irregular rate). This term means that on a cardiography the wrong sinoatrial rate with gradual reduction and increase in frequency of reductions of heart is recorded. Similar arrhythmia can be not respiratory and respiratory.
- Atrial fibrillation or ciliary arrhythmia. The similar conclusion of a cardiography of vessels and heart says that there is some disturbance of a heart rhythm most of which often is found at patients after 60 years, protekayushchey without explicit symptoms and often provoking heart failure, a brain stroke.
- Paroxysm of a ciliary arrhythmia. So call the sudden attack of a ciliary arrhythmia revealed on a cardiography. The similar state demands immediate treatment and what earlier it will be begun with, that a high probability of recovery of a normal heart rhythm.
- Atrial flutter. A kind of arrhythmia which is treated heavier, than classical arrhythmia.
- Extrasystole or premature ventricular contraction. So in the cardiogram of heart the extraordinary reduction of a muscle of heart causing an abnormal impulse is called. Premature ventricular contraction can be ventricular, atrioventrikulyany and atrial – depending on the site of heart from where there is such impulse.
- Syndrome Wolf-Parkinson-Whyte (WPW). Inborn pathology which abnormal electric impulses and dangerous attacks of arrhythmia are characteristic.
- Sinuatrial blockade. The similar formulation in interpretation of the cardiogram indicates disturbances of carrying out an impulse to an atrial myocardium from a sinus node. Such pathology often meets at a cardiosclerosis, a cardiopathy, myocarditis, a heart attack, overdose of drugs of potassium, beta adrenoblockers, cardiac glycosides, after carrying out on operation heart.
- Atrioventikulyarny blockade. It is the pathology of passing of an impulse found on a cardiography from auricles to cordial ventricles. Nonsynchronous reduction of ventricles and auricles of heart provokes such disturbance.
- Total, incomplete block of legs of a ventriculonector. Disturbance of carrying out an impulse in the thickness of a myocardium of ventricles of heart. Such deviation is shown at heart diseases, a cardiosclerosis, myocarditis, a heart attack, a myocardium hypertrophy, supertension.
- Hypertrophy of a left/right ventricle. So call increase in sizes of a ventricle or a thickening of its wall.
- Hems. The cardiography with such conclusion says that in the past the patient had a heart attack. In this case appoint preventive treatment for the prevention of a recurrence and elimination of a cause of infringement of blood supply.
- The extended QT interval. In interpretation of the cardiogram the acquired or inborn disturbance of conductivity of heart which is followed by faints, disturbances of a rhythm, a cardiac standstill is so designated.
In the course of inspection to make the cardiogram often appoint also to children, it is only necessary to consider that indicators of their cardiography differ from indicators of adults. Fluctuation of reductions of heart depending on their behavior is typical for children about one year. Average frequency of reductions at them – 138 blows, EOS – vertical. The cardiography of children of 1-6 years displays vertical, normal and sometimes a horizontal arrangement of EOS, frequency of reductions – 128 blows, the sinus respiratory arrhythmia often is found. The cardiogram of heart of children of 7-15 l indicates, that normal ChSS - 65-90 blows, the provision of EOS – vertical or normal, is characteristic a respiratory arrhythmia.
Except people, only one living being on the planet Earth – dogs suffers from prostatitis. Here really our most loyal friends.

Cold is such painful that each sigh becomes a victory, heat "knocks" down, and the ache in joints forces to think only about...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically cystitis 25-30% of women up to 40 years have. With age this indicator raises, besides many do not get to statistics because do not see a doctor. The most sad that after the regular visits to doctors, long reception of antibiotics...
Section: Articles about health
The modern person not always manages to find housing in the environmentally friendly region and such work which would not do harm to health. With food stuffs at first sight the situation is much better: shops are overflowed with goods which are positioned by producers as very useful and absolutely safe. Many Russians are absolutely sure that the choice of products with marking "bio", "эко" or "organik" guarantees them and members of their families an optimal variant of food. To a sozhala...
Section: Articles about health
The next flu epidemic leads to the next panic, from year to year we give in on these manipulations: professionally alarming goal...
Section: Articles about health
The mankind knows that some toxins at intake in the minimum quantities have therapeutic effect from an extreme antiquity. Many substances recognized poisonous are applied in the medical purposes also today, being the main deystvuyushch...
Section: Articles about health
The Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) are plants or animals (as a rule, agricultural) to whose genotype purposeful changes were made. Opposition of supporters and opponents of inclusion of such organisms in foodstuff always was very acute. Not only scientists and dietitians, but also a large number of the people who are not specialists in this question are involved in active disputes today....
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs п...
Section: Articles about health
The climax, or menopause is the normal process of the termination of genital function of the woman which is followed by serious hormonal changes in an organism. Usually the menopause begins at the age of 50-55 years, but characteristics of this process are very individual. T...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, a sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease in physical and intellectual activity and a number of other symptoms reducing quality of life. Abstinence can be strong: an essential part of attempts comes to an end leaving off smoking failure, and people are returned to the use of cigars...
Section: Articles about health
Life activity of one-celled fungi of the sort Candida is a proximate cause of development of candidiasis (milkwoman), it is related...
Section: Articles about health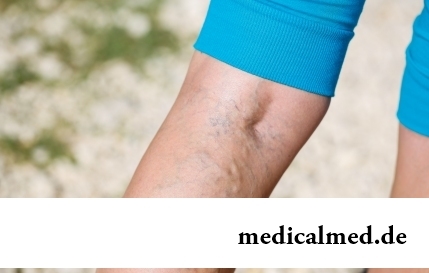
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As a rule, the varicosis affects preferential superficial vessels, and is shown by characteristic cosmetic defects. Guo...
Section: Articles about health
Impossibility to conceive the child – a trouble of many Russian families. During quite long time was considered that main "culprits" of troubles such are women. Modern physicians claim that the situation is different: about a half of failures in attempts of reproduction are connected with male infertility....
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor about age...
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one of the most ancient methods of disposal of the most different diseases. Bathtubs, souls, wrappings and inhalations, in combination with reception of water vnut...
Section: Articles about health
New year, wedding, birthday, office party – an occasion to drink at the Russian person will always be. How to reduce a negative impact of alcohol by an organism and to avoid a condition of strong intoxication? The most correct council – to refuse the use of alcoholic drinks. Council is true, but not always feasible. We offer several advice which will help you in cases when it is impossible to avoid alcohol intake....
Section: Articles about health
Kidneys perform the most important function of clarification of blood from those products of metabolic processes which cannot be used орг...
Section: Articles about health
Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary to minimize. There is a number of rules, following to which will help or to avoid absolutely infection with flu or a SARS, or to have an illness...
Section: Articles about health
The chia plant, or the Spanish sage, is from South America. The indigenous people of the continent since ancient times used its seeds in food: small, but very nutritious kernels, in a form the reminding fasolina. Indians knew about useful properties of seeds of a chia, and applied them to maintenance of vitality and increase in endurance before serious exercise stresses....
Section: Articles about health
You are office worker, the driver, the fan of winter sports or do not think of life without bicycle? You conduct a slow-moving image жизн...
Section: Articles about health
Modern footwear is extremely various. It stopped being only protection for legs long ago. Today shoes, boots, barefoot persons choose not so much proceeding from their convenience and functionality how many being guided by outward, brand and an opportunity to add with it...
Section: Articles about health
The drugs stopping or oppressing life activity of pathogenic microorganisms are widely applied in clinical practice from 40th years of the last century. Originally antibiotics were called only substances natural (animal, vegetable or microbic) origins, but over time this concept extended, and it includes also semi-synthetic and completely artificial antibacterial drugs....
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it is strong for...
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers...
Section: Articles about health
Each person supports all life a SARS about 200 times. The peak of incidence falls on cold season, but it is possible to get sick with a temperature and a pharyngalgia, and sometimes and very possibly, even during a heat. The reasons for development of catarrhal diseases there is a set: from the weakened immunity till an excess portion of ice cream....
Section: Articles about health
Diapers for adults – individual one-time means of hygiene which in some situations is irreplaceable, and from such situats...
Section: Articles about health
Vitamin complexes belong to the most popular drugs, probably, in our country there is no person who was not hearing about advantage of vitamins and never their accepting. The more vitamins, the better, we consider and as it appeared, cruelly we are mistaken. So l...
Section: Articles about health
The dietology, as well as other sciences, does not stand still. Food stuffs are exposed to comprehensive study, and scientists obtain new information on their properties and influence on a human body. Unfortunately, this reasonable and natural process gives unpleasant side effect from time to time: some types of food periodically declare "harmful" or even "deadly" without the bases, sufficient on that....
Section: Articles about health