Cholangitis
Cholangitis – an inflammation of bilious channels. This hard proceeding disease which can be independent, but is more often combined with an inflammation of a gall bladder or liver.
Cholangitis reasons
Disturbance of passability of bilious channels and accession of an infection is the main reason for a cholangitis. Disturbance of passability of bilious channels often arises at a choledocholithiasis – formation of gallstones in biliary tract. Cicatricial narrowings of biliary tract owing to chronic cholecystitis, removal of a gall bladder (a postcholecystectomy syndrome), a cyst or a tumor of the general bilious channel can be other reasons of the broken outflow of bile.
Quite often outflow of bile is broken as a result of a helminthic invasion. Bilious channels can be blocked by ascarids. Such parasitic diseases as an opisthorchosis, echinococcosis, шистостомоз, can also lead a lambliasis to emergence of a cholangitis.
The infection generally gets to bilious ways from intestines as at stagnation of bile the mechanism interfering penetration of intestinal contents into the above-located parts of digestive tract is broken. In addition to the ascending (intestinal) way of hit of an infection there is also a descending way when the infection gets into bilious ways with a blood flow or a lymph from other inflammatory center in an abdominal cavity.
Types of a cholangitis
On character of a current distinguish an acute and chronic cholangitis.
The acute cholangitis depending on a type of an inflammation can take the following forms:
- Catarral cholangitis at which there is hypostasis of a mucous membrane of bilious channels. This form in the absence of treatment passes into a chronic inflammation, and further leads to cicatricial narrowing of channels;
- Purulent cholangitis. Bilious channels are filled purulent separated, mixed with bile. This form often extends to a gall bladder and a liver, involving these bodies also in a purulent inflammation;
- Diphtheritic cholangitis. The mucous membrane of bilious ways ulcerates, and then nekrotizirutsya that leads to destruction of walls of bilious channels and purulent fusion of surrounding fabrics including a liver;
- Necrotic cholangitis. Arises at hit to bilious canals of aggressive enzymes of a pancreas that leads to development of sites of a necrosis of a mucous membrane of bilious ways.
The chronic cholangitis on character of a current can be latent (hidden), recurrent, septic and abscessing.
Special form of a chronic cholangitis – a sclerosing cholangitis. This initially chronic inflammation arising without infectious agent, presumably autoimmune character. At the same time in bilious ways there is an inflammation leading to a sklerozirovaniye – to hardening and overgrowing of a gleam of channels that in turn leads to cirrhosis. The sclerosing cholangitis will not respond to treatment, has the slow progressing current and on average within 10 years leads to heavy disturbances with a possible lethal outcome.
Cholangitis symptoms
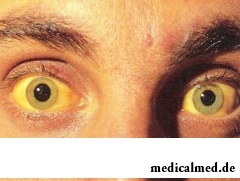
Cholangitis symptoms in an acute form are shown violently, there is fever with a fever and pouring then, pain as bilious colic – quite intensive, aching, with localization in right hypochondrium, sometimes giving to a shovel and a shoulder. It is followed by nausea, vomiting. Integuments and scleras accept yellow color, the skin itch develops.
Cholangitis symptoms in an acute form at patients of advanced age and children have some differences. At elderly people pain can be absent, and at scanty symptoms of a cholangitis the inflammation, nevertheless, takes heavy, usually purulent form.
The cholangitis in an acute form occurs at children seldom, generally as consecutive infection (usually streptococcal) at other disease. The acute cholangitis at children proceeds very violently, cholangitis symptoms in this case are not specific and inherent to any acute inflammation of digestive tract in this connection the acute cholangitis at children can be accepted to other gastrointestinal disease.
Cholangitis symptoms in a chronic form are less expressed, the megalgia is inherent only in the presence of stones in bilious channels. The main symptoms of a cholangitis in this case is the general weakness and increased fatigue, inexplicable periodic rises in temperature, a skin itch. The thickening of trailer phalanxes of fingers and reddening of palms belongs to signs of a cholangitis.
The chronic cholangitis causes decrease in body weight owing to lack of appetite and nausea in children, constant intoxication leads to anemia, pallor or yellowness of skin, physical development of the child is slowed down, there can be a lag and in the general development, chronic headaches develop.
Diagnosis of a cholangitis
The diagnosis is made on the basis of characteristic symptoms of a cholangitis, careful survey and data of hardware and laboratory researches:
- Ultrasonography of a gall bladder, liver and bilious channels;
- Radio isotope research of bilious ways;
- Intravenous holangiografiya (the roentgenoscopy of bilious ways with intravenous administration of a contrast agent allowing to see inside - and extrahepatic channels);
- Retrograde pankreatokholangiografiya (roentgenoscopy of bilious ways and a pancreas with endoscopic administration of contrast medium);
- Holangiomanometriya (measurement of pressure in bilious channels);
- Holedokhoskopiya (endoscopic research of bilious channels);
- General and biochemical analysis of blood;
- Laboratory research of bile.
Treatment of a cholangitis
Treatment of a cholangitis can be conservative or surgical, depending on a disease form. Treatment of a cholangitis is performed only in a hospital, in view of danger of development of heavy complications – purulent abscesses of a liver and gall bladder, peritonitis, and at a chronic cholangitis of cirrhosis.
Conservative methods of treatment of a cholangitis are applied when there is no mechanical obstacle to outflow of bile on biliary tract. In this case appoint antibacterial drugs (antibiotics of a broad spectrum of activity and streptocides), medicinal substances reducing intoxication (intravenous administration of Haemodesum, etc.), the improving bile outflows, spasmolysants (for example, Dyuspatalin).
In case conservative treatment does not yield results, and also in all cases when it is impossible to create normal outflow of bile medicamentous means, resort to surgical treatment of a cholangitis. A choice method now, in the absence of contraindications (purulent, necrotic processes, abscesses), is the endoscopic technique.
This way allows to carry out drainage of bilious channels, a removing calculus, elimination of stenoses (narrowings), without resorting to extensive band operation that allows to lower an operational injury, to avoid bleeding, to improve recovery. In the presence of more severe forms of a cholangitis perform band operation, deleting the sites which underwent purulent fusion or necrotic disintegration. In the post-operational period appoint antibacterial therapy.
Was considered earlier that yawning enriches an organism with oxygen. However this opinion was disproved. Scientists proved that yawning, the person cools a brain and improves its working capacity.

Physical activity is necessary for normal functioning of a human body. At a lack of the movement cease функц...
Section: Articles about health
A lot of things depend on a condition of a backbone in a human body, a backbone - not only a support for a body, it also a receptacle for a spinal cord, that is why malfunctions with a backbone are so dangerous. To treat rachis diseases very difficult and long...
Section: Articles about health
Extracorporal fertilization – one of the most modern methods of controlling with infertility. So far he already helped a significant amount of married couples to become happy parents. Usually to the EKO procedure difficult and very expensive, resort in those situations when all other ways to help couple to bring the child are inefficient. "Conception in a test tube" yields quite good results in cases of infertility of one of partners, existence at the woman of impassability of uterine tubes...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need to the visa...
Section: Articles about health
According to data of World Health Organization, the cataract is diagnosed almost for 7% of the population of Earth. The statistics of incidence is considered not full as at an initial stage the illness, as a rule, does not cause to the person of special inconveniences, and many having got sick...
Section: Articles about health
Since the moment when the child becomes a school student, his sight begins to be exposed to the strengthened loadings which are supplemented with viewing of animated films and long computer games. During this period of life of the child development of not completely created organs of sight, it is very easy to break the excessive loading which is aggravated with lack of a work-rest schedule. As a rule, and occurs: according to WHO statistics, every fourth child of school age has these or those diseases of eyes, Wednesday...
Section: Articles about health
Season of activity of viral infections in the heat. Everyone can get sick, but probability of this unpleasant event it is possible and it is necessary miny...
Section: Articles about health
Bees – really unique beings. Practically all products of their life activity are used by the person. Since the most ancient times medicinal properties of honey and other substances received in the course of beekeeping are known. The fact that all these пр is especially significant...
Section: Articles about health
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. However visit of salon where work with biological material of clients, not always harmlessly is conducted. Today more than 100 pathogenic microorganisms who can catch in beauty shop including deadly to health are known....
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant but which is not exhausting, motive...
Section: Articles about health
For anybody not a secret that the modern person eats not as his ancestors. For the last 100 years in broad access there were absolutely new products which are result of use of the latest technologies in food production. Significantly changed спо...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, at the address to doctors seven of each ten patients complain of a headache. Actually it is much more people who are periodically feeling unpleasant feelings such. Many people, apart from a headache the reason for serious fears, prefer to muffle independently the next attack medicines. Such behavior is extremely careless, especially if this symptom appears regularly and is followed by other signs of an indisposition. Constants head Bol...
Section: Articles about health
On the head of the person about one million hair follicles, or as they are called still, hair bulbs are located. At the moment he is born...
Section: Articles about health
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste, because of to...
Section: Articles about health
According to World Health Organization, every third inhabitant of Earth has excess weight, and every tenth has obesity. The reason of this phenomenon, according to specialists, roots in one not very comforting fact: most of people consume much more calories, than it is necessary. How it turns out what we overeat? Why it is so difficult to refuse an excess portion tasty or additives? Let's try to find out what factors prevent us to eat food with reasonable moderation....
Section: Articles about health
People know that thermal sources have salutary force long ago. Treatment by natural waters is one and...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning...
Section: Articles about health
Weakness of an ankle joint – very widespread problem. Its existence is demonstrated by tendency to a podvorachivaniye of legs when walking on heels, frequent painful sprains, pain on average and anonymous toes even after small loadings. Usually people with such pathology take off unpleasant effects by means of the anesthetizing pulverizing and ointments, but it does not lead to radical elimination of a problem. Meanwhile, at the known persistence it is possible to strengthen an ankle to the house...
Section: Articles about health
All parents are ready to what the baby often and pisat much. Since then, as the absorbing diapers strongly became current...
Section: Articles about health
Smoking not only exerts a negative impact on the state of health of the consumer of tobacco products, but is an air polluter the substances potentially dangerous to people around. In recent years significantly the number of people, стремящ increased...
Section: Articles about health
"Epilepsy" doctors made the diagnosis in antique times. Displays of an illness and pattern of its development are very well studied. However for nonspecialists this disease remains to not less mysterious, than in the ancient time. Many delusions are connected with epilepsy, and it sometimes very unpleasantly affects quality of life of patients and their relatives. In this article we will try to dispel the most known of similar myths....
Section: Articles about health
80% of women at least once to lives complained of discomfortable feelings to breasts, consolidations and nagrubaniye. These are mastopathy symptoms. Mas...
Section: Articles about health
Separate food - the system of meal based on digestion physiology which is carried to improvement methods. According to nutritionists, the separate use of the carbohydrate and proteinaceous products demanding different conditions of assimilation helps to get rid from Bol...
Section: Articles about health
Partial and the more so full loss of hearing significantly reduces quality of life. Difficulties with communication lead to loneliness and isolation. The person who badly hears experiences difficulties with social and professional implementation, quite often has problems in private life....
Section: Articles about health
About 20% of the population of our planet have a hypertension (permanent increase in arterial pressure). This disease negatively narrations...
Section: Articles about health
Modern footwear is extremely various. It stopped being only protection for legs long ago. Today shoes, boots, barefoot persons choose not so much proceeding from their convenience and functionality how many being guided by outward, brand and an opportunity to add with it...
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, about it there can be no disagreements: water is necessary for a human body for normal life activity, and about how and when it should be drunk, all know. It turned out that the situation is not absolutely so: for many years there are very persistent delusions connected with this question. Let's consider the most widespread of them....
Section: Articles about health