





First aid at shock
Shock is called the pathological reaction of an organism coming in response to the irritation caused by the injuring factor (or set of factors) the excessive force with which the organism is not able to cope. Shock represents disturbance of the vital functions of an organism and is direct threat of human life.

Types of shock
Depressed case various factors, both external (injury) and internal can cause (disease). Depending on a disturbing factor distinguish several types of shock, the following is basic of which:
- Cardiogenic – develops as a result of disturbance of cordial activity. Can develop at a myocardial infarction, a stenocardia attack, arrhythmias, etc.;
- Hypovolemic – is connected with critical reduction of volume of the blood circulating in a blood channel. Is caused most often by massive blood loss, is more rare – severe dehydration;
- Traumatic – is caused by the injury which is followed by considerable damages of bodies and fabrics. Multiple or just heavy fractures (a change of a basin, a backbone), gunshot wounds, craniocereberal injuries, the combined injury, etc. can be such injury;
- Infectious and toxic – is caused by hit in an organism of excessive amount of the toxins produced by pathogenic microorganisms (bacteria and viruses);
- Septic – is connected with heavy infectious inflammatory process as a result of which the fabric hypoxia – insufficient supply of fabrics with oxygen develops that leads to dysfunction of many vitals at once, so-called multiorgan insufficiency develops;
- Anaphylactic – extreme extent of allergic reaction of immediate type, usually in response to administration of medicine. Is caused by food allergy or hit in a poison organism less often (for example, at stings of insects).
Some researchers also allocate psychogenic shock which results from a heavy mental shock (a grief, horror, despair, etc.).
Most often in practice it is necessary to face cardiogenic and traumatic shock, is more rare – with psychogenic. Shock can be and combined – for example, the depressed case at extensive burns is caused by several factors at once.
There are also other classifications on which we will not stop as they have no relation to first-aid treatment. Let's note only that quite often speak about painful shock. Under this definition traumatic shock most often gets though the megalgia can be caused not only by an injury, but also heart attack (cardiogenic shock at stenocardia), and the getting wound (hypovolemic shock), and acute pathology of internals (a perforation of the ulcer, renal colic, intestinal impassability, etc.).
Degrees of shock and their signs. Shock index
For the correct first-aid treatment at shock it is necessary to define its degree. In total in a depressed case allocate four degrees, but as the last is terminal, i.e. in fact, death of an organism, usually speak about three:
- The I degree - compensation. The victim is in consciousness, is adequate, makes contact, reactions are slowed down, or, on the contrary, overexcitation is noted (can shout, swear). Person pale or red. The upper indicator of pressure (systolic pressure) is higher than 90 mm Hg, pulse of 90-100 blows/min. The forecast at this stage is favorable, all phenomena are reversible, and measures of first aid it can appear enough to normalize the victim. Nevertheless, medical examination is necessary not to be mistaken in definition of degree of shock;
- The II degree – subcompensation. The victim in consciousness, shallow breathing, pulse becomes frequent up to 140 blows/min., weak, the systolic pressure of 80-90 mm Hg. Pallor of integuments, cold sweat, a fever is noted. Reactions are slowed down, but the contact remains, the person answers questions, the speech silent and weak. It is a dangerous stage of shock which demands medical assistance as at an adverse current it can develop in the following stage;
- The III degree – a decompensation. The victim can be both in consciousness, and without it. It is slow-moving if in consciousness, then answers questions with whisper, slowly, in monosyllables, or does not answer at all. Integuments are pale, sometimes with a cyanotic shade, are covered with a cold perspiration, breath frequent, superficial. Systolic pressure of 70 mm Hg and below. The pulse of very weak filling which is speeded up – can reach up to 180 blows/min., is defined only on large arteries (sleepy or femoral). At this stage the emergency medical assistance and resuscitation actions in the conditions of a hospital is necessary for the patient;
- The IV degree – irreversible. A terminal state at which the patient is unconscious integuments of white or gray color, sometimes get a mramornost (uneven tone, coherent with disturbance of blood circulation in capillaries), lips and a nasolabial triangle blue, upper pressure less than 50 mm Hg or is not defined at all, pulse is defined as threadlike and only on large arteries, or is absent. Breath is superficial, uneven, pupils are expanded, reflexes are absent. At this stage the forecast adverse even in the presence of medical care. Despite it, first aid at shock of the IV degree, as well as medical, all the same has to appear as so far the person is living chance of recovery, though small, nevertheless is.
It is not always possible to determine shock degree by external signs therefore for convenience doctors use a so-called index of Algover, or a shock index. It is easy to calculate it in the presence of a tonometer. Algover's index is defined by the pulse relation to an upper (systolic) indicator of arterial pressure. For example, if pulse of 80 blows/min., and systolic the ABP of 120 mm Hg, then Algover's index is defined as 80: 120 = 0,66. The normal indicator is considered 0,5 – 0,7, the indicator 1 is shock of the I degree, an indicator 1,5 – shock of the II degree, an indicator 2 – shock of the III degree. Shock in the IV degree usually does not cause difficulties in definition.

First-aid treatment at shock
The depressed case constitutes serious health hazard, and to truly estimate this danger to the nonspecialist very difficult. Therefore if the victim is shocked or there are bases shock to suspect, it is necessary to call the ambulance immediately. The following signs can form the basis for suspicions:
- Pallor of integuments, cold sweat;
- Pulse of weak fullness, is speeded up, breath differs from normal (can be superficial or on the contrary, forced);
- Faintness, weakness, overexcitation or opposite, block;
- The glassy look, can be focused in one point or slowly move.
It is especially dangerous if such symptoms are observed at the person who had an injury or heart attack.
Waiting for medical assistance as measures of first aid it is necessary to make the following:
- To terminate the injuring factor if there is bleeding, to try to stop it;
- To lay the victim so that his legs were a little above the head. It will provide inflow of blood to a brain;
- As much as possible to facilitate breath. To remove what can prevent breath, weaken hard fasteners, provide inflow of fresh air to the room;
- To warm the victim, having covered with a blanket;
- If the person is unconscious, and also in cases when there is a stomatorrhagia or a nose, vomiting or emetic desires, it is necessary to lay the victim on one side or at least to turn on one side his head and to watch that it remained in such situation. It is necessary that the victim did not choke;
- Before arrival of ambulance not to leave the person of one, to watch his state. In case of the termination of breath or cordial activity immediately to start resuscitation actions (breath of companies - in - a mouth, a mouth - in - a nose, an indirect cardiac massage) and to see them to arrival of the doctor or before recovery of breath and pulse.
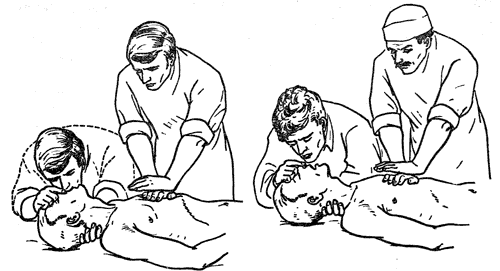
What should not be done within first-aid treatment at a depressed case?
Not to aggravate a condition of the victim, giving first aid at shock, it is not necessary to give to the victim of medicine. It concerns any medicines, including anesthetics and drugs supporting cordial activity. Even the most useful of them can distort a clinical picture, without having allowed the doctor adequately to estimate the patient's condition.
It is forbidden to allow to the victim to drink when:
- There was a craniocereberal injury;
- The area of a stomach is injured;
- There is bleeding or suspicion of internal bleeding;
- There is a heartache.
In other cases of the injured person it is possible to give to drink, avoiding at the same time any alcohol-containing and tonics.
People who got used to have breakfast regularly have obesity much less often.

Climax - process of fading of reproductive function of an organism in process of its aging. At women the main sign of its approach showing...
Section: Articles about health
Smoking not only exerts a negative impact on the state of health of the consumer of tobacco products, but is an air polluter the substances potentially dangerous to people around. In recent years significantly the number of people, стремящ increased...
Section: Articles about health
When overcomes feeling of hunger, and an opportunity to have dinner fully is absent, having a snack − the meals, small on volume, stabilizing sugar level in blood comes to the rescue. The relation of nutritionists to having a snack more often negative, but only because as snack people choose the most caloric products with the increased amount of "bystry" carbohydrates: cookies, rolls, chips, candies. Nevertheless, the advantage of having a snack is obvious to weight loss: the person avoids strong feeling of hunger...
Section: Articles about health
Summer in the heat. Many are going to spend vacation abroad. Travelers the tender seas, rest on beaches wait, for survey достоп...
Section: Articles about health
The climax, or menopause is the normal process of the termination of genital function of the woman which is followed by serious hormonal changes in an organism. Usually the menopause begins at the age of 50-55 years, but characteristics of this process are very individual. T...
Section: Articles about health
The state of health of the person depends on many factors. One of the most important is the constant, but not exhausting a physical activity. In the presence of various illnesses specialists often advise patients to do swimming which by right takes the leading place by efficiency of improvement, having at the same time a few contraindications. Today we will talk about the main directions of therapeutic impact of swimming on a human body....
Section: Articles about health
Stroke (acute disorder of cerebral circulation) – one of the most widespread neurologic diseases. Annually in the world...
Section: Articles about health
On health of the person physicians know about salutary action of animals long ago. About 7 thousand years ago great Hippocrates recommended to the patients riding walks for strengthening of a nervous system and increase in vitality....
Section: Articles about health
Life expectancy in various regions of Earth is not identical. Social stability, economic wellbeing, availability and level of medical care, household comfort, literacy of the population in the field of respect for sanitary and hygienic norms and many other factors exert impact on it. However one parameter remains to the general almost for all countries of the world: women on average live for 7-10 years longer, than men. Today we will talk about the reasons of this phenomenon....
Section: Articles about health
Olive oil – the product capable to make a powerful contribution to health of the person if it includes it in the diet. Rich vitamin...
Section: Articles about health
From the failure of work of immune system which is shown in the form of an allergy, statistically, more than 40% of the population of the globe suffer. In most cases pathological reactions cause the substances which are contained in food stuffs, hair of animals, medicines...
Section: Articles about health
Smack in a mouth can arise in the natural way – as a result of lack of morning hygiene or reception of the corresponding food. However in certain cases its existence is a sign of certain pathologies, and allows to reveal an illness at an early stage. Depending on character of aftertaste – acid, salty, bitter, sweet – distinguish also diseases which accompany it....
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, about it there can be no disagreements: water is necessary for a human body for normal zhiznedeyatet...
Section: Articles about health
Deciding to get rid of an addiction, not all imagine what effects it is necessary to face. Process of refusal of smoking causes quite essential discomfort in most of people: differences of mood, sleep disorder, fatigue, decrease физич...
Section: Articles about health
The next flu epidemic leads to the next panic, from year to year we give in on these manipulations: professionally alarming voice of the announcer in news, reports with calculation of the died patients, an interview with people in white dressing gowns and advertizing of anti-influenza means of different degree of inefficiency. All this reminds the Hollywood movies of epidemics threatening to destroy our planet. However, there is also one more similarity to cinema: everything comes to an end well. So, how to deal with the events, not in...
Section: Articles about health
The modern person not always manages to find housing in the environmentally friendly region and such work which would not do harm здо...
Section: Articles about health
So, you resolved to lose weight. And now you try to understand what to begin with: from exercise stresses or a diet? And how to make that process of weight loss did not give you an inconvenience, and, on the contrary, brought joy?...
Section: Slideshow
Several decades ago the basil (the district khan, реан, Reagan) was considered as a part of the Caucasian or east cuisine, but today it strongly took the place on tables of Russians. Greens of this plant possess a strong, pleasant smell and specific fresh taste because of which it is included almost in all dry mixes of spicy herbs, and also give to meat and fresh fish dishes....
Section: Articles about health
Many of us, probably, noticed more than once that from intellectual loadings at some point the brain as though "overheats" also "assimilation"...
Section: Articles about health
The pine is one of the most widespread plants of our woods. Its needles and pitch not without reason called by "gallipot" were since ancient times used for strengthening of protective forces of an organism, treatment of avitaminosis, anemia and many other diseases. In recent years wide п...
Section: Articles about health
Proofs of efficiency of Mildronate at treatment of coronary heart disease with stenocardia can be found in many publications of the end of the twentieth century. Researches were conducted since 1984, including placebo - controlled effects. In total clinical tests of Mildronate were carried out for more than thirty years....
Section: Articles about health
All like to sing. Small children with pleasure are engaged in a vocal, not especially thinking of hit in a melody. Adults most often...
Section: Articles about health
Obesity is called a disease of 21 centuries, for the last 100 years the number of the people suffering from excess body weight considerably increased. Statistically, on Earth already about 1,5 billion corpulent people, and 500 million from them have extreme degree of completeness, are negative...
Section: Articles about health
Contrary to popular belief, the multiple sclerosis (MS) is not connected neither with sclerous changes of walls of vessels, nor with age forgetfulness and problems with concentration of attention. This disease has the autoimmune nature. Pathological process is expressed in degradation of nervous tissue and destruction of its enveloping layer - a myelin. Multiple damages of the central nervous system which are shown by decrease in sight, bystry fatigue, on become result of development of an illness...
Section: Articles about health
The phenomenon of the panic attack is known long ago, but the reasons of its emergence still are up to the end not found out. It is established that more than 30%...
Section: Articles about health
Iodine - one of thirty most important microelements in our organism. The main role of iodine consists in synthesis of thyroid hormones of a thyroid gland - the substances which are responsible for the majority of exchange processes of an organism. It is known that thyroid hormones consist...
Section: Articles about health
Each of us repeatedly noticed that the people having the same passport age are sometimes not similar on one-years at all. One at the age of 40-45 years already looks almost an old man, and another and in 60 is young, vigorous and full of life. The matter is that the condition of our health depends not on the number of the lived years, and on degree of safety of an organism. This factor also defines biological age of the person....
Section: Articles about health
