Keloids
Keloids or keloid cicatrixes – the abnormal growth of cicatricial fabric in the field of an injury, a burn, an operative measure, infectious damage of skin or other disturbances of its integrity considerably exceeding the sizes of primary injury. Localization of keloids is various. Most often keloids are formed in a zone of a thorax and shoulders, in the field of an ear lobe, on functionally low-active sites of skin. Severity of an injury does not influence probability of emergence of a keloid, its sizes. Externally keloids have an appearance of the dense tumorous education towering over skin on the 5-8th, faintly or brightly pink, cyanotic color. The etiology of keloids still remains to the unknown.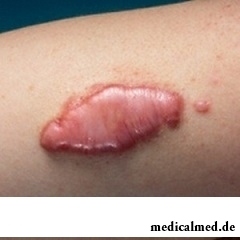
Keloids do not pose hazard to life and health of the person, however bring notable physical and psychological discomfort (not esthetic outward of a keloid). Formation of keloids is followed by the following symptoms:
- Itch when combing;
- Pain when pressing;
- Increase in sensitivity of the struck fabrics;
- Redness in the field of a keloid.
Distinguish two stages of development of keloids:
- The active stage is characterized by the dynamic growth of a keloid that brings physical discomfort to the patient (morbidity, an itch, numbness of the struck fabrics), at this stage it is accepted to speak about an active keloid;
- The inactive stage is characterized by full completion of formation of a keloid, the hem does not deliver to the patient of special discomfort. Such keloid is called inactive or stabilized, its color approaches natural skin color.
The keloid begins to form 1-3 months later from the moment of wound epithelization. The active stage of growth can last more than 12 months. Usually the keloid keeps a dense consistence and does not decrease in sizes.
It is necessary to distinguish keloids and hypertrophied hems as the type of a hem will define further tactics of treatment. The hypertrophied hem unlike a keloid is formed only in the place of injury of skin, does not exceed injury borders. Inflammations in the course of healing, accession of consecutive infection, endocrine dysfunction, decrease in local immunity are origins of a hypertrophied hem. Other signs are similar to a keloid.
At emergence of the following symptoms it is necessary to see a doctor:
- Strengthening of painful feelings as at mechanical influence (pressing, friction of a hem), and in a condition of its relative tranquility;
- Emergence of signs of an inflammation both hem, and adjacent sites of skin;
- Essential increase in a keloid for rather short period.
Risk factors of development of keloids
The exact reasons of formation of keloids are still unknown. There are factors substantially increasing risk of formation of keloids at the person from which distinguish:
- Genetic predisposition;
- The expressed xanthopathy;
- Certain localization of traumatic injuries of skin (thorax, ear lobe, area of a deltoid muscle);
- Infection of a wound in the course of healing;
- Imbalance of immune system;
- Hormonal imbalance in an organism;
- Age changes;
- Disturbance of an innervation.
Keloids on ears: etiology
Keloids most often strike an ear lobe. The puncture of a lobe of an ear or cartilage, carrying the ear rings made of the low-quality alloys irritating ear skin becomes one of the reasons of formation of keloids on ears. Keloids on ears deliver not only esthetic discomfort (a keloid arrangement in a visible place, impossibility to wear jewelry), but also physical as during an active stage of growth the keloid can cause burning sensations, an itch, the pains amplifying at mechanical impact on area (a hem zadevaniye in the course of clothing, during sleep). There is an assumption that the ear lobe puncture the gun and establishment of ear rings on screws promotes formation of keloids on ears. Now separate techniques of treatment of keloids on ears are developed.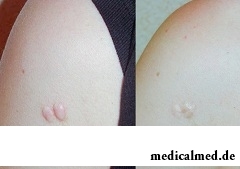
Keloid: treatment, conservative techniques
Among ways of treatment of keloids distinguish conservative and radical techniques. Regardless of type of keloids, it is more preferable to begin treatment of a hem with conservative methods among which:
- Compression – use of pressure upon the area of skin struck with a keloid. Squeezing interferes with growth of a keloid, blocks its food, squeezes hem vessels that can lead to a stop of its growth;
- Use of silicone plates – the mechanism of influence of this technique of treatment of keloids is based on squeezing of capillaries, collagen synthesis reduction, reduction of delivery of mediators of an inflammation, hydration of a hem;
- Ointment therapy – this technique is additional and is seldom used as an independent type of therapy of keloids, treatment by ointments is based on auxiliary influence of the antibacterial, antiinflammatory, normalizing blood circulation substances;
- Corticosteroids – this technique is applied locally or by administration of substance in keloids, treatment of hems is based in this case on decrease in synthesis of collagen (oppression of division of the fibroblasts generating collagen, and also increase in concentration of a collagenase – the enzyme promoting collagen splitting);
- Cryolysis – damage of fabrics of a keloid, treatment is directed to destruction of cytoplasm and organellas of cells by a cryogen. This technique allows to remove a keloid completely. Advantage of this technique is the low probability of a recurrence of keloids;
- Cosmetic correction – various techniques (peelings, dermabrasion) directed to correction of outward of a hem.
Removal of keloids: aggressive techniques of treatment
Aggressive techniques of treatment of keloids assume hem fabric excision in the surgical way or a burning out of area of a hem the laser.
Surgical removal of keloids assumes removal not only fabrics of the hem, but also removal of the site of skin on which the keloid was formed. The main shortcomings of surgical removal of keloids is the high probability of formation of a new hem on site of surgical excision. Removal of the site of skin allows to reduce risk of formation of a new keloid. A recurrence during surgical removal of keloids reaches 74-90%. Surgical treatment of keloids is a necessary measure if conservative techniques of treatment of hems were ineffective.
Laser correction of a keloid allows to delete (to cut and cauterize) a hem with the minimum injury of surrounding fabrics. Laser correction is applied to complex treatment of keloids (it is combined with local and injection corticosteroid therapy). Unlike surgical excision the percent of a recurrence of keloids at laser correction is considerably reduced and reaches only 35-43%.
At keloids treatment by nonconventional means (traditional medicine), and also self-treatment can aggravate a situation.
Many drugs initially moved ahead in the market as drugs. Heroin, for example, was initially brought to the market as children's cough medicine. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as anesthesia and as the means increasing endurance.

The thought that the mass of their body is too big at least once in life visits from 80 to 95% of women. Many...
Section: Articles about health
Cold, puffiness of a nose, itch, the watering eyes - characteristic symptoms of the allergic rhinitis resulting from hit of allergens (pollen, house dust, hair of animals, etc.) on a mucous membrane of a nose. Unpleasant feelings often deliver беспоко...
Section: Articles about health
White teeth and the Hollywood smile – a dream of many people. Long time was considered that the plaque on teeth and change of their color – destiny of those who incorrectly eat smokes and badly brushes teeth. But the paradox is available: at everything the variety of toothpastes, brushes existing today for toothbrushing and conditioners for a mouth the number of the people hesitating of a plaque on teeth does not decrease. Moreover, the plaque is formed even at small children who definitely do not smoke and have no coffee. So in what business, and опас...
Section: Articles about health
For many women the word "fat" sounds as a sentence. In aspiration to an ideal figure they try to exclude, first of all, from with...
Section: Articles about health
It is possible to find the extensive range of fruit and vegetables in modern shops. Russians already got used that on counters there is not only a seasonal domestic production, but the vegetables and fruit which are grown up in the countries with more comfortable conditions at all seasons of the year...
Section: Articles about health
Memory is an ability of the central nervous system to fix, keep and as necessary to reproduce information on knowledge or skills received by the person or an animal during life. The mechanism of this process is up to the end not studied....
Section: Articles about health
Condition of lips (their morbidity, outward) – one of indicators of health of the person. Peeling, dryness, pallor, and also трещ...
Section: Articles about health
Today about 30 diseases, sexually transmitted are known. Wide circulation of these illnesses is extremely promoted by the dual attitude towards them: on the one hand, most of people know about "shameful" diseases and not a stirrup very little...
Section: Articles about health
For most of the working people the problem of having a snack is particularly acute enough. Sooner or later there is a question: what can be eaten quickly between a breakfast and a lunch or a lunch and leaving from service so that to receive necessary power feed, but not to overload an organism with harmful components or excess calories? We bring to your attention the list of products which quite conform to these requirements....
Section: Articles about health
Household skills which to us so diligently imparted in the childhood it appears, not always bring only benefit. According to result...
Section: Articles about health
Is told about advantage of domestic animals for development of the child much. But many parents nevertheless do not hurry to bring pets as are afraid that they can do harm to health of children. What troubles can really trap kids and how to make with...
Section: Articles about health
They say that to ensure health and longevity of people it is obliged. Really, at competent approach to these questions, minimization of an adverse effect of many factors does not represent a special problem. Practically everyone has an opportunity to play sports, to pick up an optimum operating mode and rest, to adjust healthy food, to refuse addictions. It is more difficult to exclude hit in an organism of harmful substances through a respiratory organs: not all are able to afford to live in the area with хо...
Section: Articles about health
Visit of doctors – business not the most pleasant, and many people do not hurry to undergo necessary planned inspections. Such behavior...
Section: Articles about health
The immunity role in growth of the child is invaluable. The proteins-immunoglobulins produced by immune system preserve the child against the diseases capable − owing to an organism weak still − to serve as a stressful factor, to become the reason of many complications and delays in unless...
Section: Articles about health
According to doctors, more than a half of men of 25-50 years suffer from frustration of the urinogenital sphere, but the minority sees a doctor from them. And in vain - even the insignificant discomfort in the field of generative organs can serve as a symptom of an illness fraught with grave consequences for health. So - after 40 years - it is easy for most widespread disease of the sexual sphere of men to pass the first symptoms of prostatitis (weight in the bottom of a stomach, decrease in a libido), having written off for overfatigue and fatigue. Let's consider...
Section: Articles about health
The varicosity has familiarly many, statistically, this disease more than a half of all adult population. As...
Section: Articles about health
Each person knows that fervescence is an illness sign. However too low temperature (hypothermia), especially also can demonstrate existence of diseases when it is observed long enough. Such state is dangerous those...
Section: Articles about health
Life expectancy in various regions of Earth is not identical. Social stability, economic wellbeing, availability and level of medical care, household comfort, literacy of the population in the field of respect for sanitary and hygienic norms and many other factors exert impact on it. However one parameter remains to the general almost for all countries of the world: women on average live for 7-10 years longer, than men. Today we will talk about the reasons of this phenomenon....
Section: Articles about health
The fatigue, sleep debt, disturbances of food, bad mood, vagaries of the weather – all these circumstances badly are reflected in our vn...
Section: Articles about health
Sugar - the digestible refined product which is not of special value for an organism of the modern person. The use of sugar in food is based rather on the psychological dependence caused by desire to indulge itself with something tasty, and in дальнейш...
Section: Articles about health
Herpes simplex of the first type (the infectious disease which is shown periodic bubble rashes on lips is called) – one of the most widespread illnesses. Statistically, only 5% of inhabitants of our planet are unreceptive to its activator, and the reasons of this feature are still not found out. Other people are virus carriers....
Section: Articles about health
The words "disease" and "patient" not without reason come from one root – "pain". As a rule, symptoms of illnesses thoroughly spoil the patient...
Section: Articles about health
The unpleasant feelings connected with spring breakdown are familiar almost to each of us. Often happens that in March-April on the person weakness leans: he suffers from drowsiness, complains of bad mood, loss of interest in life and failures in affairs....
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" and "assimilation" of information is strongly slowed down. Especially this problem urgent for persons of age becomes more senior than fifty years. "Already badly I think", "the head will burst now", "memory as if is disconnected" - here that wants to be told at the time of information overload....
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, reason душевног...
Section: Articles about health
Each person has easy indispositions which he transfers "standing", trying not to ask for medical care. Arguments at the same time are adduced same: "it is a trifle, itself will pass", "I have too many important issues", "there are no wish to spend time on...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, a sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease in physical and intellectual activity and a number of other symptoms reducing quality of life. Abstinence can be strong: an essential part of attempts comes to an end leaving off smoking failure, and people are returned to the use of cigars...
Section: Articles about health