





Ксанакс
Application instruction:
 Ксанакс – derivative triazolo-benzodiazepine, anxiolytic means (tranquilizer) with myorelaxation, anticonvulsant, sedative and somnolent action.
Ксанакс – derivative triazolo-benzodiazepine, anxiolytic means (tranquilizer) with myorelaxation, anticonvulsant, sedative and somnolent action.
Form of release and structure
- Tablets (on 10 pieces in planimetric strip packagings, 3 packagings in a pack cardboard);
- Tablets ретард (on 10 pieces in blisters, 3 blisters in a pack cardboard).
Active agent – to alprazola:
- 1 tablet – 0,25 or 0,5 mg;
- 1 tablet ретард – 0,5 or 1 mg.
Indications to use
- The neurotic reactive and depressive and mixed alarming depressions which are followed by a sleep disorder, decrease in mood and vigor, psychomotor agitation, loss of interest to surrounding, disturbance of cognitive activity, somatic complaints, deterioration in appetite, changes of body weight, suicide thoughts (low-value, feeling of fault), etc., including at organic and functional diseases (digestive, cardiovascular, dermatological) at somatic frustration, an alcoholic abstinence syndrome;
- The alarming states and neurosises which are followed by deterioration in a dream, irritability, somatic disturbances, concern, feeling of tension, alarm;
- Attacks of a phobia and panic at patients with an agoraphobia;
- The panic states including which are combined with phobia symptoms.
Contraindications
Absolute:
- Diseases of a thyroid gland (tablet of 0,5 mg);
- Closed-angle glaucoma or predisposition to it;
- Acute respiratory insufficiency;
- Chronic obstructive respiratory diseases with initial manifestations of respiratory insufficiency;
- Myasthenia;
- Shock;
- Coma;
- Acute alcoholic poisonings (the state which are followed by weakening of the vital functions), hypnotic drugs and psychotropic drugs, opioid analgetics;
- Age up to 18 years;
- Pregnancy period (especially I trimester) and lactations;
- Hypersensitivity to drug or other benzodiazepines.
Ксанакс it is not intended for treatment of psychotic depressions (is not effective).
With extra care drug should be used at renal failures and a liver, panic frustration, a suicide mood, heavy depressions.
Route of administration and dosage
Ксанакс it is necessary to accept inside.
The optimum therapeutic dose is established individually for each patient depending on weight of manifestation of symptomatology of a disease and expressiveness of clinical effect of drug.
As a rule, standard doses are sufficient for most of patients. In some cases higher doses are required. Increase should be made with care and gradually. At purpose of a high dose the bigger amount of drug should be accepted before going to bed.
Periodically during treatment it is necessary to revaluate a condition of the patient and, if necessary, to adjust a dose.
In case of development of side effects Ksanaks's dose is reduced.
Treatment of alarming and depressive frustration can last up to 6 months, panic frustration – up to 8 months.
Drug withdrawal should be carried out gradually, reducing a dose no more than by 0,5 mg of times in 3 days, in certain cases – even more slowly.
Tablets
The recommended doses depending on indications:
- Alarm: the initial dose – to 0,25-0,5 mg is 3 times/days, a maintenance dose – 0,5-4 mg/days divided into several receptions;
- Panic frustration: an initial dose – on 0,5 mg 3 times a day or on 0,5-1 mg before going to bed. The maintenance dose is selected individually taking into account expressiveness of clinical effect, increase is carried out no more than on 1 mg of times in 3-4 days. The optimum average dose, according to data of clinical trials, makes 5,7± 2,27 mg/days, use of the maximum daily dose of 10 mg in some cases was required;
- Depression: an initial dose – on 0,5 mg 3 times/days, a maintenance dose – 1,5-4,5 mg/days divided into several receptions.
For elderly people and the weakened patients the initial dose makes on 0,25 mg 2-3 times/days, a maintenance dose – 0,5-0,75 mg/days in stages, if necessary the dose is gradually raised.
Tablets ретард
The recommended doses depending on indications:
- Alarm: an initial dose – 1 mg/days in 1 or 2 receptions, a maintenance dose – 0,5-4 mg/days in 1-2 receptions;
- Panic frustration: an initial dose – on 0,5 mg 2 times/days or on 0,5-1 mg before going to bed. The maintenance dose is selected individually taking into account expressiveness of clinical effect, increase is carried out no more than on 1 mg of times in 3-4 days. The optimum average dose, according to data of clinical trials, makes 5-6 mg/days in 1-2 receptions, use of the maximum daily dose of 10 mg in some cases was required;
- Depression: an initial dose – on 1 mg/days in 1-2 receptions, a maintenance dose – 0,5-4,5 mg/days in 1-2 receptions.
For elderly people the initial dose makes on 0,5-1 mg/days in 1-2 receptions, a maintenance dose – 0,5-1 mg/days, if necessary the dose is gradually raised.
Side effects
- Alimentary system: hypersalivation or dryness in a mouth, locks or diarrhea, a loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, increase in activity of hepatic transaminases and an alkaline phosphatase, an abnormal liver function, jaundice;
- Central nervous system: in an initiation of treatment (especially at elderly people) – the increased fatigue, drowsiness, dizziness, delay of motor and mental reactions, decline in the ability to concentration of attention, instability of gait, a disorientation, an ataxy; seldom – dystonic extrapyramidal reactions (the uncontrollable movements, including an eye), a memory impairment, a headache, an incoordination of movements, a tremor, depression of mood, weakness, confusion of consciousness, euphoria, a dysarthtia, a myasthenia, a depression; in some cases – paradoxical reactions (psychomotor arousing, confusion of consciousness, irritability, hallucinations, aggressive flashes, uneasiness, excitement, sleeplessness, a muscular spasm, fear, suicide bent);
- Cardiovascular system: lowering of arterial pressure, tachycardia;
- System of a hemostasis: agranulocytosis (pharyngalgias, hyperthermia, fever, excessive fatigue or weakness), thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, leukopenia, anemia;
- Urinary system: dysmenorrhea, incontience or ischuria, decrease or increase in a libido, renal failure;
- Endocrine system: change of body weight, disturbance of a menstrual cycle and libido;
- Allergic reactions: skin rash, itch.
Special instructions
In comparison with the patients who are suffering from an alcoholism or earlier receiving anxiolytics or antidepressants at patients who did not accept the drugs influencing the central nervous system earlier to alprazola it is effective in lower doses.
Treatment of endogenous depressions can be performed Ksanaks's combination with antidepressants. With depressions drug can cause development of a maniacal and hypomaniacal state in patients.
At prolonged treatment by high doses of an alprazolam development of accustoming and medicinal dependence, especially at the patients inclined to abuse of medicines is possible.
At sharp cancellation or a bystry dose decline of drug the withdrawal which is shown symptoms of various degree of manifestation – from sleeplessness and a small dysphoria to a heavy syndrome with a tremor, sweating strengthening, vomiting, spasms in a stomach and skeletal muscles, spasms is observed. Most often the withdrawal is noted at the patients receiving Ksanaks is long (more than 8-12 weeks).
During treatment it is necessary to refrain from the use of alcoholic beverages, driving of the car and occupations potentially dangerous types of activity demanding the high speed of reactions and special attention.
Ксанакс it is not necessary to apply along with other tranquilizers.
Medicinal interaction
- Anticonvulsant and psychotropic drugs, ethanol, blockers histamine H2 receptors: the oppressing action of an alprazolam on the central nervous system (CNS) amplifies;
- Antibiotics from group of macroleads: the clearance of an alprazolam decreases;
- Oral hormonal contraceptives: the elimination half-life of an alprazolam increases;
- Dextropropoxyphene: concentration of an alprazolam in a blood plasma because of what perhaps more expressed oppression of TsNS, than in cases of use of an alprazolam with other benzodiazepines increases;
- Digoxin: the risk of development of intoxication by cardiac glycosides increases;
- Imipraminum: its concentration in a blood plasma increases;
- Paroksetin, итраконазол, кетоконазол and, presumably, erythromycin: effects of an alprazolam amplify;
- Fluoxetine, флувоксамин: concentration of an alprazolam in a blood plasma increases, the risk of development of its side effects increases.
Terms and storage conditions
To store in the place, unavailable to children. To observe temperature condition 20-25 ºС.
Period of validity – 3 years.
Statistically, on Mondays the risk of getting injured of a back increases by 25%, and risk of heart attack – for 33%. Be careful.

Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only food, N...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow
There comes the season of issues. Many Russians already dream of outdoor recreation, trips, beautiful seaside beaches. At this time there is no wish to think of problems with health and other unpleasant things, however there are subjects which require attention. In the summer repeatedly the risk increases to ache with some very dangerous illnesses, we also will talk about them today....
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create since early years...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, pathologies of a thyroid gland in the world more than 500 million people have. Failures in work of this body lead to heavy disbolism, development of heart diseases, vessels, a reproductive and nervous system. In hard cases excessive...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing an optimum set of nutrients, and which is best adapted in order that the baby normally developed and it was protected from harmful factors of external environment, unusual for it. Unfortunately, breastfeeding process not always does without complications. Sometimes, that the kid begins to bite a breast, giving to mother an essential inconvenience. Some women...
Section: Articles about health
What is in our understanding weeds? It plants which are considered to be suitable only for compost pits and feeding жи...
Section: Articles about health
The body of the person almost for 60% consists of water. It is so important for normal functioning of an organism that loss of only one and a half percent of liquid already leads to the most unpleasant effects. The problems connected with deficit of water can overtake and...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of use of table salt in the therapeutic purposes contains not one century. Applications which do by means of the fabric impregnated with saline solution are considered especially effective. They have antibacterial and antiinflammatory effect, help to heal wounds, exempt fabrics from excess liquid. Hypertonic salt solution of potassium chloride is applied outwardly at many morbid conditions. Let's tell about the most known of them....
Section: Articles about health
Smack in a mouth can arise in the natural way – as a result of lack of morning hygiene or reception of the corresponding food. Odn...
Section: Articles about health
Diapers for adults – individual one-time means of hygiene which in some situations is irreplaceable and from such situations any person is not insured. Though nobody perceives need of their use with enthusiasm, however without it to a sra...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly ways of storage and transportation of food ingredients changed, and people of the whole world had an opportunity to regularly use those products about which their grandfathers and grandmothers did not even know....
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to receive to a toast...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – unique body on the structure thanks to which the person obtains about 80% of information on the world around: about a form, color, size, the movement, and also many other parameters of objects or phenomena. But whether much we know about the most valuable sense body which, according to the scientist Sechenov, provides us about one thousand various feelings a minute? Let's consider 10 most surprising facts about eyes and sight....
Section: Articles about health
All the known slogan "Protect Men!" arose not from scratch. In a sense, the nature created representatives of strong...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning...
Section: Articles about health
The naturopathy sometimes moves as the new direction of medicine, something like fashionable hobby, and there is nothing farther from the truth. This most ancient direction, the word "naturopathy" is translated as "treatment by the nature", and, no doubt, treatment by natural gifts was the first and only, available to the person in ancient times. Despite modern achievements of medicine, the naturopathy remains urgent and today, anyway the person - a part of the nature, and природн...
Section: Articles about health
Cystitis, or inflammation of a mucous membrane of a bladder, this very widespread disease, which, owing to some persons...
Section: Articles about health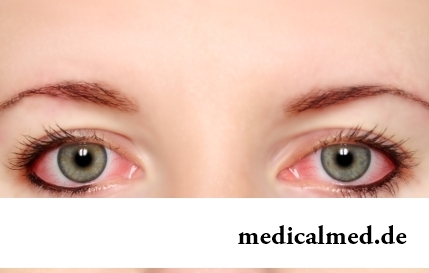
The sclera and mucous membrane of an eye are intensively supplied with blood vessels which problem - to saturate nervous tissues of body with nutrients and oxygen. In a normality vessels are almost not noticeable, however at their expansion (owing to истонч...
Section: Articles about health
When overcomes feeling of hunger, and an opportunity to have dinner fully is absent, having a snack − the meals, small on volume, stabilizing sugar level in blood comes to the rescue. The relation of nutritionists to having a snack more often negative, but only because as snack people choose the most caloric products with the increased amount of "bystry" carbohydrates: cookies, rolls, chips, candies. Nevertheless, the advantage of having a snack is obvious to weight loss: the person avoids strong feeling of hunger...
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? So far physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the bet industry...
Section: Articles about health
Phobia – the persuasive fear of a certain contents shown in a specific situation against the will of the person. Concepts of a phobia and fear are similar, however if the fear is natural protective function of mentality, then the phobia is its deviation. So the person can an ispytyva...
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications of the end of the twentieth century. Researches were conducted since 1984, including placebo - controlled effects. In total clinical tests of Mildronate were carried out for more than thirty years....
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on food. The organism will well function if during food it are...
Section: Articles about health
For the help to doctors in the choice of optimal solutions for treatment of various diseases the Cochrane scientific organization (Cochrane) conducts joint researches with representatives of scientific community around the world. The analysis of a series became carried out by one of the last methanolyses...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person weakness leans: he suffers from drowsiness, complains of bad mood, loss of interest in life and failures in affairs....
Section: Articles about health
