





Monopril
Application instruction:
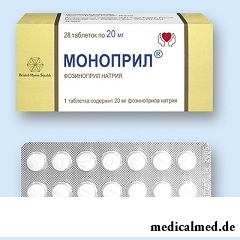 Monopril – inhibitor of an angiotensin-converting enzyme (APF).
Monopril – inhibitor of an angiotensin-converting enzyme (APF).
Form of release and structure
Dosage form – tablets: a round biconvex form with dividing risky on one party and an engraving "609" – on another, can have almost white or white color, without specific smell (on 14 pieces in blisters, in a cardboard pack 2 blisters).
– fozinoprit active ingredient of Monopril sodium, in 1 tablet – 20 mg.
Auxiliary components: кросповидон, cellulose microcrystallic, lactose anhydrous, the sodium stearylfumarating povidone.
Indications to use
- Arterial hypertension;
- Combination therapy of heart failure.
Contraindications
- Age up to 18 years;
- Lactose intolerance, syndrome of glyukozo-galaktozny malabsorption, deficit of lactase;
- Hereditary and idiopathic Quincke's disease in the anamnesis, including against the background of use of other APF inhibitors;
- Period of pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- Hypersensitivity to components of drug and APF inhibitors in the anamnesis.
With care patients need to appoint Monopril with a renal failure, a stenosis of an artery of the only kidney or a bilateral stenosis of renal arteries, a hyponatremia (threat of dehydration, chronic renal failure, arterial hypotension), coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular diseases (including insufficiency of cerebral circulation), chronic heart failure of III and IV functional classes (on NYHA classification), an aortal stenosis; at oppression of a marrowy hemopoiesis, desensitization, a state after transplantation of a kidney, system pathologies of connecting fabric (including a system lupus erythematosus, a scleroderma), a hemodialysis, a diabetes mellitus, gout, a hyperpotassemia, a diet with salt restriction, at the states which are followed by decrease in volume of the circulating blood (including vomiting, diarrhea), the previous treatment by diuretics; at advanced age.
Route of administration and dosage
Pill is taken orally 1 time a day.
The dose is established by the doctor on the basis of clinical indications.
The recommended daily dosing of Monopril:
- Arterial hypertension: an initial dose – 10 mg. The dose is selected individually, considering dynamics of a lowering of arterial pressure (ABP), its size can make 10-40 mg. At insufficiency of hypotensive effect co-administration of diuretics is shown. If use is begun against the background of treatment with diuretics, then the initial dose should not exceed 10 mg and use has to be followed by regular control of the doctor. The maximum dose of drug – 40 mg a day;
- Chronic heart failure (as a part of a combination therapy with diuretic): an initial dose – 10 mg. Within the first week of use it is regularly necessary to control a condition of the patient, his reaction to drug. If he is had well, the dose is recommended to be raised gradually (once a week) to the most admissible – 40 mg. Co-administration of digoxin is optional.
Or to a liver and patients of advanced age (65 years are also more senior) dose adjustment usually is not required to patients with functional disorder of kidneys.
Side effects
- Cardiovascular system: a heart consciousness, strong decrease in the ABP, rushes of blood to face skin, tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, a syncope, stenocardia, arrhythmia, disturbance of conductivity of heart, peripheral hypostases, a myocardial infarction, increase in the ABP, a cardiac standstill, sudden death;
- Alimentary system: appetite disturbance, nausea, vomiting, meteorism, diarrhea or lock, abdominal pains, intestinal impassability, bleedings, hepatitis, pancreatitis, cholestatic jaundice, stomatitis, dysphagy, glossitis, change of body weight, anorexia, xerostomia;
- Respiratory system: short wind, dry cough, bronchospasm, pneumonia, pulmonary infiltrates, rhinorrhea, dysphonia, laryngitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, tracheobronchitis, nasal bleedings;
- Urinary system: renal failure, hyperplasia and/or adenoma of a prostate, proteinuria, oliguria, polyuria;
- Sense bodys: sonitus, ear pain, hearing disorder and sight, taste change;
- Nervous system: dizziness, headache, brain ischemia, stroke, balance disturbances, memory disturbance, weakness, sleep disorders, depression, uneasiness, confusion of consciousness, paresthesia, drowsiness;
- Lymphatic system: inflammation of lymph nodes;
- Metabolism: exacerbation of gout;
- Musculoskeletal system: muscular weakness in extremities, a mialgiya, arthritis, musculoskeletal pains;
- Allergic reactions: itch, skin rash, dermatitis, Quincke's disease;
- Laboratory indicators: increase in concentration of urea, giperkreatininemiya, increase in activity of enzymes of a liver, hyperbilirubinemia, hyponatremia, hyperpotassemia, decrease in level of concentration of a hematocrit and hemoglobin, increase in the blood sedimentation rate (BSR), neutropenia, leukopenia, eosinophilia;
- Influence on a fruit: contractures of extremities, hypoplasia of bones of a skull, hypoplasia of lungs, disturbance of development of kidneys of a fruit, renal failure, decrease in the ABP of a fruit and newborns, олигогидрамнион, hyperpotassemia;
- Others: hyperhidrosis, fervescence, disturbance of sexual function.
Special instructions
Treatment is required to be begun after the careful analysis of extent of increase in the ABP, the previous anti-hypertensive therapy, decrease in a diet of content of liquid and/or salt and other clinical factors. Earlier carried out hypotensive treatment, it is desirable to stop some days before the beginning of use of Monopril.
For decrease in risk of development of arterial hypotension, reception of diuretics is cancelled in 2-3 days prior to therapy.
Use of drug has to be followed by regular control of the ABP, function of kidneys, level of concentration of creatinine, potassium ions, urea, contents of electrolytes and activity of liver enzymes in blood serum.
At development of a Quincke's disease of lips, persons, language, throats or drinks, mucous membranes, extremities against the background of administration of drug, it is necessary to cancel Monopril. Often the termination of treatment provides normalization of a condition of the patient if hypostasis does not pass it is necessary to appoint the corresponding therapy, including hypodermic administration of solution of Epinephrinum (adrenaline) (1:1000). The untimely help can lead to obstruction of respiratory tracts with risk of a lethal outcome.
In rare instances reception of APF inhibitors can cause the hypostasis of a mucous membrane of intestines which is followed by abdominal pains. As it can proceed without symptoms of a face edema, at normal activity of C1 esterase and absence at the patient of nausea or vomiting, it needs to be included in differential diagnosis of patients with complaints to abdominal pains. Symptoms of hypostasis pass after drug withdrawal.
Patients with anaphylactic reactions against the background of dialysis with use of high-permeability membranes or an afereza of lipoproteids of low density with adsorption need to appoint hypotensive drugs of other class or use of dialysis membranes of other type to sulfate of a dextran.
Because of risk of development of anaphylactic reactions when performing desensitization of patients it is necessary to observe extra care.
Not to allow development of suppression of function of marrow and an agranulocytosis before use of APF inhibitors and in the course of therapy follows regularly (within the first 3-6 months once a month) to carry out definition of leukocytes and a leukocytic formula. At patients with the increased risk (a renal failure, general diseases of connecting fabric) researches continue to be conducted for the first year of therapy.
Against the background of carrying out dialysis, an intensive care diuretics, the diet limiting consumption of table salt, development of symptomatic arterial hypotension happens more often. At tranzitorny arterial hypotension use of drug is continued after recovery of volume of the circulating blood.
Use of APF inhibitors is shown to patients with chronic heart failure, but it can cause the excess anti-hypertensive action exponentiating development of an azotemia and oliguria, in rare instances – an acute renal failure with a lethal outcome. Therefore each increase in a dose of Monopril or diuretic demands careful observation of their state from patients of this category, especially within the first two weeks of therapy. To the normal or low ABP who were earlier accepting diuretic means the diuretic dose decline can be necessary for patients with a hyponatremia.
Insignificant decrease in the system ABP in an initiation of treatment of patients with chronic heart failure is the typical and desired effect. The maximum decrease in the ABP is observed at early stages of therapy and stabilized within 1-2 weeks without decrease in therapeutic effect.
In rare instances reception of APF inhibitors can cause the syndrome beginning with cholestatic jaundice which approach of a fulminant necrosis of a liver follows (with risk of a lethal outcome). As the nature of this syndrome is not established, at significant increase in activity of enzymes of a liver and emergence in the patient of noticeable yellowness drug it is necessary to cancel and appoint the corresponding therapy.
At an abnormal liver function the increased maintenance of a fozinopril can be noted in a blood plasma. At cirrhosis the general clearance of a fozinoprilat seeming to normal is reduced, and approximately AUC, in comparison with patients with normal function of a liver is twice higher.
At arterial hypertension with a stenosis of an artery of the only kidney or about one - or a bilateral stenosis of renal arteries use of APF inhibitors can cause reversible processes of increase in concentration of creatinine of blood serum and an urea nitrogen of blood in patients (in this case drug withdrawal is required). This category of patients needs regular control of function of kidneys in the first weeks of therapy. Increase in concentration of creatinine of blood serum and an urea nitrogen of blood (usually insignificant and passing) with normal function of kidneys can be caused in patients by a concomitant use of Monopril and diuretics (in this case the drug dose decline is required).
At the expressed chronic heart failure use of APF inhibitors can be followed by the progressing azotemia and/or an oliguria, in rare instances – risk of development of an acute renal failure with a lethal outcome.
The patients with a diabetes mellitus of 1 type, a renal failure and also accepting the kaliysoderzhashchy nutritional supplements, kaliysberegayushchy diuretics and other means promoting increase in level of maintenance of potassium ions in blood serum are subject to big risk of development of a hyperpotassemia against the background of administration of drug.
In case of cough it is necessary to consider administration of drug as the possible reason when carrying out the differential diagnosis.
By preparation for carrying out surgery it is necessary to warn the anesthesiologist about Monopril's reception.
Patients are recommended to carry out with care exercise stresses, including in hot weather.
Because of possible developing of dizziness, it is necessary to be careful at control of vehicles and mechanisms.
Medicinal interaction
During treatment by Monopril simultaneous use of other medicines can be begun only after consultation with the attending physician who can estimate interaction of drugs that will allow to avoid development of undesirable effects.
Terms and storage conditions
To store in the place, dry, unavailable to children, at a temperature of 15-25 °C.
Period of validity – 2 years.
Name of drug
Price
Drugstore
Monopril тбл 20 mg No. 28, Bristol-Myers Squibb
486 rub.
 Network of the Moscow drugstores of IFC
Network of the Moscow drugstores of IFCIn Great Britain there is a law according to which the surgeon can refuse to do to the patient operation if he smokes or has excess weight. The person has to refuse addictions, and then, perhaps, he will not need an operative measure.

Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs п...
Section: Articles about health
Let's begin with the fact that a separate illness which is called "adjournment of salts", just does not exist. In practice this household name of disbolism leading to development of a number of diseases. Pathological process consists that in an organism проис...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need of a visit to the gynecologist. Certainly, it is possible to establish the exact diagnosis only after inspection, but on the basis of some signs it is possible to assume existence of this or that pathology. Let's consider symptoms of the female diseases which are found most often....
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against diseases...
Section: Articles about health
Cellulitis - very widespread cosmetic shortcoming which arises approximately at 80% of women sooner or later. Emergence it is connected with change of structure of a hypodermic fatty layer. At the same time on the surface of skin at first there are roughnesses (cambers...
Section: Articles about health
All diseases from nerves – in this joke a big element of truth, are said by doctors. Constant stresses lead to decrease in protective forces of an organism, and it becomes vulnerable for a set of diseases. It is wrong to think that the stress is a problem of the present. Life of people and hundred, and one thousand years ago also abounded with problems therefore need of a relaxation understood in ancient times – to some techniques more than one thousand years. The person needs knowledge of how it is possible to relax, this knowledge пригод...
Section: Articles about health
Obesity is called by a disease of 21 centuries, for the last 100 years by the number of the people suffering from excess body weight, considerably increased...
Section: Articles about health
According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but the minority sees a doctor from them. And in vain - even the insignificant discomfort in the field of generative organs can serve as a symptom of an illness fraught heavy посл...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist of iodine more than for 65%. The lack of iodine leads to decrease in production of hormones and, as a result, development of a hypothyroidism. The long condition of deficit can become a source of problems of the cardiovascular, bone, digestive SI...
Section: Articles about health
The endocrine system carries out in a human body extremely important role, practically all processes of life activity регулируютс...
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In most cases pathological reactions cause the substances which are contained in food stuffs, hair of animals, medicines...
Section: Articles about health
The words "disease" and "patient" not without reason come from one root – "pain". As a rule, symptoms of illnesses thoroughly spoil to patients life. However from this rule there are exceptions. Some diseases are shown by signs which can cause even positive emotions. It is a pity only that the majority of such illnesses are heavy and incurable....
Section: Articles about health
Practice of use of table salt in the therapeutic purposes contains not one century. Appl are considered especially effective...
Section: Articles about health
The healthy nutrition is the invariable principle of health and good health for long years of the woman. Nevertheless, in a diet at each stage of life there are the features allowing to support an organism by those substances which are most necessary...
Section: Articles about health
The winter swimming in open reservoirs called in our country by "winter swimming" – officially recognized sport and one of the most extreme ways of a hardening of an organism. This occupation has an old story and adherents in many countries. The international competitions in winter heats on open water, and every two years – the World Cup are annually held. Despite huge popularity and the proved advantage for health, winter swimming is still surrounded with hardy delusions. Ра...
Section: Articles about health
All know that self-treatment is dangerous. However absolutely it is almost impossible to do without it. Rate of modern life not on...
Section: Articles about health
The business lady, the become mother, it is necessary to solve an array of problems. But of them is main: how to combine the beloved child and work? What traps trap the working mother and how she needs to behave?...
Section: Slideshow
You heard that laughter prolongs life? Researchers did not manage to establish longevity direct link with sincere fun yet, but several facts confirming beneficial influence of risibility on the state of health are clinically proved....
Section: Articles about health
One of the useful properties presented to the person by the nature is ability to feel fear. This ability is called a signal...
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to get access to various apparatuses and an opportunity to train under the leadership of the experienced consultant. Many consider fitness on...
Section: Articles about health
History of mankind contains several tens of epidemics whose emergence was compared by eyewitnesses and historians to doomsday. The most terrible of them claimed the lives of millions of people, having made even the whole people to the person of the earth. What they − the diseases striking terror? Whether it managed to the person to find treatment, or he is still powerless before forces of nature?...
Section: Articles about health
Health and attractiveness - eternal values, pursuing which people often use the most unusual ingredients and technicians...
Section: Articles about health
New year, wedding, birthday, office party – an occasion to drink at the Russian person will always be. How to reduce a negative impact of alcohol by an organism and to avoid a condition of strong intoxication? The most correct council – to refuse the use spirits напитк...
Section: Articles about health
All of us, unfortunately, should face flu nearly an every year. It would seem, so frequent disease has to be studied already up and down, and each person, at least once to them had (and the number of such people in our country aims at 100%), has to know the basic rules of its treatment. However as shows experience of doctors, there is no it, and often people, self-confidently thinking what is known as it is necessary to be treated, make mistakes....
Section: Articles about health
According to World Health Organization, every third inhabitant of Earth has excess weight, and every tenth suffers ожирен...
Section: Articles about health
Producers of milk mixes for children assure: mixes are ideally balanced and adapted for needs of babies. If mother should raise artificially the kid owing to serious problems with health, to do nothing – m substitutes...
Section: Articles about health
Transfusion of donor blood has almost century history. In spite of the fact that this procedure is quite usual for many people, process of blood donation is still surrounded with numerous myths. Today we aimed to discredit the most widespread of them....
Section: Articles about health

