Vazokardin
Application instruction:
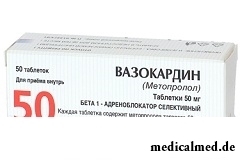 Vazokardin – the drug with anti-hypertensive, antiarrhytmic and anti-anginal action applied at arterial hypertension and some other disturbances of cordial activity.
Vazokardin – the drug with anti-hypertensive, antiarrhytmic and anti-anginal action applied at arterial hypertension and some other disturbances of cordial activity.
Form of release and structure
Vazokardin produce in the form of tablets (flat, round, from color, white to white with a creamy shade, with risky and a facet on one of the parties, the easy mramornost is possible), 10 pieces in blisters, on 2 or 5 blisters in cardboard packs.
50 mg or 100 mg of active agent – a metoprolol of tartrate are a part of 1 tablet.
The auxiliary components which are a part of drug: K25 povidone, monohydrate of lactose, silicon dioxide colloid, corn starch, microcrystallic cellulose, calcium stearate, silicon dioxide metilirovanny, sodium carboxymethylstarch.
Indications to use
Vazokardin appoint at:
- Arterial hypertension (in monotherapy or along with other anti-hypertensive drugs);
- Coronary heart disease: myocardial infarction (complex therapy, secondary prevention), prevention of attacks of stenocardia;
- The functional disturbances of cordial activity which are followed by tachycardia;
- Hyperthyroidism (as a part of complex therapy);
- Disturbance of a heart rhythm (ventricular premature ventricular contraction, supraventricular tachycardia);
- To prevention of attacks of migraine.
Contraindications
Vazokardin's use is contraindicated at:
- Cardiogenic shock;
- To sinuatrial blockade;
- To AV blockade of the II-III degree (without artificial pacemaker);
- Sick sinus syndrome;
- Printsmetal's stenocardias;
- The expressed disturbances of peripheric circulation;
- Chronic heart failure in a decompensation stage;
- Sinus bradycardia (at the heart rate (HR) less than 50 beats per minute);
- Acute myocardial infarction (ChSS is less than 45 beats per minute, PQ interval more than 0,25 seconds, systolic arterial pressure is less than 100 mm hg);
- Arterial hypotension (in case of use at secondary prevention of a myocardial infarction – systolic arterial pressure is less than 100 mm hg, ChSS is less than 45 beats per minute);
- Hereditary diseases – deficit of lactase, a lactose intolerance or glyukozo-galaktozny malabsorption (because of the lactose which is a part of drug);
- To pheochromocytoma (without simultaneous use of alpha adrenoblockers);
- Hypersensitivity to a metoprolol, other components of drug and other beta adrenoblockers.
Also Vazokardin do not appoint:
- Along with MAO inhibitors, intravenous administration of blockers of calcium channels like verapamil;
- To the feeding women;
- To patients aged up to 18 years (safety and efficiency of use of drug for this age group are not established).
Drug should be used with care to patients of advanced age, and also patients at:
- Metabolic acidosis;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Depressions (including in the anamnesis);
- Renal failure (KK less than 40 ml a minute);
- Abnormal liver function;
- To AV blockade of the I degree;
- Myasthenias;
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (emphysema of lungs, chronic obstructive bronchitis);
- Psoriasis;
- Thyrotoxicosis;
- Allergic reactions in the anamnesis (decrease in the therapeutic answer to adrenaline, weighting of arterial hypertension and strengthening of sensitivity to allergens is possible);
- Obliterating diseases of peripheral vessels (Reynaud's syndrome, the alternating lameness);
- To bronchial asthma.
Route of administration and dosage
Vazokardin accept inside, washing down with a small amount of water, in time or right after food. In need of a tablet it is possible to halve and swallow without chewing.
At arterial hypertension drug 1-2 times a day appoint in a daily dosage 50-100 mg with frequency rate of reception (in the morning and in the evening). At insufficient effect it is possible to raise gradually a daily dose to 100-200 mg and/or in addition to accept other anti-hypertensive means. The maximum daily dosage of drug – 200 mg.
At a hyperthyroidism, a daily dose - 150-200 mg a day in 3-4 receptions.
At arrhythmias, stenocardia, for prevention of attacks of migraine, a daily dose - 100-200 mg in 2 receptions (in the morning and in the evening).
At secondary prevention of a myocardial infarction, a daily dose - 200 mg in 2 receptions (in the morning and in the evening).
At the functional disturbances of cordial activity which are followed by tachycardia, a daily dose - 100 mg in 2 receptions (in the morning and in the evening).
To patients of advanced age, patients with functional disturbances of kidneys (KK is less than 40 ml in a minute), and also in need of carrying out a hemodialysis the dosage is not adjusted.
At the expressed abnormal liver functions depending on a clinical state the dosage of drug should be lowered.
Side effects
Side effects at Vazokardin's use depend on individual sensitivity of the patient. As a rule, they are poorly expressed and pass after drug withdrawal.
From the central nervous system: weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness, confusion of consciousness, a headache, spasms, delay of speed of motor and mental reactions, paresthesias in extremities (at patients with Reynaud's syndrome and the alternating lameness), alarm, depression, a depression, decrease in concentration of attention, concern, the increased nervous irritability, sleeplessness, "dreadful" dreams, amnesia, hallucinations, short-term disturbance of memory, muscular weakness.
From cardiovascular system: the expressed lowering of arterial pressure, arrhythmias, a sinus bradycardia, heartbeat, orthostatic hypotension (dizziness, sometimes a loss of consciousness), cardiogenic shock at patients with a myocardial infarction, AV blockade of the I degree, decrease in sokratitelny ability of a myocardium, manifestation of a vasomotor spasm (strengthening of disturbance of peripheric circulation, a cold snap of the lower extremities, Reynaud's syndrome, gangrene), temporary aggravation of symptoms of chronic heart failure (puffiness of the lower part of shins and/or feet, an asthma), disturbance of conductivity of a myocardium.
From system of a hemopoiesis: agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia (unusual hemorrhages and bleedings), leukopenia.
From sense bodys: morbidity and xerophthalmus, decrease in sight, sonitus, decrease in secretion of the lacrimal liquid, conjunctivitis.
From respiratory system: rhinitis, a nose congestion, an asthma, difficulty of an exhalation (a bronchospasm at appointment in high dosages – loss of selectivity and/or at predisposed patients).
From the alimentary system: taste change, increase in activity of liver enzymes, hepatitis, dryness in a mouth, vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, lock, abnormal liver function, hyperbilirubinemia.
From a musculoskeletal system: arthralgia, dorsodynia;
From endocrine system: a hypoglycemia, at patients with a diabetes mellitus of 1 type – a hyperglycemia (seldom).
Allergic reactions: rash, skin itch, small tortoiseshell.
Dermatological reactions: psoriazopodobny skin reactions, dieback, aggravation of a course of psoriasis, sweating strengthening, dermahemia, photodermatosis, reversible alopecia.
Influence on a fruit: development of a pre-natal growth inhibition, bradycardia, a hypoglycemia is possible.
Others: sexual dysfunction, decrease in a libido and/or potentiality, insignificant increase in body weight.
At Vazokardin's overdose the first signs are shown in 20-120 minutes after administration of drug. The overdose is usually expressed by such symptoms as arrhythmia, dizziness, the expressed sinus bradycardia, nausea, cyanosis, vomiting, the expressed lowering of arterial pressure, a bronchospasm, ventricular premature ventricular contraction, a syncope. At acute overdose development of cardiogenic shock, a loss of consciousness, a coma, AV blockade (is possible up to development of a cardiac standstill and total cross block), a hyperpotassemia, a cardialgia, spasms, a hypoglycemia, an apnoea.
For treatment of overdose the gastric lavage, use of the adsorbing drugs, symptomatic therapy is shown. At the expressed lowering of arterial pressure the patient needs to adopt the provision of Trendelenburga. At excessive pressure decrease, development of heart failure and bradycardia intravenously enter (at an interval of 2-5 minutes) beta адреностимуляторы before achievement of desirable effect or 0,5-2 mg of Atropini sulfas. In the absence of effect introduction of Dobutaminum, dopamine or Norepinephrinum (noradrenaline) is shown. The hemodialysis is not effective.
Special instructions
At Vazokardin's use the patient should be trained in a technique of calculation of ChSS and to instruct about need of the address to the doctor at ChSS less than 50 beats per minute.
Control of the patients accepting drug includes regular observation of ChSS, arterial pressure, concentration of glucose in blood at a diabetes mellitus. For patients with a diabetes mellitus correction of a dosage of insulin or the hypoglycemic means accepted inside can be required. Drug can mask the tachycardia caused by a hypoglycemia.
At the smoking patients efficiency of drug is lower.
At reception of a dose more than 200 mg a day decrease cardioselectivity.
At chronic heart failure drug can be accepted only after achievement of a stage of compensation.
Vazokardin's cancellation is carried out gradually, reducing a dosage within 10 days. At the sharp termination of therapy there can be a withdrawal (increase in arterial pressure, strengthening of attacks of stenocardia).
At an angina of exertion the picked-up dosage of drug has to provide ChSS at rest within 55-60 beats per minute, at loading – to 110 beats per minute.
The patients using contact lenses need to consider that during treatment decrease in products of the lacrimal liquid is possible.
Drug can mask some symptoms of a hyperthyroidism (for example, tachycardia). Sharp cancellation of Vazokardin at patients with a thyrotoxicosis is contraindicated (because of possible strengthening of symptomatology).
At chronic obstructive bronchitis, a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma, emphysema drug should be accepted in minimum effective dosage and only at inefficiency of other antihypertensives or their bad portability.
It is necessary to carry out special control of a condition of patients with depressive frustration. At development of the depression connected with administration of drug, therapy is recommended to be stopped.
At elderly patients it is recommended to exercise control of function of a liver regularly. In case of development of the accruing bradycardia (less than 50 beats per minute), the expressed lowering of arterial pressure (systolic pressure is lower than 100 mm hg), a bronchospasm, AV blockade, heavy abnormal liver functions, ventricular arrhythmias correction of the mode of dosing or Vazokardin's cancellation is required.
Patients with a heavy renal failure (KK less than 40 ml a minute) are recommended to control functions of kidneys.
During treatment it is necessary to avoid excess insolation as drug can cause allergic reaction to the sun.
At the beginning of Vazokardin's use patients can test fatigue and dizziness owing to what it is recommended to be careful when driving the car and when performing potentially dangerous types of the works demanding from patients of speed of psychomotor reactions and the increased concentration of attention.
Analogs
Vazokardin's analogs on active agent are: Betalok, Vazokardin Retard, Betalok of ZOK, Metokard Retard, Corvitolum 100, Corvitolum 50, Metozok, Emzok, Metokard, Metokor Adifarm, Metolol, Metoprolol, Metoprolol Zentiva, Serdol, Metoprolol Organika, Metoprolol-OBL, Metoprolol-Acre, Metoprolol-ratiofarm, Egilok, Egilok Retard, Egilok S.
Terms and storage conditions
To store in the protected from light, dry place at a temperature of 15-21 °C. To protect from children.
Period of validity – 2 years.
People who got used to have breakfast regularly have obesity much less often.

The Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO) are plants or animals (as a rule, agricultural) in whose genotype...
Section: Articles about health
Doctors claim that the people not so familiar with a dorsodynia occur among adult Russians very seldom. At the same time the vast majority of the patients who are periodically testing this indisposition do not hurry to ask for medical care at all. With one St...
Section: Articles about health
One of the useful properties presented to the person by the nature is ability to feel fear. This ability is designed to signal about approach of a dangerous situation and to help to avoid in advance it to keep life. However if the fear is persuasive and is not reasonable, it can seriously limit possibilities of the person in respect of socialization and self-realization. Such pathological fear is called a phobia....
Section: Articles about health
For the city dweller the fitness is the most convenient sport. It is enough to acquire the subscription to the gym to receive to a toast...
Section: Articles about health
Ability of an organism to resist to adverse environmental factors (to impact of temperature drops, humidity and pressure, to the attacks of causative organisms, etc.) directly depends on what the person eats. Business here not only in, that C...
Section: Articles about health
Condition of lips (their morbidity, outward) – one of indicators of health of the person. The peeling, dryness, pallor, and also cracks in corners of a mouth can be not only the cosmetic shortcoming which arose owing to physical damages and weather conditions but also the satellite of some diseases and disturbances in an organism needing treatment. Let's consider 10 possible reasons of emergence of angular cracks (perleches) in corners of a mouth and ways of their elimination....
Section: Articles about health
The saying "the rich do not know how the other half lives" is known to all. In a broad sense it is that we can not always understand the person, about...
Section: Articles about health
Cold – a state known to everyone which is followed by cold, cough, high temperature, a pharyngalgia. Often the first that we begin to do in hope again to become healthy – to accept medicines which are not always harmless, then...
Section: Articles about health
Summer in the heat. Many are going to spend vacation abroad. Travelers the tender seas, rest on beaches wait, for sightseeing, campaigns on natural and cultural reserves. But, unfortunately, on vacation also problems with health can wait for us. On a foreign trip it is possible to face also diseases which not only will spoil long-awaited issue, but also will force to be treated within long months after its termination. To be insured completely from troubles of it a sort...
Section: Articles about health
More than a half of the married couples which faced prostatitis – leave. The new broadcast "Female View of Prostatitis" will help to learn...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, at the address to doctors seven of each ten patients complain of a headache. Actually it is much more people who are periodically feeling unpleasant feelings such. Many people, apart from a headache the reason for serious fear...
Section: Articles about health
Life activity of one-celled fungi of the sort Candida, related to yeast is a proximate cause of development of candidiasis (milkwoman). Normal these microorganisms are a part of the microflora living in an oral cavity and intestines of most of people and also in a female genital tract. The pathological phenomena are observed when fungi begin to breed too violently. At the same time there is an inflammatory process affecting mucous membranes and which is shown very nepr...
Section: Articles about health
Practice of hypnotic impact on consciousness of the person contains about two millennia. During this time scientists were in time a lot of things узн...
Section: Articles about health
Smack in a mouth can arise in the natural way – as a result of lack of morning hygiene or reception of the corresponding food. However in certain cases its existence is a sign of certain pathologies, and allows to reveal an illness at an early stage. In we depend...
Section: Articles about health
Statistically, pathologies of a thyroid gland in the world more than 500 million people have. Failures in work of this body lead to heavy disbolism, development of heart diseases, vessels, a reproductive and nervous system. In hard cases excess or insufficient production of the main hormones of a thyroid gland (thyroxine and triiodothyronine) leads to essential decline in quality of life and disability....
Section: Articles about health
Life expectancy in various regions of Earth is not identical. Exert impact on it social stability, economic бл...
Section: Articles about health
The business lady, the become mother, it is necessary to solve an array of problems. But of them is main: how to combine the beloved child and work? What traps trap the working mother and how she needs to behave?...
Section: Slideshow
Each person supports all life a SARS about 200 times. The peak of incidence falls on cold season, but it is possible to get sick with a temperature and a pharyngalgia, and sometimes and very possibly, even during a heat. The reasons for development of catarrhal diseases there is a set: from the weakened immunity till an excess portion of ice cream....
Section: Articles about health
It would seem, to buy drugs in Moscow does not make a problem – a drugstore, and not one, is available for each resident of the capital in step a toast...
Section: Articles about health
Cold is such painful that each sigh becomes a victory, heat "knocks" down, and the ache in joints forces to think only of pain. Some people with approach of the first symptoms of cold make the self-sacrificing decision to have a disease standing, and to a beam...
Section: Articles about health
Maternal milk is the best food for the newborn. It is the unique natural product containing an optimum set of nutrients, and which is best adapted in order that the baby normally developed and it was protected from harmful factors of external environment, unusual for it. Unfortunately, breastfeeding process not always does without complications. Sometimes, that the kid begins to bite a breast, giving to mother an essential inconvenience. Some women...
Section: Articles about health
Women quite often suffer from complexes concerning the sizes of the bust. Strangely enough, reason душевног...
Section: Articles about health
Radiological methods of a research are applied in medicine more than hundred years, and thanks to them millions of lives were saved. In many cases without X-ray it is impossible to make exact idea of a condition of bodies and fabrics, it is correct to make the diagnosis. Those...
Section: Articles about health
What they, women? Beautiful, gentle, passionate and at the same time windy, gusty, and nervous. And what is stranger: have all these qualities of the woman at the same time. But here only the mood their time sharply changes on completely opposite: in the morning they laugh and joke, and in the evening cry or are irritated....
Section: Articles about health
What woman does not dream of a beautiful and thick hair? So far physicians developed difficult schemes on hair transplant, in the bet industry...
Section: Articles about health
The majority of gynecologic diseases prove three main signs, each of which speaks about need of a visit to the gynecologist. Certainly, it is possible to establish the exact diagnosis only after inspection, but on the basis of some signs it is possible пр...
Section: Articles about health
Many parents of children at the age of 2-4 years face excessively whimsical behavior of the child. The kid exhausts constant crying and whims not only the parents, but also himself. In what the reasons of children's whims. And how to fight with them?...
Section: Slideshow