Spirometry
 Spirometry call the ventilating test which is carried out for diagnosis of a condition of respiratory system. The spirometry gives the chance to measure the volume of respiratory system, volume speed of an air flow and their ratio, vital capacity of lungs, capacity of an exit and entrance, maximal ventilation.
Spirometry call the ventilating test which is carried out for diagnosis of a condition of respiratory system. The spirometry gives the chance to measure the volume of respiratory system, volume speed of an air flow and their ratio, vital capacity of lungs, capacity of an exit and entrance, maximal ventilation.
The spirometry gives the chance to reveal diseases of lungs and cardiovascular pathologies, to estimate their weight, efficiency of treatment. Besides the test helps to learn to breathe correctly.
It is considered that smokers need to study annually spirometry: inspection will help to reveal pulmonary dysfunction at an early stage, to carry out differential diagnosis of bronchial asthma, obstructive chronic diseases of lungs, a sarcoidosis.
This diagnostic method has no contraindications including age limits: carry out spirometry at children and at adults.
Order of carrying out inspection at spirometry
The spirometry is carried out by means of the special device for continuous graphic record of change of volumes of the exhaled and inhaled air – the spirocount. For each patient put on a new one-time mouthpiece the device.
The examinee ask to make very deep breath, to hold the breath, to nestle a mouth as it is possible more densely to a mouthpiece (record on the device from this point begins to be kept) and evenly and to quietly exhale all gathered air. It can take about 15 seconds the patients having a chronic obstructive disease of lungs. After a quiet exhalation the patient needs to make the same, but to make a best effort.
The patient repeats the similar procedure two more times, and the received three groups of indicators are used by the doctor for interpretation of spirometry.
Spirometry indicators
 The majority of indicators of spirometry are expressed percentage of average values of physiological sizes. Norma hesitates within 80-120%. In interpretation of spirometry it is possible to meet such indicators:
The majority of indicators of spirometry are expressed percentage of average values of physiological sizes. Norma hesitates within 80-120%. In interpretation of spirometry it is possible to meet such indicators:
- respiratory volume – the volume of the air coming for one breath to lungs at a quiet exhalation. Norm – 500-800ml;
- ZhEL - the vital capacity of lungs – the lung volume which leaves at an exhalation. This indicator significantly goes down at restrictive diseases of lungs;
- FZhEL1-the forced vital capacity of lungs. This indicator of spirometry is similar previous, but the patient needs to make an exhalation at the greatest possible speed and with the greatest possible effort.
- OFV1 - the volume of the forced exhalation in 1 second. Amount of air which leaves lungs in the first second of an exhalation, with a best effort. These data of spirometry at children and adults reflect a condition of big respiratory tracts, are expressed in a percentage ratio from the vital capacity of lungs. Norm of the forced exhalation – 75%.
- Tiffno's index. A percentage ratio of OFV1 to FZhEL. Its norm – 70% and more.
- Average volume speed. It is measured as a percentage – 25-75%. Shows in what state there are small respiratory tracts. Volume speed is useful to identification of early obstructive disturbances.
- Peak of volume speed on an exhalation. The maximum speed which the person can show at the strengthened exhalation.
- Passability of respiratory tracts. Depends on effort of muscles, displays in what state there are respiratory tracts at the level of large bronchial tubes, tracheas.
As all these indicators undertake at the patient three times, at interpretation of spirometry the doctor takes the best result for the analysis and compares it to norm indicators for the corresponding group of people: in attention growth, a sex, age of the patient undertakes.
During sneezing our organism completely stops working. Even heart stops.

Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on is called...
Section: Articles about health
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. However visit of salon where work with biological material of clients, not always harmlessly is conducted. Today it is known Bol...
Section: Articles about health
Kidneys perform the most important function of clarification of blood from those products of metabolic processes which cannot be used by an organism for obtaining energy and construction of new cells. With the urine produced by kidneys from a body of the person the bulk of the toxins getting to it with food and water is removed. Normal functioning of kidneys provides removal from an organism of excess liquid and maintenance of optimum ionic balance. At emergence of failures in work of secretory system...
Section: Articles about health
The pancreas performs two functions in a human body: release of enzymes without which digestion carbohydrate is impossible...
Section: Articles about health
Antibiotics - - it is possible to call the chemical compounds suppressing growth of bacteria the break in the field of medicine which allowed to save mankind from many diseases incurable earlier: tuberculosis, plague, syphilis and many others. A contribution of drugs to rescue of people from...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot replace completely modern synthetic drugs, but their use becomes frequent serious help in simplification of a course of many illnesses and improvement of quality of life of chronic patients....
Section: Articles about health
Long time antibiotics were considered as a panacea from all diseases and were appointed even at insignificant symptoms of an infection. Even now...
Section: Articles about health
Good appetite was always considered as a sign of good health. The correct operation of the mechanism which is responsible for the need for nutrients and receiving pleasure from process of its satisfaction demonstrates that the organism functions without special from...
Section: Articles about health
The saying "the rich do not know how the other half lives" is known to all. In a broad sense it is that we can not always understand the person whose features of a state are unknown to us. If with physiological characters of diseases the situation is more or less clearly (having noticed them, we realize that to the person nezdorovitsya), then with symptoms of the illnesses affecting the mental sphere everything is much more difficult. Not absolutely usual behavior is quite often perceived surrounding as a ridiculous eccentricity, or that much ху...
Section: Articles about health
Coffee - the tonic loved by many for the invigorating aroma and deep taste. Having the stimulating effect, coffee raises ра...
Section: Articles about health
High temperature - a frequent symptom of such widespread diseases as a SARS, quinsy, pneumonia, etc. To reduce heat, having facilitated a condition of the patient, doctors recommend to accept antipyretics, however their use is not always possible. Too h...
Section: Articles about health
Turnip, radish, horse-radish – once these and other products enjoyed wide popularity at our ancestors, being not only the food sating an organism but also the medicines curing of many diseases. Unfortunately, the use of some of them got out of fashion long ago, and once favourite plants and vegetables almost ceased to make a contribution to human health. Inclusion of such products in a modern diet − an effective measure of prevention and treatment of diseases which seldom suffered...
Section: Articles about health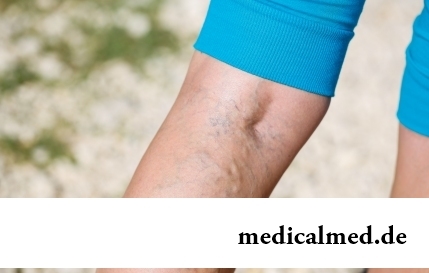
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person in many respects depends on chemical composition of biological liquids of an organism. Specialists consider that PH value of these solutions has to be in range of 7,35-7, 45. A deviation in the smaller party (so-called "acidulation") to a chra...
Section: Articles about health
Within several decades of our compatriots convinced that the use of butter nasty affects a condition of coronary vessels. As a result the reputation of a product was impaired thoroughly a little, and many almost ceased to include it in the diet, having given preference "to safer" to vegetable fats. Meanwhile, the last researches showed that harm of butter for health is strongly exaggerated. But the product has a number of unique properties, to...
Section: Articles about health
Such trouble as the milkwoman's attack, at least once in life happened almost to each woman. Prevalence забол...
Section: Articles about health
No, probably, the person who would not have cold. Cold, cough, a headache – these symptoms are known to everyone. The peak of catarrhal diseases is the share of fall. SARS already came to schools and kindergartens, flu slowly makes the way to the cities, in a word, з...
Section: Articles about health
The dietology, as well as other sciences, does not stand still. Food stuffs are exposed to comprehensive study, and scientists obtain new information on their properties and influence on a human body. Unfortunately, this reasonable and natural process gives unpleasant side effect from time to time: some types of food periodically declare "harmful" or even "deadly" without the bases, sufficient on that....
Section: Articles about health
For many women the word "fat" sounds as a sentence. In aspiration to an ideal figure they try to exclude, first of all, from with...
Section: Articles about health
Stability of a hormonal background is one of the most important conditions of preservation of health of the woman. At the same time endocrine system – the thin device extremely sensitive to any external influences. Changes of an image жиз can become the reason of hormonal failure...
Section: Articles about health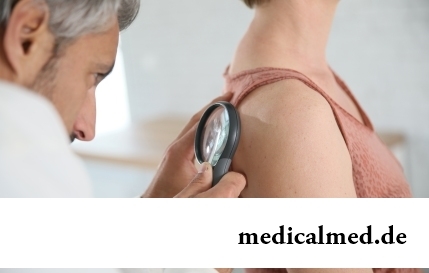
Scientists have no unambiguous opinion on a proximate cause of emergence of a carcinoma cutaneum today. Only the factors promoting development of this illness are precisely established. Treat them: long impact on skin of ultraviolet rays, radiation exposure, thermal injuries, injuries of skin by aggressive chemicals (pitches, acids, alkalis, etc.), genetic predisposition (existence of malignant new growths of skin in the family anamnesis), at...
Section: Articles about health
Childbirth is the most important event in life of each woman. We are women we give birth to the new little man on this light. Now...
Section: Articles about health
Eyes – unique body on the structure thanks to which the person obtains about 80% of information on the world around: about a form, color, size, the movement, and also many other parameters of objects or phenomena. But whether much we know about the most valuable body...
Section: Articles about health
Producers of milk mixes for children assure: mixes are ideally balanced and adapted for needs of babies. If mother should raise artificially the kid owing to serious problems with health, to do nothing – it is necessary to feed with substitutes of milk. However pediatricians note that not seldom women without good reasons refuse feeding of the child a breast and pass to milk mixes. Common causes of such decision – the aspiration to leave quicker...
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor about age...
Section: Articles about health
The popular expression "run from a heart attack" became the motto of the people supporting active lifestyle. Moreover, run became a peculiar fashionable tendency: sales of racetracks and the accompanying goods for run are at permanently high level. Really...
Section: Articles about health