





Chronic nephrite
Chronic nephrite – the disease developing as a result of not cured acute nephrite.
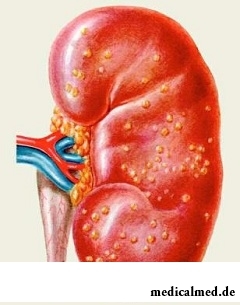 The disease, as a rule, as a result of long impact on kidneys of the infectious centers develops. Chronic nephrite can sometimes develop also without acute stage of nephrite in the past. First of all, the chronic nature of a disease depends on existence of infections in an organism, insufficient treatment in the past of acute nephrite and unfavorable conditions of the environment.
The disease, as a rule, as a result of long impact on kidneys of the infectious centers develops. Chronic nephrite can sometimes develop also without acute stage of nephrite in the past. First of all, the chronic nature of a disease depends on existence of infections in an organism, insufficient treatment in the past of acute nephrite and unfavorable conditions of the environment.
At chronic nephrite in kidneys there are anatomic changes leading to formation of cellular exudate in capsules (a so-called semilunum), to widespread defeat of vessels of kidneys, degenerative changes of a canalicular epithelium. All listed changes lead to a zapustevaniye of separate balls and a granular kidney as a result of an atrophy of some sites of a renal parenchyma eventually.
Course of chronic nephrite
During chronic nephrite it is necessary to allocate such stages:
- Stage of renal compensation, sufficiency of azotovydelitelny function of kidneys. As a rule, this stage is followed by such symptoms of chronic nephrite as hypostases, a hamaturia, an albuminuria, increase in arterial pressure. Sometimes these symptoms carry not expressed character, only the albuminuria takes place.
- Stage of a renal decompensation, insufficiency of azotovydelitelny function of kidneys. At this stage the amount of protein can fall in urine, hypostases can also decrease, however the hypertension becomes, on the contrary, steadier. The main symptoms of chronic nephrite at this stage are initial insufficiency of kidneys and increase in blood of slag nitrogen. Azotemic uraemia is characteristic of this stage.
As a rule, outcome of chronic nephrite deadly. Duration of disease is various and can fluctuate within 1-20 years and more. Death can come also from a hematencephalon, heart failure, from consecutive infections, etc.
Types of chronic nephrite
- Subacute ekstrakapillyarny nephrite. Formation of cellular exudate in a cavity of capsules is characteristic of this form. Approximately in half a year after the beginning of a disease the persistent hypertension and a persistent hamaturia is shown. It is quite often possible to observe such symptoms of chronic nephrite as persistent hypostases, existence of an azotemia, the accruing anemia, high concentration in blood of creatinine and aromatic connections, and also uraemic symptoms which as a result lead to the fact that by the end of the first two years of a disease the patient dies.
- Nephrotic chronic nephrite. Such symptoms of chronic nephrite as persistent hypostases, a considerable albuminuria and normal arterial pressure are characteristic of this look. Anatomically intracapillary nephrite with nephrotic changes of tubules is characteristic of this look. Hypostases are not followed by a Jacob's ladder and an asthma, amplify from reception of salty food and can keep a long time (from several months to several years). If patients throughout the long edematous period do not die of infections, then there comes the period bezotechny, characterized by the general improvement of a condition of the patient. However this temporary phenomenon, and comes further death from chronic true uraemia.
- The mixed chronic nephrite. Persistent hypostases of lipoid and nephrotic type, increase in arterial pressure and cardiovascular symptoms are characteristic of this type of nephrite. Afterwards the renal failure joins these signs. As a rule, patients die as a result of heavy chronic uraemia. Also death from a hematencephalon, heart failure and infections is characteristic of this form of chronic nephrite.
- Chronic nephrite of hypertensive type. This type of a disease can proceed a long span almost asymptomatically. A characteristic sign are only hypertensive symptoms arising usually at an idiopathic hypertensia (vascular spasms, paresthesias, spasms of gastrocnemius muscles, etc.). Anatomically it is possible to observe intracapillary nephrite with strong indications of a sclerosis of small arteries. This disease usually is found absolutely accidentally when passing inspection. Chronic nephrite of this look can last many years then at the patient the picture of chronic true uraemia develops.
Prevention of chronic nephrite
Prevention of chronic nephrite first of all consists in prevention of nephrite in an acute form, its early diagnosis, timely and adequate treatment.
The course of chronic nephrite can be facilitated by carrying out the rational mode and treatment of focal infection, to detain thereby approach of a stage of the renal failure which is not giving in to treatment.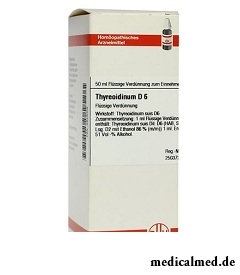
Treatment of chronic nephrite
Long since at chronic renal diseases of the patient a certain hygienic mode was recommended: wearing woolen linen, the strengthening not irritating food, accommodation in a warm and arid climate. At treatment of chronic nephrite patients should avoid overcooling, a heavy exercise stress, stressful situations, drugs irritating kidneys and the excessive use of food. All these actions are directed not only to creation of optimal conditions for work of the damaged body, but also for the facilitated activity of all organism in general.
In case of an inflammatory exacerbation of a disease, developing of severe hypostases, weakening of a cardiac muscle and at manifestation of uraemic symptoms patients need a bed rest.
At treatment of chronic nephrite of nephrotic type appoint an electrolyte-deficient diet, protein-rich, Thyreoidinum, mercusal. In case of complications streptococci and pneumococci appoint penicillin, sulphonamide drugs. Stay in a warm and arid climate and reception of heart and vasodilating medicines is shown to the patient.
If the infection center is found, to the patient treatment of chronic nephrite by means of sulphonamide drugs and penicillin, physiotherapeutic methods is appointed. In case of satisfactory function of kidneys to the patient can recommend to carry out surgical intervention. Removal of the infectious center aims to stop before itself toxi-infectious impact on an organism, and also to eliminate action of a source of nervnoreflektorny irritation.
At treatment of chronic nephrite to the patient appoint glucose solution under skin and inside in large numbers for the purpose of counteraction of uraemic intoxication. At emergence of symptoms of uraemic acidosis to the patient appoint alkalis and use of alkaline saline solutions.
Bloodletting favorably influences at manifestation of hypertensive and vascular symptoms. Against separate symptoms of uraemia use the drugs influencing the centers of a brain.
There are very curious medical syndromes, for example, persuasive swallowing objects. In a stomach of one patient suffering from this mania 2500 foreign objects were revealed.
The sclera and mucous membrane of an eye are intensively supplied with blood vessels which problem - to sate nervous tissues of body to a pitata...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
Each failure in work of bodies and systems of a human body is, as a rule, shown by the whole complex of symptoms. In particular, malfunctions with health often cause emergence of cosmetic defects in the form of rashes on a face. Experienced doctors know that localization of heat-spots usually depends on what disease the patient has....
Section: Articles about health
Small appetite at the child – the complaint which pediatricians should hear practically from each mother. Most often it is carried to разр...
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn – whether you have or your relatives problems....
Section: Articles about health
The sudden heat on all body which is followed by perspiration and a cardiopalmus – the phenomenon familiar to many people. Most often such states called by "inflows" result from nervous or physical overworks and disappear right after rest. However in certain cases similar reaction of an organism can speak about diseases which need treatment. What? About it below....
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications to...
Section: Articles about health
Practically each person is familiar with the annoying, pulling, unscrewing pains caused by overcooling of muscles of a back. In certain cases inflammatory process is not limited to discomfort, being followed by emergence of hypostasis, consolidations, increase температ...
Section: Articles about health
The problem of diagnosis was and remains to one of the most important in medicine. From that, the reason of an indisposition of the patient will be how precisely defined, eventually success of treatment depends. In spite of the fact that the majority of the diagnostic methods applied in official clinical practice has very high informational content and reliability, mistakes directed by diagnoses nevertheless are not excluded....
Section: Articles about health
No, probably, the person who would not have cold. Cold, cough, a headache – these symptoms are known to everyone. Peak to Prost...
Section: Articles about health
Dietary supplements (dietary supplements) for the last decades were so thoroughly included into our life that, apparently, it is already impossible to find the person who at least once did not try them. At the same time, most of our compatriots have a vague idea about...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning they laugh and joke, and in the evening cry or are irritated....
Section: Articles about health
Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on lips is called) – one of the most widespread illnesses. Statistically, only 5% of inhabitants of our planet are unreceptive to its activator, and the reasons of this feature are still not found out. Other people are virus carriers....
Section: Articles about health
Life does not indulge the modern woman special emotional comfort and carelessness. Fatigue, troubles at work, misunderstanding...
Section: Articles about health
Osteoporosis this general disease which main sign is decrease in density of a bone tissue. On distribution width it takes the fourth place among noninfectious diseases. The illness develops at mature age more often: in our country to them harvest seasons...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of hypnotic impact on consciousness of the person contains about two millennia. During this time scientists managed to learn a lot of things about a phenomenon of hypnosis and learned to facilitate a condition of the patients having heavy illnesses with its help....
Section: Articles about health
Beauty shop – the place which is associated only with positive emotions: joy, pleasure, relaxation. One...
Section: Articles about health
Use of medicinal plants in therapy is urgent today, more than ever. The drugs made of curative herbs cannot replace completely modern synthetic drugs, but their use becomes frequent serious help in simplification a leak...
Section: Articles about health
The nature does not stand stagnation and monotony. It is known that tissues of a human body atrophy if do not receive necessary loadings. It fully belongs also to a cerebral cortex: when it is not given full-time job, it begins to function worse. As a result memory decreases, the person becomes less bright, acquires information more slowly, hardly switches from one thought to another. There are problems at work, difficulties with communication and career development. These it is unpleasant...
Section: Articles about health
Any of us is not insured from a heavy illness of the loved one. Happens and so that someone from family members becomes lying бо...
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters there is not only a seasonal domestic production, but the vegetables and fruit which are grown up in the countries with more comfortable conditions at all seasons of the year...
Section: Articles about health
Feeding by a breast - the integral part of ideal motherhood allowing to come into contact with the kid and to create to it healthy immunity since early years. Nevertheless, this important process in life of mother and child can be saddened laktostazy − by a milk delay in a mammary gland. What main reasons for a laktostaz? How not to allow problems with breastfeeding? Let's consider 10 premises resulting in stagnation of milk at the nursing mother....
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, pathologies of a thyroid gland in the world more than 500 million people have. Failures in work of this body conduct to is heavy...
Section: Articles about health
Wood louse – the ordinary-looking unpretentious plant extended in all territory of our country. It quickly expands, and sometimes fills sites, bringing a lot of chagrin to gardeners. Perhaps, they would be upset less if knew that the wood louse is the prices...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person weakness leans: he suffers from drowsiness, complains of bad mood, loss of interest in life and failures in affairs....
Section: Articles about health


